
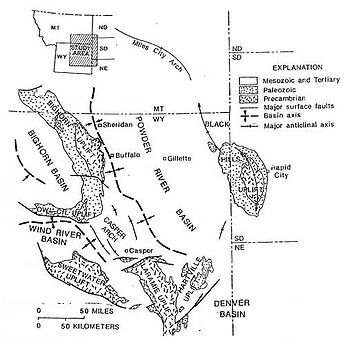
Wind River Basin
Encyclopedia
Intermontane
Intermontane is a physiographic adjective formed from the prefix "inter-" and the adjective "montane" Usage includes intermontane basin such as New Zealand's Mackenzie Basin and intermontane...
structural basin in central Wyoming
Wyoming
Wyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High...
, USA. It is bounded by Laramide
Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute, as is the cause. The Laramide...
uplifts on all sides. On the west is the Wind River Range
Wind River Range
The Wind River Range , is a mountain range of the Rocky Mountains in western Wyoming in the United States. The range runs roughly NW-SE for approximately 100 miles . The Continental Divide follows the crest of the range and includes Gannett Peak, which at 13,804 feet , is the highest peak...
and on the North are the Absaroka Range
Absaroka Range
The Absaroka Range is a sub-range of the Rocky Mountains in the United States. The range stretches about 150 mi across the Montana-Wyoming border, forming the eastern boundary of Yellowstone National Park and the western side of the Bighorn Basin. The range borders the Beartooth Mountains...
and the Owl Creek Mountains
Owl Creek Mountains
The Owl Creek Mountains are a subrange of the Rocky Mountains in central Wyoming in the United States, running east to west to form a bridge between the Absaroka Range to the northwest and the Bridger Mountains to the east. The range forms the boundary between the Bighorn Basin to the north and the...
. The Casper Arch separates the Wind River from the Powder River Basin
Powder River Basin
The Powder River Basin is a geologic region in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about east to west and north to south, known for its coal deposits. The region supplies about 40 percent of coal in the United States. It is both a topographic drainage and geologic structural basin...
to the east and the Sweetwater Uplift (Granite Range
Granite Mountains (Wyoming)
The Granite Mountains are a short subrange of the Rocky Mountains in central Wyoming of the United States. The range runs approximately 100 mi E-W along the south side of the Shoshone Basin, and north of the Sweetwater River, in eastern Fremont County and western Natrona County. The highest...
) lies to the south. The basin contains a sequence of 10,000-12,000 feet (3000-3700 meters) of predominantly marine sediments deposited during the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
and Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
Eras. During the Laramide over 18,000 feet (5500 meters) of Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
lacustrine
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
and fluvial sediments were deposited within the basin. Following the Eocene an additional 3,000 feet (900 meters) of sediments were deposited before, and as the basin was uplifted in the late Tertiary
Tertiary
The Tertiary is a deprecated term for a geologic period 65 million to 2.6 million years ago. The Tertiary covered the time span between the superseded Secondary period and the Quaternary...
.
The formations within the basin are significant producers of petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
and natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
. The basin contains over 60 oil and gas fields mostly as structural traps within seventeen different formations. The primary reservoirs include the Pennsylvanian
Pennsylvanian
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain...
Tensleep Sandstone, the Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
Phosphoria Formation
Phosphoria Formation
The Permian Phosphoria Formation of the western United States represents some 15 million years of sedimentation, reaches a thickness of and covers an area of . The formation is a phosphorite and an important resource of phosphorus....
and the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
Muddy Creek and Frontier sandstones.
The first oil strike within the basin was from the Dallas dome in the western part of the basin. This discovery in 1884 was the first commercial production in Wyoming.
Major towns in the Wind River Basin include Riverton
Riverton, Wyoming
Riverton is a city in Fremont County, Wyoming, United States. It is both the largest city in the county and the largest within the historical boundaries of the Wind River Indian Reservation. The city's population was 9,310 at the 2000 census...
, Shoshoni
Shoshoni, Wyoming
Shoshoni is a town in Fremont County, Wyoming, United States. The population was 635 at the 2000 census. The town is named for the Shoshone tribe of Native Americans, most of whom live on the nearby Wind River Indian Reservation...
, and Lander
Lander, Wyoming
Lander is a city in, and the county seat of, Fremont County, Wyoming, United States. Named for transcontinental explorer Frederick W. Lander, Lander is located in central Wyoming, along the Middle Fork of the Popo Agie River. A tourism center with several dude ranches nearby, Lander is located just...
. Much of the Wind River Basin is within the boundaries of the Wind River Indian Reservation
Wind River Indian Reservation
Wind River Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation shared by the Eastern Shoshone and Northern Arapaho tribes of Native Americans in the central western portion of the U.S. state of Wyoming...
. The basin is drained primarily by the Wind River
Wind River (Wyoming)
The Wind River is the name applied to the upper reaches of the Bighorn River in Wyoming in the United States. The Wind River is long. The two rivers are sometimes referred to as the Wind/Bighorn.-Course:...
and its tributaries.

