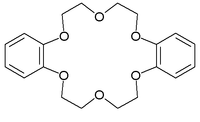
18-Crown-6
Encyclopedia
18-Crown-6 is an organic compound
with the formula [C2H4O]6 and the IUPAC name of 1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane. The compound is a crown ether
. Crown ethers coordinate some metal cations in their central cavity; 18-crown-6 displays a particular affinity for potassium cations. The synthesis of the crown ethers led to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Charles J. Pedersen
.
as well as the oligomerization of ethylene oxide
in the presence of a templating cation.
It can be purified by distillation
, where its tendency to supercool becomes evident. 18-Crown-6 can also be purified by precipitation with acetonitrile
, with which it initially forms an insoluble complex. The acetonitrile may be removed in vacuo to obtain the desired compound. Rigorously dry material can be made by dissolving the compound in THF
followed by the addition of NaK
to give [K(18-crown-6)]Na, an alkalide
salt.
s. In the presence of 18-crown-6 potassium permanganate
dissolves in benzene, although this application is eclipsed by the use of quaternary ammonium/phosphonium salts.
Using 18-crown-6, potassium acetate
is a more powerful nucleophile in organic solvents.
.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula [C2H4O]6 and the IUPAC name of 1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane. The compound is a crown ether
Crown ether
Crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups. The most common crown ethers are oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., -CH2CH2O-. Important members of this series are the tetramer , the pentamer , and the hexamer...
. Crown ethers coordinate some metal cations in their central cavity; 18-crown-6 displays a particular affinity for potassium cations. The synthesis of the crown ethers led to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Charles J. Pedersen
Charles J. Pedersen
Charles John Pedersen was an American organic chemist best known for describing methods of synthesizing crown ethers. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1987 with Donald J. Cram and Jean-Marie Lehn...
.
Synthesis
This compound can be prepared by a modified Williamson ether synthesisWilliamson ether synthesis
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and an alcohol. This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction...
as well as the oligomerization of ethylene oxide
Ethylene oxide
Ethylene oxide, also called oxirane, is the organic compound with the formula . It is a cyclic ether. This means that it is composed of two alkyl groups attached to an oxygen atom in a cyclic shape . This colorless flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor is the simplest epoxide, a three-membered...
in the presence of a templating cation.
It can be purified by distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
, where its tendency to supercool becomes evident. 18-Crown-6 can also be purified by precipitation with acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
, with which it initially forms an insoluble complex. The acetonitrile may be removed in vacuo to obtain the desired compound. Rigorously dry material can be made by dissolving the compound in THF
ThF
Follicular B helper T cells , are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleens and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5...
followed by the addition of NaK
NaK
NaK, or sodium-potassium alloy, an alloy, of potassium , and sodium , is usually liquid at room temperature. Various commercial grades are available. NaK is highly reactive with water and may catch fire when exposed to air, so must be handled with special precautions...
to give [K(18-crown-6)]Na, an alkalide
Alkalide
An alkalide is a chemical compound in which alkali metals are anions . Such species are notable because alkali metals were previously thought to appear in salts only as cations...
salt.
Applications
Crown ethers are useful as phase transfer catalystPhase transfer catalyst
In chemistry, a phase transfer catalyst or PTC is a catalyst that facilitates the migration of a reactant from one phase into another phase where reaction occurs. Phase transfer catalysis is a special form of heterogeneous catalysis. Ionic reactants are often soluble in an aqueous phase but...
s. In the presence of 18-crown-6 potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula KMnO4. It is a salt consisting of K+ and MnO4− ions. Formerly known as permanganate of potash or Condy's crystals, it is a strong oxidizing agent. It dissolves in water to give intensely purple solutions, the...
dissolves in benzene, although this application is eclipsed by the use of quaternary ammonium/phosphonium salts.
Using 18-crown-6, potassium acetate
Potassium acetate
Potassium acetate is the potassium salt of acetic acid.-Preparation:It can be prepared by reacting a potassium-containing base such as potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate with acetic acid:...
is a more powerful nucleophile in organic solvents.
Related compounds
A related and generally superior complexant for alkali metal cations is dibenzo-18-crown-6Dibenzo-18-crown-6
Dibenzo-18-crown-6 is a benzannulated crown ether. It is related to the non-benzannulated 18-crown-6. This compound may be synthesized from catechol and bisether:...
.