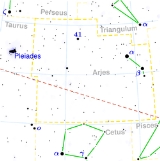
41 Arietis
Encyclopedia
41 Arietis or c Arietis is a star
in the constellation
Aries
. It does not possess a Greek letter Bayer designation
, since this star was once part of the now-obsolete constellation Musca Borealis
, but is sometimes designated c Arietis.
41 Arietis belongs to the spectral class
B8Vn, and has a stellar magnitude of +3.61. It is 160 light-year
s from Earth.
41 Ari is part of the Bharani
lunar mansion in Hindu astrology.
In Chinese
, , meaning Stomach
(asterism), refers to an asterism consisting of 41 Arietis, 35 Arietis
and 39 Arietis. Consequently, 41 Arietis itself is known as
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Aries
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac, located between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. Its name is Latin for ram, and its symbol is , representing a ram's horns...
. It does not possess a Greek letter Bayer designation
Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek letter, followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name...
, since this star was once part of the now-obsolete constellation Musca Borealis
Musca Borealis
Musca Borealis was a constellation located between the constellations of Aries and Perseus.It was first described as such by Hevelius in his catalogue of 1690, to distinguish it from the southern fly, Musca Australis....
, but is sometimes designated c Arietis.
41 Arietis belongs to the spectral class
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
B8Vn, and has a stellar magnitude of +3.61. It is 160 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s from Earth.
41 Ari is part of the Bharani
Bharani
Bharani is the second nakshatra in Hindu astronomy, corresponding to 35, 39, and 41 Arietis. In Jyotiṣa, Bharani is ruled by Shukra ....
lunar mansion in Hindu astrology.
In Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, , meaning Stomach
Stomach (Chinese constellation)
The Stomach mansion is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger.-Asterisms:...
(asterism), refers to an asterism consisting of 41 Arietis, 35 Arietis
35 Arietis
35 Arietis is a star in the constellation Aries. Its apparent magnitude is 4.65.-References:*...
and 39 Arietis. Consequently, 41 Arietis itself is known as
Components
| NAME | Right ascension Right ascension Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:... |
Declination Declination In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... (V) |
Spectral type | Database references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDS 02441+2651 B (BD+26 471B) | 02h 49m 56.8s | +27° 15' 45 | 10.29 | Simbad | |
| IDS 02441+2651 C (BD+26 471C) | 02h 49m 57.3s | +27° 15' 16 | 10.35 | Simbad | |
| IDS 02441+2651 D (BD+26 470) | 02h 49m 51.363s | +27° 14' 30.04 | 8.6 | K0 | Simbad |

