
Warrant (finance)
Encyclopedia
In finance
, a warrant is a security
that entitles the holder to buy the underlying stock of the issuing company at a fixed exercise price until the expiry date.
Warrants and option
s are similar in that the two contractual financial instruments allow the holder special rights to buy securities. Both are discretionary and have expiration dates. The word warrant simply means to "endow with the right", which is only slightly different than the meaning of option.
Warrants are frequently attached to bonds or preferred stock
as a sweetener, allowing the issuer to pay lower interest rates or dividends. They can be used to enhance the yield
of the bond, and make them more attractive to potential buyers. Warrants can also be used in private equity
deals. Frequently, these warrants are detachable, and can be sold independently of the bond or stock.
In the case of warrants issued with preferred stocks, stockholders may need to detach and sell the warrant before they can receive dividend payments. Thus, it is sometimes beneficial to detach and sell a warrant as soon as possible so the investor can earn dividends.
Warrants are actively traded in some financial markets such as Deutsche Börse and Hong Kong. In Hong Kong Stock Exchange, warrants accounted for 11.7% of the turnover in the first quarter of 2009, just second to the callable bull/bear contract
.
The warrant parameters, such as exercise price, are fixed shortly after the issue of the bond. With warrants, it is important to consider the following main characteristics:
Warrants are longer-dated options and are generally traded over-the-counter.
. But often, warrants are privately held or not registered, which makes their prices less obvious. Warrants can be easily tracked by adding a "w" after the company’s ticker symbol
to check the warrant's price. Unregistered warrant transactions can still be facilitated between accredited parties, and in fact several secondary markets have been formed to provide liquidity for these investments.
s. For instance, many warrants confer the same rights as equity options, and warrants often can be traded in secondary markets like options. However, there also are several key differences between warrants and equity options:
(known as a warrant-linked bond), and represent the right to acquire shares
in the entity issuing the bond. In other words, the writer of a traditional warrant is also the issuer of the underlying instrument. Warrants are issued in this way as a "sweetener
" to make the bond issue more attractive, and to reduce the interest rate that must be offered in order to sell the bond issue.
. They are typically issued by banks and securities firms. These are also called covered warrant
s, and are settled for cash, e.g. do not involve the company who issues the shares that underlie the warrant. In most markets around the world, covered warrants are more popular than the traditional warrants described above. Financially they are also similar to call options, but are typically bought by retail investors, rather than investment funds or banks, who prefer the more keenly priced options which tend to trade on a different market. Covered warrants normally trade alongside equities, which makes them easier for retail investors to buy and sell them.
or an IOU
issued by a governmental agency. California differentiates between regular warrants, which can be exchanged immediately for cash and registered warrants which are IOUs.
In the late 1990s, when the State of California
had a budget crisis due to a disagreement between the governor and the legislature, the state treasurer was forced to issue warrants paying 18% interest in lieu of being able to pay the state's bills with real money. The state had not issued warrants since before the Depression
of the 1930s. Many institutions accepted them at face value because of the interest provision. Interestingly, the controller of Los Angeles County
was buying the warrants because the county had surplus funds to take advantage of the higher interest rates on the warrants.
In some states, a warrant is a demand draft drawn on a government's treasury to pay its bills. Checks or electronic payments have replaced these warrants, but in Arkansas
, some counties and school districts uses warrants for non-electronic payments
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, a warrant is a security
Security (finance)
A security is generally a fungible, negotiable financial instrument representing financial value. Securities are broadly categorized into:* debt securities ,* equity securities, e.g., common stocks; and,...
that entitles the holder to buy the underlying stock of the issuing company at a fixed exercise price until the expiry date.
Warrants and option
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
s are similar in that the two contractual financial instruments allow the holder special rights to buy securities. Both are discretionary and have expiration dates. The word warrant simply means to "endow with the right", which is only slightly different than the meaning of option.
Warrants are frequently attached to bonds or preferred stock
Preferred stock
Preferred stock, also called preferred shares, preference shares, or simply preferreds, is a special equity security that has properties of both an equity and a debt instrument and is generally considered a hybrid instrument...
as a sweetener, allowing the issuer to pay lower interest rates or dividends. They can be used to enhance the yield
Yield (finance)
In finance, the term yield describes the amount in cash that returns to the owners of a security. Normally it does not include the price variations, at the difference of the total return...
of the bond, and make them more attractive to potential buyers. Warrants can also be used in private equity
Private equity
Private equity, in finance, is an asset class consisting of equity securities in operating companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange....
deals. Frequently, these warrants are detachable, and can be sold independently of the bond or stock.
In the case of warrants issued with preferred stocks, stockholders may need to detach and sell the warrant before they can receive dividend payments. Thus, it is sometimes beneficial to detach and sell a warrant as soon as possible so the investor can earn dividends.
Warrants are actively traded in some financial markets such as Deutsche Börse and Hong Kong. In Hong Kong Stock Exchange, warrants accounted for 11.7% of the turnover in the first quarter of 2009, just second to the callable bull/bear contract
Callable bull/bear contract
A callable bull/bear contract, or CBBC in short form, is a derivative that provides investors with a leveraged investment in underlying assets, which can be a single stock, or an index. They are usually issued by third parties, mostly investment banks, but neither stock exchanges nor asset owners...
.
Structure and features
Warrants have similar characteristics to that of other equity derivatives, such as options, for instance:- Exercising: A warrant is exercised when the holder informs the issuer their intention to purchase the shares underlying the warrant.
The warrant parameters, such as exercise price, are fixed shortly after the issue of the bond. With warrants, it is important to consider the following main characteristics:
- Premium: A warrant's "premium" represents how much extra you have to pay for your shares when buying them through the warrant as compared to buying them in the regular way.
- Gearing (leverage): A warrant's "gearing" is the way to ascertain how much more exposure you have to the underlying shares using the warrant as compared to the exposure you would have if you buy shares through the market.
- Expiration Date: This is the date the warrant expires. If you plan on exercising the warrant you must do so before the expiration date. The more time remaining until expiry, the more time for the underlying security to appreciate, which, in turn, will increase the price of the warrant (unless it depreciates). Therefore, the expiry date is the date on which the right to exercise ceases to exist.
- Restrictions on exercise: Like options, there are different exercise types associated with warrants such as American style (holder can exercise anytime before expiration) or European style (holder can only exercise on expiration date).
Warrants are longer-dated options and are generally traded over-the-counter.
Over-the-counter (finance)
Within the derivatives markets, many products are traded through exchanges. An exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity and also mitigates all credit risk concerning the default of a member of the exchange. Products traded on the exchange must be well standardised to transparent trading....
Secondary market
Sometimes the issuer will try to establish a market for the warrant and to register it with a listed exchange. In this case, the price can be obtained from a brokerStock broker
A stock broker or stockbroker is a regulated professional broker who buys and sells shares and other securities through market makers or Agency Only Firms on behalf of investors...
. But often, warrants are privately held or not registered, which makes their prices less obvious. Warrants can be easily tracked by adding a "w" after the company’s ticker symbol
Ticker symbol
A stock symbol or ticker symbol is a short abbreviation used to uniquely identify publicly traded shares of a particular stock on a particular stock market. A stock symbol may consist of letters, numbers or a combination of both. "Ticker symbol" refers to the symbols that were printed on the ticker...
to check the warrant's price. Unregistered warrant transactions can still be facilitated between accredited parties, and in fact several secondary markets have been formed to provide liquidity for these investments.
Comparison with call options
Warrants are very similar to call optionCall option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
s. For instance, many warrants confer the same rights as equity options, and warrants often can be traded in secondary markets like options. However, there also are several key differences between warrants and equity options:
- Warrants are issued by private parties, typically the corporation on which a warrant is based, rather than a public options exchangeFutures exchangeA futures exchange or futures market is a central financial exchange where people can trade standardized futures contracts; that is, a contract to buy specific quantities of a commodity or financial instrument at a specified price with delivery set at a specified time in the future. These types of...
. - Warrants issued by the company itself are dilutiveStock dilutionStock dilution is a general term that results from the issue of additional common shares by a company. This increase in common shares of a stock can result from a secondary market offering, employees exercising stock options, or by conversion of convertible bonds, preferred shares or warrants into...
. When the warrant issued by the company is exercised, the company issues new shares of stock, so the number of outstanding shares increases. When a call option is exercised, the owner of the call option receives an existing share from an assigned call writer (except in the case of employee stock optionEmployee stock optionAn employee stock option is a call option on the common stock of a company, issued as a form of non-cash compensation. Restrictions on the option attempt to align the holder's interest with those of the business shareholders. If the company's stock rises, holders of options generally experience a...
s, where new shares are created and issued by the company upon exercise). Unlike common stock shares outstanding, warrants do not have voting rights. - Warrants are considered over the counterOver-the-counter (finance)Within the derivatives markets, many products are traded through exchanges. An exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity and also mitigates all credit risk concerning the default of a member of the exchange. Products traded on the exchange must be well standardised to transparent trading....
instruments, and thus are usually only traded by financial institutions with the capacity to settle and clear these types of transactions. - A warrant's lifetime is measured in years (as long as 15 years), while options are typically measured in months. Even LEAPS (long-term equity anticipation securities), the longest stock options available, tend to expire in two or three years. Upon expiration, the warrants are worthless unless the price of the common stock is greater than the exercise price.
- Warrants are not standardized like exchange-listed options. While investors can write stock options on the ASXAustralian Securities ExchangeThe Australian Securities Exchange was created by the merger of the Australian Stock Exchange and the Sydney Futures Exchange in July 2006. It is the primary stock exchange group in Australia....
(or CBOEChicago Board Options ExchangeThe Chicago Board Options Exchange , located at 400 South LaSalle Street in Chicago, is the largest U.S. options exchange with annual trading volume that hovered around one billion contracts at the end of 2007...
), they are not permitted to do so with ASX-listed warrants, since only companies can issue warrants, and while each option contract is over 1000 underlying ordinary shares (100 on CBOE), the number of warrants that must be exercised by the holder to buy the underlying asset depends on the conversion ratio set out in the offer documentation for the warrant issue.
Types of warrants
A wide range of warrants and warrant types are available. The reasons you might invest in one type of warrant may be different from the reasons you might invest in another type of warrant.- Equity warrants: Equity warrants can be call and put warrants.
- Callable warrants: Callable warrants give the Company the right to force the warrant holder to exercise the warrants into their predetermined number of shares at a predetermined price (or using a predetermined price formula) after certain contractual conditions are met
- Putable warrants: Putable warrants give the warrant holder the right to force the Company to issue the underlying securities at a predetermined price after certain contractual conditions are met
- Covered warrants: A covered warrantCovered warrantIn finance a covered warrant is a type of warrant that has been issued without an accompanying bond or equity...
s is a warrant that has some underlying backing, for example the issuer will purchase the stock beforehand or will use other instruments to cover the option. - Basket warrants: As with a regular equity index, warrants can be classified at, for example, an industry level. Thus, it mirrors the performance of the industry.
- Index warrants: Index warrants use an index as the underlying asset. Your risk is dispersed—using index call and index put warrants—just like with regular equity indexes. It should be noted that they are priced using index points. That is, you deal with cash, not directly with shares.
- Wedding warrants: are attached to the host debentures and can be exercised only if the host debentures are surrendered
- Detachable warrants: the warrant portion of the security can be detached from the debenture and traded separately.
- Naked warrants: are issued without an accompanying bond, and like traditional warrants, are traded on the stock exchange.
Traditional
Traditional warrants are issued in conjunction with a BondBond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holders a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use and/or to repay the principal at a later date, termed maturity...
(known as a warrant-linked bond), and represent the right to acquire shares
Share (finance)
A joint stock company divides its capital into units of equal denomination. Each unit is called a share. These units are offered for sale to raise capital. This is termed as issuing shares. A person who buys share/shares of the company is called a shareholder, and by acquiring share or shares in...
in the entity issuing the bond. In other words, the writer of a traditional warrant is also the issuer of the underlying instrument. Warrants are issued in this way as a "sweetener
Sweetener
Sweetener is a sugar substitute.Sweetener may also refer to:* Sugar alcohol* Honey* Syrup...
" to make the bond issue more attractive, and to reduce the interest rate that must be offered in order to sell the bond issue.
Example
- Price paid for bond with warrants
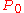
- Coupon payments C
- Maturity T
- Required rate of return r
- Face value of bond F
- Value of warrants =
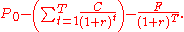
Naked
Naked warrants are issued without an accompanying bond, and like traditional warrants, are traded on the stock exchangeStock exchange
A stock exchange is an entity that provides services for stock brokers and traders to trade stocks, bonds, and other securities. Stock exchanges also provide facilities for issue and redemption of securities and other financial instruments, and capital events including the payment of income and...
. They are typically issued by banks and securities firms. These are also called covered warrant
Covered warrant
In finance a covered warrant is a type of warrant that has been issued without an accompanying bond or equity...
s, and are settled for cash, e.g. do not involve the company who issues the shares that underlie the warrant. In most markets around the world, covered warrants are more popular than the traditional warrants described above. Financially they are also similar to call options, but are typically bought by retail investors, rather than investment funds or banks, who prefer the more keenly priced options which tend to trade on a different market. Covered warrants normally trade alongside equities, which makes them easier for retail investors to buy and sell them.
Third-party warrants
Third-party warrant is a derivative issued by the holders of the underlying instrument. Suppose a company issues warrants which give the holder the right to convert each warrant into one share at $500. This warrant is company-issued. Suppose, a mutual fund that holds shares of the company sells warrants against those shares, also exercisable at $500 per share. These are called third-party warrants. The primary advantage is that the instrument helps in the price discovery process. In the above case, the mutual fund selling a one-year warrant exercisable at $500 sends a signal to other investors that the stock may trade at $500-levels in one year. If volumes in such warrants are high, the price discovery process will be that much better; for it would mean that many investors believe that the stock will trade at that level in one year. Third-party warrants are essentially long-term call options. The seller of the warrants does a covered call-write. That is, the seller will hold the stock and sell warrants against them. If the stock does not cross $500, the buyer will not exercise the warrant. The seller will, therefore, keep the warrant premium.Traded warrants
- "Traditional" warrant
- Naked warrant
- Exotic warrant
- Barrier warrant
- Covered warrantCovered warrantIn finance a covered warrant is a type of warrant that has been issued without an accompanying bond or equity...
- Hit-warrant
- Turbo warrantTurbo warrantTurbo warrant is a kind of stock option. Specifically, it is a barrier option of the Down and Out type. It is similar to a vanilla contract, but with two additional features: It has a low vega, meaning that the option price is much less affected by the implied volatility of the stock market, and it...
- Snail warrant
- Covered warrant
- Barrier warrant
- Third party warrants
Pricing
There are various methods (models) of evaluation available to value warrants theoretically, including the Black-Scholes evaluation model. However, it is important to have some understanding of the various influences on warrant prices. The market value of a warrant can be divided into two components:- Intrinsic value: This is simply the difference between the exercise (strike) price and the underlying stock price. Warrants are also referred to as in-the-money or out-of-the-money, depending on where the current asset price is in relation to the warrant's exercise price. Thus, for instance, for call warrants, if the stock price is below the strike price, the warrant has no intrinsic value (only time value—to be explained shortly). If the stock price is above the strike, the warrant has intrinsic value and is said to be in-the-money.
- Time value: Time value can be considered as the value of the continuing exposure to the movement in the underlying security that the warrant provides. Time value declines as the expiry of the warrant gets closer. This erosion of time value is called time decay. It is not constant, but increases rapidly towards expiry. A warrant's time value is affected by the following factors:
- Time to expiry: The longer the time to expiry, the greater the time value of the warrant. This is because the price of the underlying asset has a greater probability of moving in-the-money which makes the warrant more valuable.
- Volatility: The more volatile the underlying instrument, the higher the price of the warrant will be (as the warrant is more likely to end up in-the-money).
- Dividends: To include the factor of receiving dividends depends on if the holder of the warrant is permitted to receive dividends from the underlying asset.
- Interest rates: An increase in interest rates will lead to more expensive call warrants and cheaper put warrants. The level of interest rates reflects the opportunity cost of capitalOpportunity cost of capitalThe opportunity cost of capital is the expected rate of return forgone by bypassing of other potential investment activities for a given capital.It is a rate of return that investors could earn in financial markets....
.
Uses
- Portfolio protection: Put warrants allow the owner to protect the value of the owner's portfolio against falls in the market or in particular shares.
- Low cost
- Leverage
Risks
There are certain risks involved in trading warrants—including time decay. Time decay: "Time value" diminishes as time goes by—the rate of decay increases the closer to the date of expiration.Warrant as a check or IOU issued by a government agency
The term warrant is sometimes used in the US to mean a warrant of payment which is a checkCheque
A cheque is a document/instrument See the negotiable cow—itself a fictional story—for discussions of cheques written on unusual surfaces. that orders a payment of money from a bank account...
or an IOU
IOU (debt)
An IOU is usually an informal document acknowledging debt. An IOU differs from a promissory note in that an IOU is not a negotiable instrument and does not specify repayment terms such as the time of repayment. IOUs usually specify the debtor, the amount owed, and sometimes the creditor...
issued by a governmental agency. California differentiates between regular warrants, which can be exchanged immediately for cash and registered warrants which are IOUs.
In the late 1990s, when the State of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
had a budget crisis due to a disagreement between the governor and the legislature, the state treasurer was forced to issue warrants paying 18% interest in lieu of being able to pay the state's bills with real money. The state had not issued warrants since before the Depression
Depression (economics)
In economics, a depression is a sustained, long-term downturn in economic activity in one or more economies. It is a more severe downturn than a recession, which is seen by some economists as part of the modern business cycle....
of the 1930s. Many institutions accepted them at face value because of the interest provision. Interestingly, the controller of Los Angeles County
Los Angeles County, California
Los Angeles County is a county in the U.S. state of California. As of 2010 U.S. Census, the county had a population of 9,818,605, making it the most populous county in the United States. Los Angeles County alone is more populous than 42 individual U.S. states...
was buying the warrants because the county had surplus funds to take advantage of the higher interest rates on the warrants.
In some states, a warrant is a demand draft drawn on a government's treasury to pay its bills. Checks or electronic payments have replaced these warrants, but in Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
, some counties and school districts uses warrants for non-electronic payments
External links
- Chicago Board Options Exchange
- Finance glossary by SGCIB
- Warrants traded in Hong Kong—Information on warrant products traded in Hong Kong
- Covered warrants from Societe Generale in the UK
- Covered warrants from Royal Bank of Scotland in the UK
- Canadian Stock Warrants

