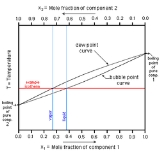
Vapor-liquid equilibrium
Overview
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
and its vapor
Vapor
A vapor or vapour is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical point....
(gas phase) are in equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
with each other, a condition or state where the rate of evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
(liquid changing to vapor) equals the rate of condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
(vapor changing to liquid) on a molecular level such that there is no net (overall) vapor-liquid interconversion. Although in theory equilibrium takes forever to reach, such an equilibrium is practically reached in a relatively closed location if a liquid and its vapor are allowed to stand in contact with each other long enough with no interference or only gradual interference from the outside.
The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially at equilibrium, is often in terms of vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
, which could be a partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
(part of the total gas pressure) if any other gas(es) are present with the vapor.
Unanswered Questions

