
Yahalom (protocol)
Encyclopedia
Yahalom is an authentication and secure key-sharing protocol designed for use on an insecure network such as the Internet. Yahalom uses a trusted arbitrator to distribute a shared key between two people. This protocol can be considered as an improved version of Wide Mouth Frog protocol
(with additional protection against man-in-the-middle attack
), but less secure than Needham-Schroeder.
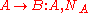
(A) initiates the communication to Bob (B) with S is a server trusted by both parties, the protocol can be specified as follows using security protocol notation
:
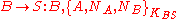
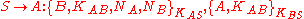
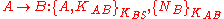
Wide Mouth Frog protocol
The Wide-Mouth Frog protocol is a computer network authentication protocol designed for use on insecure networks . It allows individuals communicating over a network to prove their identity to each other while also preventing eavesdropping or replay attacks, and provides for detection of...
(with additional protection against man-in-the-middle attack
Man-in-the-middle attack
In cryptography, the man-in-the-middle attack , bucket-brigade attack, or sometimes Janus attack, is a form of active eavesdropping in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them, making them believe that they are talking directly to each other...
), but less secure than Needham-Schroeder.
Protocol description
If AliceAlice and Bob
The names Alice and Bob are commonly used placeholder names for archetypal characters in fields such as cryptography and physics. The names are used for convenience; for example, "Alice sends a message to Bob encrypted with his public key" is easier to follow than "Party A sends a message to Party...
(A) initiates the communication to Bob (B) with S is a server trusted by both parties, the protocol can be specified as follows using security protocol notation
Security protocol notation
In cryptography, security protocol notation is a way of expressing a protocol of correspondence between entities of a dynamic system, such as a computer network...
:
- A and B are identities of Alice and Bob respectively
-
 is a symmetric key known only to A and S
is a symmetric key known only to A and S -
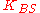 is a symmetric key known only to B and S
is a symmetric key known only to B and S -
 and
and 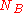 are noncesCryptographic nonceIn security engineering, nonce is an arbitrary number used only once to sign a cryptographic communication. It is similar in spirit to a nonce word, hence the name. It is often a random or pseudo-random number issued in an authentication protocol to ensure that old communications cannot be reused...
are noncesCryptographic nonceIn security engineering, nonce is an arbitrary number used only once to sign a cryptographic communication. It is similar in spirit to a nonce word, hence the name. It is often a random or pseudo-random number issued in an authentication protocol to ensure that old communications cannot be reused...
generated by A and B respectively -
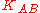 is a symmetric, generated key, which will be the session keySession keyA session key is a single-use symmetric key used for encrypting all messages in one communication session. A closely related term is traffic encryption key or TEK, which refers to any key used to encrypt messages, as opposed to other uses, like encrypting other keys .Session keys can introduce...
is a symmetric, generated key, which will be the session keySession keyA session key is a single-use symmetric key used for encrypting all messages in one communication session. A closely related term is traffic encryption key or TEK, which refers to any key used to encrypt messages, as opposed to other uses, like encrypting other keys .Session keys can introduce...
of the session between A and B

- Alice sends a message to Bob requesting communication.
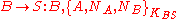
- Bob sends a message to the Server encrypted under
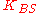 .
.
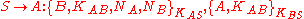
- The Server sends to Alice a message containing the generated session key
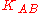 and a message to be forwarded to Bob.
and a message to be forwarded to Bob.
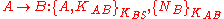
- Alice forwards the message to Bob and verifies
 has not changed. Bob will verify
has not changed. Bob will verify 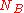 has not changed when he receives the message.
has not changed when he receives the message.
See also
- Kerberos
- Needham-Schroeder
- Otway-Rees
- Neuman-StubblebineNeuman-Stubblebine protocolThe Neuman–Stubblebine protocol is a computer network authentication protocol designed for use on insecure networks . It allows individuals communicating over such a network to prove their identity to each other...
- Wide Mouth Frog protocolWide Mouth Frog protocolThe Wide-Mouth Frog protocol is a computer network authentication protocol designed for use on insecure networks . It allows individuals communicating over a network to prove their identity to each other while also preventing eavesdropping or replay attacks, and provides for detection of...

