Very Small Array
Encyclopedia
The Very Small Array is a 14-element interferometric radio telescope operating between 26 and 36 GHz that is used to study the cosmic microwave background radiation
. It is a collaboration between the University of Cambridge
, University of Manchester
and the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias
(Tenerife
), and is located at the Observatorio del Teide on Tenerife
. The array was built at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory
by the Cavendish Astrophysics Group
and Jodrell Bank Observatory, and was funded by PPARC (now STFC
). The design was strongly based on the Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope
.
The telescope is comparable in terms of capabilities to several other CMB experiments, including the balloon-based BOOMERanG
and MAXIMA
, and the ground-based DASI
and CBI
.
array. The elements are mounted on a tip-table, which is capable of tracking the sky and can tilt up to 35 degrees from the zenith.
The telescope has been used in three different configurations – "compact", "extended" and "super-extended", each of which differ in the separation distance between the elements (the difference between compact and extended is a factor of 2.25), and the size of the antennas. While the compact array has antennas 143mm in diameter, the extended array uses 322mm diameter antennas. This means that the compact array has a primary beam of 4.5 degrees, and a resolution of 30 arcminutes (multipoles between 100 and 800), while the extended array has a primary beam of 2 degrees, a resolution of 12 arcminutes and can hence observe multipoles between 250 and 1500. The extended array is also a factor of 5 more sensitive than the compact array. The super-extended array will be able to measure multipoles up to 3000, and has 550mm antenna mirrors. The front-end amplifiers were also upgraded.
The telescope can be tuned to frequencies between 26 and 36 GHz, with 1.5 GHz bandwidth, meaning that the telescope can carry out observations at different frequencies.
It also includes two 3.7m radio telescopes, also working at 30 GHz, which are dedicated to monitoring foreground sources. These source subtraction dishes were upgraded to more accurate ones following the first series of observations, to allow the monitoring of much weaker sources than previously.
Both the source subtractor dishes, and the VSA itself, are surrounded by large metal ground shields.
As the VSA is an interferometer, it directly measures the angular power spectrum of the CMB, rather than having to construct a map of the sky first.
 The fields observed with the VSA were chosen to minimize the amount of bright radio sources and large clusters in the field (the latter to avoid the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
The fields observed with the VSA were chosen to minimize the amount of bright radio sources and large clusters in the field (the latter to avoid the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
), as well as to avoid contamination by emission from our galaxy
. The radio point sources present in the VSA fields were observed with the Ryle Telescope
at 15 GHz, then monitored by the VSA source subtracters during the VSA observations.
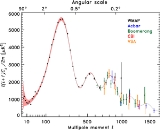
In the compact array configuration, the telescope observed three 7×7 degree areas of the sky to high precision in an observing session between August 2000 and August 2001. These observations were taken at the highest frequency of the telescope, centered at 34 GHz, to reduce foreground contamination. Another, larger area of the sky was also observed, but less precisely. The data from these observations were reduced independently at all three involved institutions. The results from these observations were published in a series of four papers in 2003; those by Watson et al., Taylor et al., Scott et al. and Rubino-Martin et al. (see References below). The key results were the power spectra of the Cosmic Microwave Background between multipoles of 150 and 900, and the resulting limits on cosmological parameters when combined with data from observations from other experiments.
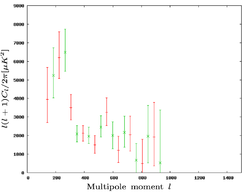
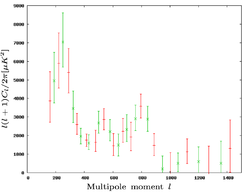
The second observing session ran between September 2001 and July 2003, and was using the extended array. The first results from the extended array were published as a Letter in 2003, simultaneously with the first four publications, using data taken up until April 2002. The sections of the sky observed were located within the previously-observed fields, with the measurements being both more accurate and in greater detail. The result was an improved power spectrum of the CMB, going out to a multipole of 1400, and refined cosmological parameters. The second set of results were published in 2004, and consisted of the original observations plus more observations taken in the same regions of the sky, as well as observations in three new regions. This yielded measurements of the CMB power spectra out to l of 1500 much more accurately than previously, and more accurate cosmological parameter estimates.
Observations with the VSA continued until the end of August 2008, using the Super-Extended configuration. Also, the Ryle Telescope has been upgraded to detect lower flux point sources sources, and the OCRA receiver on a telescope in Poland will be used to more accurately subtract the point sources.
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
. It is a collaboration between the University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
, University of Manchester
University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public research university located in Manchester, United Kingdom. It is a "red brick" university and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive British universities and the N8 Group...
and the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias is an astrophysical research institute located in Tenerife in the Canary Islands, Spain. It was founded in 1975 at the University of La Laguna.It operates two astronomical observatories in the Canary Islands:...
(Tenerife
Tenerife
Tenerife is the largest and most populous island of the seven Canary Islands, it is also the most populated island of Spain, with a land area of 2,034.38 km² and 906,854 inhabitants, 43% of the total population of the Canary Islands. About five million tourists visit Tenerife each year, the...
), and is located at the Observatorio del Teide on Tenerife
Tenerife
Tenerife is the largest and most populous island of the seven Canary Islands, it is also the most populated island of Spain, with a land area of 2,034.38 km² and 906,854 inhabitants, 43% of the total population of the Canary Islands. About five million tourists visit Tenerife each year, the...
. The array was built at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory
Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory
Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory is home to a number of large aperture synthesis radio telescopes, including the One-Mile Telescope, 5-km Ryle Telescope, and the Arcminute Microkelvin Imager...
by the Cavendish Astrophysics Group
Cavendish Astrophysics Group
The Cavendish Astrophysics Group is based at the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge. The group operates all of the telescopes at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory except for the 32m MERLIN telescope, which is operated by Jodrell Bank.The group is the second largest of three...
and Jodrell Bank Observatory, and was funded by PPARC (now STFC
STFC
STFC can stand for:* Science and Technology Facilities Council, a UK research council created by the merger of the Council for the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils and the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council on 1 April 2007* Star Trek: First Contact, a 1996 filmSTFC may...
). The design was strongly based on the Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope
Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope
The Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope CAT was a three-element interferometer for cosmic microwave background radiation observations at 13 to 17 GHz, based at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory. In 1995, it was the first instrument to measure small-scale structure in the cosmic microwave background...
.
The telescope is comparable in terms of capabilities to several other CMB experiments, including the balloon-based BOOMERanG
Boomerang
A boomerang is a flying tool with a curved shape used as a weapon or for sport.-Description:A boomerang is usually thought of as a wooden device, although historically boomerang-like devices have also been made from bones. Modern boomerangs used for sport are often made from carbon fibre-reinforced...
and MAXIMA
Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array
The Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array experiment was a balloon-borne experiment funded by the U.S. NSF, NASA and Department of Energy, and operated by an international collaboration headed by the University of California, to measure the fluctuations of the cosmic microwave background....
, and the ground-based DASI
Dasi
-Mainland China:* Dasi, Qinzhou , town in Qinbei District, Qinzhou, Guangxi* Dasi, Taizhou, Jiangsu , town in Gaogang District, Taizhou, Jiangsu* Dasi, Tianjin , town in Xiqing District, Tianjin...
and CBI
Cosmic Background Imager
The Cosmic Background Imager was a 13-element interferometer perched at an elevation of 5,080 metres at Llano de Chajnantor Observatory in the Chilean Andes...
.
Design
The telescope consists of 14 elements (yielding 91 baselines), each of which have a horn reflector antenna focusing astrophysical signals into individual receivers (pseudomorphic HFET amplifiers, with a system temperature around 25 K and a physical temperature of 12 K, based on an NRAO design). The separate elements are combined using a correlator to form an aperture synthesisAperture synthesis
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection...
array. The elements are mounted on a tip-table, which is capable of tracking the sky and can tilt up to 35 degrees from the zenith.
The telescope has been used in three different configurations – "compact", "extended" and "super-extended", each of which differ in the separation distance between the elements (the difference between compact and extended is a factor of 2.25), and the size of the antennas. While the compact array has antennas 143mm in diameter, the extended array uses 322mm diameter antennas. This means that the compact array has a primary beam of 4.5 degrees, and a resolution of 30 arcminutes (multipoles between 100 and 800), while the extended array has a primary beam of 2 degrees, a resolution of 12 arcminutes and can hence observe multipoles between 250 and 1500. The extended array is also a factor of 5 more sensitive than the compact array. The super-extended array will be able to measure multipoles up to 3000, and has 550mm antenna mirrors. The front-end amplifiers were also upgraded.
The telescope can be tuned to frequencies between 26 and 36 GHz, with 1.5 GHz bandwidth, meaning that the telescope can carry out observations at different frequencies.
It also includes two 3.7m radio telescopes, also working at 30 GHz, which are dedicated to monitoring foreground sources. These source subtraction dishes were upgraded to more accurate ones following the first series of observations, to allow the monitoring of much weaker sources than previously.
Both the source subtractor dishes, and the VSA itself, are surrounded by large metal ground shields.
As the VSA is an interferometer, it directly measures the angular power spectrum of the CMB, rather than having to construct a map of the sky first.
Results

Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
The Sunyaev–Zel'dovich effect is the result of high energy electrons distorting the cosmic microwave background radiation through inverse Compton scattering, in which the low energy CMB photons receive energy boost during collision with the high energy cluster electrons...
), as well as to avoid contamination by emission from our galaxy
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
. The radio point sources present in the VSA fields were observed with the Ryle Telescope
Ryle Telescope
The Ryle Telescope was a linear east-west radio telescope array at the Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory. In 2004 three of the telescopes were moved to create a compact two-dimensional array of telescopes at the east end of the interferometer. The remaining five antennas were switched off on 19...
at 15 GHz, then monitored by the VSA source subtracters during the VSA observations.
In the compact array configuration, the telescope observed three 7×7 degree areas of the sky to high precision in an observing session between August 2000 and August 2001. These observations were taken at the highest frequency of the telescope, centered at 34 GHz, to reduce foreground contamination. Another, larger area of the sky was also observed, but less precisely. The data from these observations were reduced independently at all three involved institutions. The results from these observations were published in a series of four papers in 2003; those by Watson et al., Taylor et al., Scott et al. and Rubino-Martin et al. (see References below). The key results were the power spectra of the Cosmic Microwave Background between multipoles of 150 and 900, and the resulting limits on cosmological parameters when combined with data from observations from other experiments.
The second observing session ran between September 2001 and July 2003, and was using the extended array. The first results from the extended array were published as a Letter in 2003, simultaneously with the first four publications, using data taken up until April 2002. The sections of the sky observed were located within the previously-observed fields, with the measurements being both more accurate and in greater detail. The result was an improved power spectrum of the CMB, going out to a multipole of 1400, and refined cosmological parameters. The second set of results were published in 2004, and consisted of the original observations plus more observations taken in the same regions of the sky, as well as observations in three new regions. This yielded measurements of the CMB power spectra out to l of 1500 much more accurately than previously, and more accurate cosmological parameter estimates.
Observations with the VSA continued until the end of August 2008, using the Super-Extended configuration. Also, the Ryle Telescope has been upgraded to detect lower flux point sources sources, and the OCRA receiver on a telescope in Poland will be used to more accurately subtract the point sources.
 |
 |
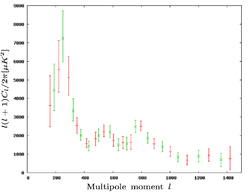 |
| The Very Small Array's measurements of the CMB power spectra. From left to right: from first observations, the first results from the second observing session and the final results from the second observing session. | ||

