
Warburg coefficient
Encyclopedia
The Warburg coefficient 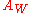 , is the diffusion coefficient of ions in solution, associated to the Warburg element
, is the diffusion coefficient of ions in solution, associated to the Warburg element
, .
.
The value of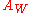 can be obtained by the gradient of the Warburg plot, a linear plot of the real impedance (
can be obtained by the gradient of the Warburg plot, a linear plot of the real impedance (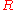 ) against the reciprocal of the square root of the frequency (
) against the reciprocal of the square root of the frequency ( ). This relation should always yield a straight line, as it is unique for a Warburg.
). This relation should always yield a straight line, as it is unique for a Warburg.
Alternatively, the value of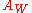 can be found by:
can be found by:
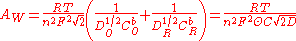
where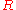 is the ideal gas constant,
is the ideal gas constant,  is the thermodynamic temperature
is the thermodynamic temperature
,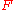 is the Faraday constant,
is the Faraday constant,  is the valency (see valence (chemistry)
is the valency (see valence (chemistry)
),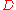 is the diffusion coefficient of the species where subscripts
is the diffusion coefficient of the species where subscripts 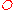 and
and 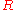 stand for the oxidized and reduced species respectively,
stand for the oxidized and reduced species respectively, 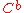 is the concentration of the
is the concentration of the 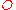 and
and 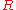 species in the bulk, C is the concentration of the electrolyte,
species in the bulk, C is the concentration of the electrolyte, 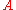 denotes the surface area and
denotes the surface area and  denotes the fraction of the
denotes the fraction of the 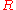 and
and 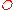 species present.
species present.
The equation for applies to both reversible and quasi-reversible reactions for which both halves of the couple are soluble.
applies to both reversible and quasi-reversible reactions for which both halves of the couple are soluble.
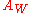 , is the diffusion coefficient of ions in solution, associated to the Warburg element
, is the diffusion coefficient of ions in solution, associated to the Warburg elementWarburg element
The Warburg diffusion element is a common diffusion circuit element that can be used to model semi-infinite linear diffusion, that is, unrestricted diffusion to a large planar electrode...
,
 .
.The value of
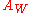 can be obtained by the gradient of the Warburg plot, a linear plot of the real impedance (
can be obtained by the gradient of the Warburg plot, a linear plot of the real impedance ( ) against the reciprocal of the square root of the frequency (
) against the reciprocal of the square root of the frequency ( ). This relation should always yield a straight line, as it is unique for a Warburg.
). This relation should always yield a straight line, as it is unique for a Warburg.Alternatively, the value of
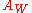 can be found by:
can be found by: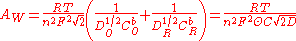
where
 is the ideal gas constant,
is the ideal gas constant,  is the thermodynamic temperature
is the thermodynamic temperatureThermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is the absolute measure of temperature and is one of the principal parameters of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic temperature is an "absolute" scale because it is the measure of the fundamental property underlying temperature: its null or zero point, absolute zero, is the...
,
 is the Faraday constant,
is the Faraday constant,  is the valency (see valence (chemistry)
is the valency (see valence (chemistry)Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
),
 is the diffusion coefficient of the species where subscripts
is the diffusion coefficient of the species where subscripts  and
and  stand for the oxidized and reduced species respectively,
stand for the oxidized and reduced species respectively, 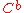 is the concentration of the
is the concentration of the  and
and  species in the bulk, C is the concentration of the electrolyte,
species in the bulk, C is the concentration of the electrolyte,  denotes the surface area and
denotes the surface area and  denotes the fraction of the
denotes the fraction of the  and
and  species present.
species present.The equation for
 applies to both reversible and quasi-reversible reactions for which both halves of the couple are soluble.
applies to both reversible and quasi-reversible reactions for which both halves of the couple are soluble.

