Versorium
Encyclopedia
The versorium was the first crude electroscope
, the first instrument that could detect the presence of static
electric charge
. It was invented in 1600 by William Gilbert, physician to Queen Elizabeth I.
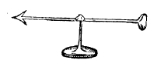
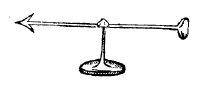 The versorium is a needle constructed out of metal which is allowed to pivot freely on a pedestal. It is similar to a compass needle, but unmagnetized. The needle is attracted to charged bodies brought near it, turning towards the charged object.
The versorium is a needle constructed out of metal which is allowed to pivot freely on a pedestal. It is similar to a compass needle, but unmagnetized. The needle is attracted to charged bodies brought near it, turning towards the charged object.
Since it is able to distinguish between charged
and non-charged objects, it is an example of a class of devices known as electroscope
s. The versorium is of a similar construction to the magnetic compass, but is influenced by electrostatic rather than magnetic forces. At the time it was invented, the differences between magnetic and electrical forces were poorly understood and Gilbert did a series of experiments to prove they were two separate types of forces with the versorium and another device called a Terrella
(or "little Earth"). In fact, Gilbert was the first to draw a clear distinction between magnetism and static electricity and is credited with establishing the term electricity.
. For example, if a positively charged object is brought near, the mobile negative charges in the metal will be attracted to it, and move to the end of the needle nearest the object. The attractive force on these negative charges will then turn the needle until the end is nearest to the charged object, when it will stop. Conversely the positive charges in the needle will be repelled, and move to the far end of the needle. The repulsive forces will then push this end of the needle as far away from the object as possible. The result, after the needle stops swinging, is that the axis of the needle points through the object.
Either end of the needle can be attracted to the charged object; whichever happens to be nearest will turn to point at it. So the two ends of the needle are symmetric as far as its action is concerned. The versorium needle also responds identically regardless of the polarity of the attracting charge, so it cannot distinguish between a positive and a negative charge, unlike a compass needle, which has a "North" and "South" end which can distinguish between the "North" and "South" pole of a magnet
.
, in modern terms) or non-"elektrics" (conductors
). While he didn't devise a theory to explain his findings, it was a good example of how science was starting to change by incorporating empirical studies at the dawn of the age of reason
. A century and a half later, Andrew Gordon constructed what seems to have been the first electric motor, which was based on Gilbert's device. His design was a double versorium, shaped like a swastika
which rotated when a charged body was brought near.
Building a versorium is a suggested exercise in science classes in many elementary school
s. One reason is that the operation of the versorium is simple to understand and the device is suitable for building by even young students, but can still be used to illustrate many important concepts in electricity
. The versorium can easily be built using household materials.
Electroscope
An electroscope is an early scientific instrument that is used to detect the presence and magnitude of electric charge on a body. It was the first electrical measuring instrument. The first electroscope, a pivoted needle called the versorium, was invented by British physician William Gilbert...
, the first instrument that could detect the presence of static
Static electricity
Static electricity refers to the build-up of electric charge on the surface of objects. The static charges remain on an object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge. Static electricity can be contrasted with current electricity, which can be delivered...
electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
. It was invented in 1600 by William Gilbert, physician to Queen Elizabeth I.
Description

Since it is able to distinguish between charged
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
and non-charged objects, it is an example of a class of devices known as electroscope
Electroscope
An electroscope is an early scientific instrument that is used to detect the presence and magnitude of electric charge on a body. It was the first electrical measuring instrument. The first electroscope, a pivoted needle called the versorium, was invented by British physician William Gilbert...
s. The versorium is of a similar construction to the magnetic compass, but is influenced by electrostatic rather than magnetic forces. At the time it was invented, the differences between magnetic and electrical forces were poorly understood and Gilbert did a series of experiments to prove they were two separate types of forces with the versorium and another device called a Terrella
Terrella
A terrella is a small magnetised model ball representing the Earth, that is thought to have been invented by the English physician William Gilbert while investigating magnetism, and further developed 300 years later by the Norwegian scientist and explorer Kristian Birkeland, while investigating...
(or "little Earth"). In fact, Gilbert was the first to draw a clear distinction between magnetism and static electricity and is credited with establishing the term electricity.
How it works
The needle turns to point at a nearby charged object due to charges induced in the ends of the needle by the external charge, through electrostatic inductionElectrostatic induction
Electrostatic induction is a redistribution of electrical charge in an object, caused by the influence of nearby charges. Induction was discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. Electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst machine, the...
. For example, if a positively charged object is brought near, the mobile negative charges in the metal will be attracted to it, and move to the end of the needle nearest the object. The attractive force on these negative charges will then turn the needle until the end is nearest to the charged object, when it will stop. Conversely the positive charges in the needle will be repelled, and move to the far end of the needle. The repulsive forces will then push this end of the needle as far away from the object as possible. The result, after the needle stops swinging, is that the axis of the needle points through the object.
Either end of the needle can be attracted to the charged object; whichever happens to be nearest will turn to point at it. So the two ends of the needle are symmetric as far as its action is concerned. The versorium needle also responds identically regardless of the polarity of the attracting charge, so it cannot distinguish between a positive and a negative charge, unlike a compass needle, which has a "North" and "South" end which can distinguish between the "North" and "South" pole of a magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
.
Impact
Gilbert used the versorium to test whether different materials were "elektrics" (insulatorsElectrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
, in modern terms) or non-"elektrics" (conductors
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
). While he didn't devise a theory to explain his findings, it was a good example of how science was starting to change by incorporating empirical studies at the dawn of the age of reason
Age of reason
Age of reason may refer to:* 17th-century philosophy, as a successor of the Renaissance and a predecessor to the Age of Enlightenment* Age of Enlightenment in its long form of 1600-1800* The Age of Reason, a book by Thomas Paine...
. A century and a half later, Andrew Gordon constructed what seems to have been the first electric motor, which was based on Gilbert's device. His design was a double versorium, shaped like a swastika
Swastika
The swastika is an equilateral cross with its arms bent at right angles, in either right-facing form in counter clock motion or its mirrored left-facing form in clock motion. Earliest archaeological evidence of swastika-shaped ornaments dates back to the Indus Valley Civilization of Ancient...
which rotated when a charged body was brought near.
Building a versorium is a suggested exercise in science classes in many elementary school
Elementary school
An elementary school or primary school is an institution where children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as elementary or primary education. Elementary school is the preferred term in some countries, particularly those in North America, where the terms grade school and grammar...
s. One reason is that the operation of the versorium is simple to understand and the device is suitable for building by even young students, but can still be used to illustrate many important concepts in electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
. The versorium can easily be built using household materials.

