
X-ray telescope
Encyclopedia
An X-ray telescope is a telescope
that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray
spectrum. In order to get above the Earth's atmosphere, which is opaque to X-rays, X-ray telescopes must be mounted on high altitude rockets or artificial satellites.
and coded aperture
s. The limitations of X-ray optics
result in much narrower fields of view than visible or UV telescopes.
The mirrors can be made of ceramic or metal foil. The most commonly used grazing angle incidence materials for X-ray mirrors are gold
and iridium
. The critical reflection angle is energy dependent. For gold at 1 keV, the critical reflection angle is 3.72 degrees.
A limit for this technology in the early 2000s with Chandra and XMM-Newton was about 15 keV light. Using new multi-layered coatings, computer aided manufacturing, and other techniques the x-ray mirror for the NuStar
telescope pushed this up to 79 keV light. To reflect at this level, glass layers were multi-coated with Tungsten (W)/Silicon (Si) or Platinum(Pt)/Siliconcarbite(SiC).
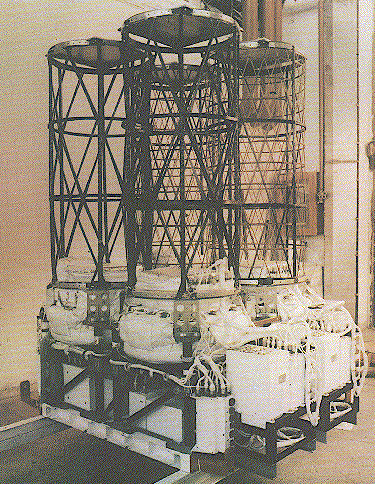

used Wolter
I X-ray optics
and were equipped with two focal plane detectors:
was a hard X-ray telescope. Its effective energy range: 7–550 keV, field of view (FOV) 6.5°, effective area ~64 cm2.
, consisted of four gas flow proportional counters, three of which had a total detection surface of 450 cm2 in the energy range 2–10 keV, and one of which has an effective surface of 37 cm2 for the range 0.2–2 keV. The FOV was limited by a slit collimator to 3° x 10° FWHM. The instrumentation included optical sensors mounted on the outside of the station together with the X-ray detectors. The power supply and measurement units were inside the station. Ground based calibration of the detectors occurred along with in-flight operation in three modes: inertial orientation, orbital orientation, and survey. Data were collected in 4 energy channels: 2–3.1 keV, 3.1–5.9 keV, 5.9–9.6 keV, and 2–9.6 keV in the larger detectors. The smaller detector had discriminator levels set at 0.2 keV, 0.55 keV, and 0.95 keV.
was 15 arcmin. The energy resolution was 8% at 511 keV. Its imaging capabilities were derived from the association of a coded mask and a position sensitive detector based on the Anger camera principle.
together with a URA coded mask. Each module had an effective area of approximately 600 cm2, producing a FOV
of 1.8° x 1.8°. The angular resolution
was 5 arcmin
; temporal and energy resolutions were 3.9 ms
and 22% at 6 keV, respectively. The instrument achieved a sensitivity of 0.001 of the Crab nebula
source (= 1 "mCrab") in an eight-hour exposure. The maximum time resolution was 4 ms.
(BBXRT) was flown on the Space Shuttle Columbia
(STS-35
) as part of the ASTRO-1 payload. BBXRT was the first focusing X-ray telescope operating over a broad energy range 0.3–12 keV with a moderate energy resolution (90 eV at 1 keV and 150 eV at 6 keV). The two Co-Aligned Telescopes with a segmented Si(Li) solid state spectrometer each (detector A and B) composite of five pixels. Total FOV 17.4´ diameter, Central pixel FOV 4´ diameter. Total area 765 cm2 at 1.5 keV, and 300 cm2 at 7 keV.
MIDEX mission (0.2–10 keV energy range) uses a Wolter I telescope to focus X-rays onto a thermoelectrically cooled CCD. It was designed to measure the fluxes, spectra, and lightcurves of Gamma-ray bursters (GRBs) and afterglows over a wide dynamic range covering more than 7 orders of magnitude in flux. The XRT can pinpoint GRBs to 5-arcsec accuracy within 10 seconds of target acquisition for a typical GRB and can study the X-ray counterparts of GRBs beginning 20–70 seconds from burst discovery and continuing for days to weeks.
The overall telescope length is 4.67 m with a focal length of 3.500 m and a diameter of 0.51 m. The primary structural element is an aluminum optical bench interface flange at the front of the telescope that supports the forward and aft telescope tubes, the mirror module, the electron deflector, and the internal alignment monitor optics and camera, plus mounting points to the Swift observatory.
The 508 mm diameter telescope tube is made of graphite fiber/cyanate ester in two sections. The outer graphite fiber layup is designed to minimize the longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion, whereas the inner composite tube is lined internally with an aluminum foil vapor barrier to guard against outgassing of water vapor or epoxy contaminants into the telescope interior. The telescope has a forward tube which encloses the mirrors and supports the door assmebly and star trackers, and an aft tube which supports the focal plane camera and internal optical baffles.
The mirror module consists of 12 nested Wolter I grazing incidence mirrors held in place by front and rear spiders. The passively heated mirrors are gold-coated, electroformed nickel shells 600 mm long with diameters ranging from 191 to 300 mm.
The X-ray imager has an effective area of >120 cm2 at 1.15 keV, a field of view of 23.6 x 23.6 arcmin, and angular resolution
(θ) of 18 arcsec at half-power diameter (HPD). The detection sensitivity is 2 x 10−14 erg cm−2s−1 in 104 s. The mirror point spread function (PSF) has a 15 arcsec HPD at the best on-axis focus (at 1.5 keV). The mirror is slightly defocused in the XRT to provide a more uniform PSF for the entire field of view hence the instrument PSF θ = 18 arcsec.
, NIXT
used normal incidence reflective multilayer optics.
. The first X-ray picture of the Sun was taken in 1963, by a rocket-borne telescope.
Einstein Observatory
(1978–1981) was the first focusing X-ray telescope in space. Its main optic was a Wolter Type I, which worked from 0.1 to 4 keV.
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
spectrum. In order to get above the Earth's atmosphere, which is opaque to X-rays, X-ray telescopes must be mounted on high altitude rockets or artificial satellites.
Optical design
X-ray telescopes can use a variety of different designs to image X-rays. The most common methods used in X-ray telescopes are grazing incidence mirrorsWolter telescope
A Wolter telescope is a telescope for X-rays using only grazing incidence optics. Visible light telescopes are built with lenses or parabolic mirrors at nearly normal incidence. Neither works well for X-rays. Lenses for visible light are made of a transparent material with an index of refraction...
and coded aperture
Coded aperture
Coded Apertures or Coded-Aperture Masks are grids, gratings, or other patterns of materials opaque to various wavelengths of light. The wavelengths are usually high-energy radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. By blocking and unblocking light in a known pattern, a coded "shadow" is cast upon a...
s. The limitations of X-ray optics
X-ray optics
X-ray optics is the branch of optics which manipulates X-rays instead of visible light. While lenses for visible light are made of transparent materials that can have a refractive index substantially larger than 1, for X-rays the index of refraction is slightly smaller than unity. The principal...
result in much narrower fields of view than visible or UV telescopes.
Mirrors
The utilization of X-ray mirrors for extrasolar X-ray astronomy simultaneously requires:- the ability to determine the location at the arrival of an X-ray photon in two dimensions and
- a reasonable detection efficiency.
The mirrors can be made of ceramic or metal foil. The most commonly used grazing angle incidence materials for X-ray mirrors are gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
and iridium
Iridium
Iridium is the chemical element with atomic number 77, and is represented by the symbol Ir. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum family, iridium is the second-densest element and is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C...
. The critical reflection angle is energy dependent. For gold at 1 keV, the critical reflection angle is 3.72 degrees.
A limit for this technology in the early 2000s with Chandra and XMM-Newton was about 15 keV light. Using new multi-layered coatings, computer aided manufacturing, and other techniques the x-ray mirror for the NuStar
Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array
Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array is a planned space-based X-ray telescope that will use grazing incidence mirrors to focus high energy X-rays at 5 to 79 keV from astrophysical sources, especially for nuclear spectroscopy...
telescope pushed this up to 79 keV light. To reflect at this level, glass layers were multi-coated with Tungsten (W)/Silicon (Si) or Platinum(Pt)/Siliconcarbite(SiC).
Coded apertures
Some X-ray telescopes use coded aperture imaging. This technique uses a flat aperture grille in front of the detector, which weighs much less than any kind of focusing X-ray lens, but requires considerably more post-processing to produce an image.Telescopes


Exosat
The two low-energy imaging telescopes onboard ExosatEXOSAT
The European X-ray Observatory Satellite , originally named HELOS, was operational from May 1983 until April 1986 and in that time made 1780 observations in the X-ray band of most classes of astronomical object including active galactic nuclei, stellar coronae, cataclysmic variables, white dwarfs,...
used Wolter
Wolter telescope
A Wolter telescope is a telescope for X-rays using only grazing incidence optics. Visible light telescopes are built with lenses or parabolic mirrors at nearly normal incidence. Neither works well for X-rays. Lenses for visible light are made of a transparent material with an index of refraction...
I X-ray optics
X-ray optics
X-ray optics is the branch of optics which manipulates X-rays instead of visible light. While lenses for visible light are made of transparent materials that can have a refractive index substantially larger than 1, for X-rays the index of refraction is slightly smaller than unity. The principal...
and were equipped with two focal plane detectors:
- a position-sensitive proportional counter (PSD) and
- a channel multiplier array (CMA).
Hard X-ray telescope
On board OSO 7OSO 7
OSO 7 is the seventh in the series of American Orbiting Solar Observatory satellites launched by NASA between 1962 and 1975...
was a hard X-ray telescope. Its effective energy range: 7–550 keV, field of view (FOV) 6.5°, effective area ~64 cm2.
Filin telescope
The Filin telescope carried aboard Salyut 4Salyut 4
Salyut 4 was a Salyut space station launched on December 26, 1974 into an orbit with an apogee of 355 km, a perigee of 343 km and an orbital inclination of 51.6 degrees. It was essentially a copy of the DOS 3, and unlike its ill-fated sibling it was a complete success...
, consisted of four gas flow proportional counters, three of which had a total detection surface of 450 cm2 in the energy range 2–10 keV, and one of which has an effective surface of 37 cm2 for the range 0.2–2 keV. The FOV was limited by a slit collimator to 3° x 10° FWHM. The instrumentation included optical sensors mounted on the outside of the station together with the X-ray detectors. The power supply and measurement units were inside the station. Ground based calibration of the detectors occurred along with in-flight operation in three modes: inertial orientation, orbital orientation, and survey. Data were collected in 4 energy channels: 2–3.1 keV, 3.1–5.9 keV, 5.9–9.6 keV, and 2–9.6 keV in the larger detectors. The smaller detector had discriminator levels set at 0.2 keV, 0.55 keV, and 0.95 keV.
SIGMA telescope
The hard X-ray and low-energy gamma-ray SIGMA telescope covered the energy range 35–1300 keV, with an effective area of 800 cm2 and a maximum sensitivity field of view of ~5° × 5°. The maximum angular resolutionAngular resolution
Angular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
was 15 arcmin. The energy resolution was 8% at 511 keV. Its imaging capabilities were derived from the association of a coded mask and a position sensitive detector based on the Anger camera principle.
ART-P X-ray telescope
The ART-P X-ray telescope covered the energy range 4 to 60 keV for imaging and 4 to 100 keV for spectroscopy and timing. There were four identical modules of the ART-P telescope, each consisting of a position sensitive multi-wire proportional counter (MWPC)Wire chamber
A multi-wire chamber is a detector for particles of ionizing radiation which is an advancement of the concept of the Geiger counter and the proportional counter....
together with a URA coded mask. Each module had an effective area of approximately 600 cm2, producing a FOV
Field of view
The field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
of 1.8° x 1.8°. The angular resolution
Angular resolution
Angular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
was 5 arcmin
Minute of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute, or minute of angle , is a unit of angular measurement equal to one sixtieth of one degree. In turn, a second of arc or arcsecond is one sixtieth of one minute of arc....
; temporal and energy resolutions were 3.9 ms
Millisecond
A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond....
and 22% at 6 keV, respectively. The instrument achieved a sensitivity of 0.001 of the Crab nebula
Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus...
source (= 1 "mCrab") in an eight-hour exposure. The maximum time resolution was 4 ms.
Focusing X-ray telescope
The Broad Band X-ray TelescopeBroad Band X-ray Telescope
The Broad Band X-ray Telescope was flown on the space shuttle Columbia on 1990 December 2-December 11, as part of the ASTRO-1 payload...
(BBXRT) was flown on the Space Shuttle Columbia
Space Shuttle Columbia
Space Shuttle Columbia was the first spaceworthy Space Shuttle in NASA's orbital fleet. First launched on the STS-1 mission, the first of the Space Shuttle program, it completed 27 missions before being destroyed during re-entry on February 1, 2003 near the end of its 28th, STS-107. All seven crew...
(STS-35
STS-35
-Crew notes:Prior to the Challenger disaster, this mission was slated to launch in March 1986 as STS-61-E. Jon McBride was originally assigned to command this mission, which would have been his second spaceflight. He chose to retire from NASA in May 1989 and was replaced as mission commander by...
) as part of the ASTRO-1 payload. BBXRT was the first focusing X-ray telescope operating over a broad energy range 0.3–12 keV with a moderate energy resolution (90 eV at 1 keV and 150 eV at 6 keV). The two Co-Aligned Telescopes with a segmented Si(Li) solid state spectrometer each (detector A and B) composite of five pixels. Total FOV 17.4´ diameter, Central pixel FOV 4´ diameter. Total area 765 cm2 at 1.5 keV, and 300 cm2 at 7 keV.
XRT on the Swift MIDEX mission
The XRT on the SwiftSwift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission
The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission consists of a robotic spacecraft called Swift, which was launched into orbit on 20 November 2004, 17:16:00 UTC on a Delta II 7320-10C expendable launch vehicle. Swift is managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and was developed by an international...
MIDEX mission (0.2–10 keV energy range) uses a Wolter I telescope to focus X-rays onto a thermoelectrically cooled CCD. It was designed to measure the fluxes, spectra, and lightcurves of Gamma-ray bursters (GRBs) and afterglows over a wide dynamic range covering more than 7 orders of magnitude in flux. The XRT can pinpoint GRBs to 5-arcsec accuracy within 10 seconds of target acquisition for a typical GRB and can study the X-ray counterparts of GRBs beginning 20–70 seconds from burst discovery and continuing for days to weeks.
The overall telescope length is 4.67 m with a focal length of 3.500 m and a diameter of 0.51 m. The primary structural element is an aluminum optical bench interface flange at the front of the telescope that supports the forward and aft telescope tubes, the mirror module, the electron deflector, and the internal alignment monitor optics and camera, plus mounting points to the Swift observatory.
The 508 mm diameter telescope tube is made of graphite fiber/cyanate ester in two sections. The outer graphite fiber layup is designed to minimize the longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion, whereas the inner composite tube is lined internally with an aluminum foil vapor barrier to guard against outgassing of water vapor or epoxy contaminants into the telescope interior. The telescope has a forward tube which encloses the mirrors and supports the door assmebly and star trackers, and an aft tube which supports the focal plane camera and internal optical baffles.
The mirror module consists of 12 nested Wolter I grazing incidence mirrors held in place by front and rear spiders. The passively heated mirrors are gold-coated, electroformed nickel shells 600 mm long with diameters ranging from 191 to 300 mm.
The X-ray imager has an effective area of >120 cm2 at 1.15 keV, a field of view of 23.6 x 23.6 arcmin, and angular resolution
Angular resolution
Angular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
(θ) of 18 arcsec at half-power diameter (HPD). The detection sensitivity is 2 x 10−14 erg cm−2s−1 in 104 s. The mirror point spread function (PSF) has a 15 arcsec HPD at the best on-axis focus (at 1.5 keV). The mirror is slightly defocused in the XRT to provide a more uniform PSF for the entire field of view hence the instrument PSF θ = 18 arcsec.
Normal incidence X-ray telescope
Like MSSTAMSSTA
The Multi-spectral solar telescope array, or MSSTA, was a sounding rocket payload built by Professor A.B.C. Walker, Jr. at Stanford University in the 1990s to test EUV/XUV imaging of the Sun using normal incidence EUV-reflective multilayer optics...
, NIXT
NIXT
The NIXT, or Normal Incidence X-ray Telescope, was a sounding rocket payload flown in the 1990s by Professor Leon Golub of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, to prototype normal-incidence optical designs in extreme ultraviolet solar imaging...
used normal incidence reflective multilayer optics.
History of X-ray telescopes
The first X-ray telescope was used to observe the SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. The first X-ray picture of the Sun was taken in 1963, by a rocket-borne telescope.
Einstein Observatory
Einstein Observatory
Einstein Observatory was the first fully imaging X-ray telescope put into space and the second of NASA's three High Energy Astrophysical Observatories...
(1978–1981) was the first focusing X-ray telescope in space. Its main optic was a Wolter Type I, which worked from 0.1 to 4 keV.
External links
See also
- List of telescope types
- Solar X-ray astronomy
- Sounding rocket X-ray astronomy
- Synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy
- X-ray astronomyX-ray astronomyX-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and...
- Wolter telescopeWolter telescopeA Wolter telescope is a telescope for X-rays using only grazing incidence optics. Visible light telescopes are built with lenses or parabolic mirrors at nearly normal incidence. Neither works well for X-rays. Lenses for visible light are made of a transparent material with an index of refraction...
: A type of X-ray telescope built with glancing incidence mirrors.

