
Wasting
Encyclopedia
In medicine, wasting refers to the process by which a debilitating disease
causes muscle
and fat
tissue
to "waste" away. Wasting is sometimes referred to as "acute malnutrition" because it is believed that episodes of wasting have a short duration, in contrast to stunting
, which is regarded as chronic malnutrition.
), nutrient losses due to infection, or a combination of low intake and high loss. Infections and conditions associated with wasting include tuberculosis
, chronic diarrhea
, AIDS
, and Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
. The mechanism may involve cachectin - also called tumor necrosis factor, a macrophage-secreted cytokine
.
Caretakers and health providers can sometimes contribute to wasting if the patient is placed on an improper diet.
Voluntary weight loss and eating disorder
s are excluded as causes of wasting.
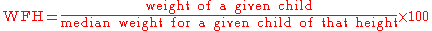
Cutoff points may vary, but <80% (close to -2 Z-score) is often used.
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
causes muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
and fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
to "waste" away. Wasting is sometimes referred to as "acute malnutrition" because it is believed that episodes of wasting have a short duration, in contrast to stunting
Stunted growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition in early childhood, including malnutrition during fetal development brought on by the malnourished mother. In developing countries, stunted growth is a common problem affecting a large...
, which is regarded as chronic malnutrition.
Causes
Wasting can be caused by an extremely low energy intake (e.g., caused by famineFamine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including crop failure, overpopulation, or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompanied or followed by regional malnutrition, starvation, epidemic, and increased mortality. Every continent in the world has...
), nutrient losses due to infection, or a combination of low intake and high loss. Infections and conditions associated with wasting include tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
, chronic diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, AIDS
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
, and Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is a very rare, life-threatening gastro-vascular disorder characterized by a compression of the third portion of the duodenum by the abdominal aorta and the overlying superior mesenteric artery...
. The mechanism may involve cachectin - also called tumor necrosis factor, a macrophage-secreted cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
.
Caretakers and health providers can sometimes contribute to wasting if the patient is placed on an improper diet.
Voluntary weight loss and eating disorder
Eating disorder
Eating disorders refer to a group of conditions defined by abnormal eating habits that may involve either insufficient or excessive food intake to the detriment of an individual's physical and mental health. Bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa, and binge eating disorder are the most common specific...
s are excluded as causes of wasting.
Classification
- Children: Weight-for-height (WFH). In infants under 24 months, recumbent (supine) length is used. WFH as % of median reference value is calculated this way:
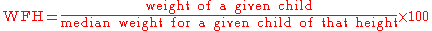
Cutoff points may vary, but <80% (close to -2 Z-score) is often used.
- Adults:
- Body Mass IndexBody mass indexThe body mass index , or Quetelet index, is a heuristic proxy for human body fat based on an individual's weight and height. BMI does not actually measure the percentage of body fat. It was invented between 1830 and 1850 by the Belgian polymath Adolphe Quetelet during the course of developing...
(BMI) is the quotient between weight and height squared (kg/m2). An individual with a BMI < 18.5 is regarded as a case of wasting. - Percent of body weight lost (At Tufts, an unintentional loss of 6% or more in 6 months is regarded as wasting)
- Body Mass Index
See also
- AtrophyAtrophyAtrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations , poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself...
- CachexiaCachexiaCachexia or wasting syndrome is loss of weight, muscle atrophy, fatigue, weakness, and significant loss of appetite in someone who is not actively trying to lose weight...
- Weight lossWeight lossWeight loss, in the context of medicine, health or physical fitness, is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon and other connective tissue...
- AnorexiaAnorexia (symptom)Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
- Superior mesenteric artery syndromeSuperior mesenteric artery syndromeSuperior mesenteric artery syndrome is a very rare, life-threatening gastro-vascular disorder characterized by a compression of the third portion of the duodenum by the abdominal aorta and the overlying superior mesenteric artery...
External links
- http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol10no6/03-1082.htm
- http://www.tufts.edu/med/nutrition-infection/hiv/health_weight_loss.html
- http://www.annalsnyas.org/cgi/content/abstract/587/1/325

