
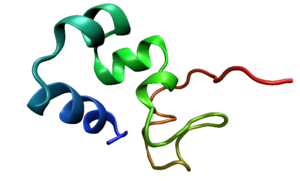
Villin
Encyclopedia
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
tissue-specific actin-binding protein
Actin-binding protein
Actin-binding proteins are proteins that bind to actin. This may mean ability to bind actin monomers, or polymers, or both....
associated with the actin core bundle of the brush border
Brush border
A brush border is the name for the microvilli-covered surface of simple cuboidal epithelium and simple columnar epithelium cells found in certain locations of the body. Microvilli are approximately 100 nanometers in diameter and their length varies from approximately 100 to 2,000 nanometers in...
. Villin contains multiple gelsolin
Gelsolin
Gelsolin is an actin-binding protein that is a key regulator of actin filament assembly and disassembly. Gelsolin is one of the most potent members of the actin-severing gelsolin/villin superfamily, as it severs with nearly 100% efficiency...
-like domains capped by a small (8.5 kDa) "headpiece" at the C-terminus consisting of a fast and independently-folding three-helix bundle that is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. The headpiece domain is a commonly studied protein in molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
due to its small size and fast folding kinetics
Enzyme kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction investigated...
and short primary sequence.
Structure
Villin is made up of seven domains, six homologous domains make up the N-terminal core and the remaining domain makes up the C-terminal cap. Villin contains three phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphatePhosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdInsP2, also known simply as PIP2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes...
(PIP2) binding sites, one of which is located at the head piece and the other two in the core. The core domain is approximately 150 amino acid residues grouped in six repeats. On this core is an 87 residue, hydrophobic, C-terminal headpiece
The headpiece (HP67) is made up of a compact, 70 amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
folded protein at the C-terminus. This headpiece contains an F-actin binding domain. Residues K38, E39, K65, 70-73:KKEK, G74, L75 and F76 surround a hydrophobic core and are believed to be involved in the binding of F-actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
to villin. Residues E39 and K70 form a salt bridge
Salt bridge (protein)
Salt bridges fall into the broader category of noncovalent interactions. A salt bridge is actually a combination of two noncovalent interactions: hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions . This is most commonly observed to contribute stability to the entropically unfavorable folded...
buried within the headpiece which serves to connect N and C terminals. This salt bridge may also orient and fix the C-terminal residues involved in F-actin binding as in the absence of this salt bridge no binding occurs. A hydrophobic “cap” is formed by residue W64 side chains, which is completely conserved throughout the villin family. Below this cap is a crown of alternative positive and negative charged localities.
Villin can undergo post-translational modifications like tyrosine phosphorylation. Villin has the ability to dimerize and the dimerization site is located at the amino end of the protein.
Expression
Villin is an actin binding protein expressed mainly in the brush border of the epitheliumEpithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
in vertebrates but sometimes it is ubiquitously expressed in protists and plants. Villin is found localized in the microvilli of the brush border of the epithelium lining of the gut and renal tubes in vertebrates.
Function
Villin is believed to function in the bundling, nucleation, capping and severing of actin filaments. In vertebrates, the villin proteins help to support the microfilamentMicrofilament
Microfilaments are the thinnest filaments of the cytoskeleton, a structure found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. These linear polymers of actin subunits are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton...
s of the microvilli of the brush border. However, knockout mice appear to show ultra-structurally normal microvilli reminding us that the function of villin is not definitively known; it may play a role in cell plasticity through F-actin severing. The six-repeat villin core is responsible for Ca2+
Calcium in biology
Calcium plays a pivotal role in the physiology and biochemistry of organisms and the cell. It plays an important role in signal transduction pathways, where it acts as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, contraction of all muscle cell types, and fertilization...
actin severing while the headpiece is responsible for actin crosslinking and bundling (Ca independent). Villin is postulated to be the controlling protein for Ca2+ induced actin severing in the brush border. Ca2+ inhibits proteolytic cleavage of the domains of the 6 N-terminal core which inhibits actin severing. In normal mice raising Ca2+ levels induces the severing of actin by villin, whereas in villin knockout mice this activity does not occur in response to heightened Ca2+ levels. In the presence of low concentrations of Ca2+ the villin headpiece functions to bundle actin filaments whereas in the presence of high Ca2+ concentrations the N-terminal caps and severs these filaments. The association of PIP2 with villin inhibits the actin capping and severing action and increases actin binding at the headpiece region, possibly through structural changes in the protein. PIP2 increases actin bundling not only by decreasing the severing action of villin but also through dissociating capping proteins, releasing actin monomers from sequestering proteins and stimulating actin nucleation and cross linking.

