
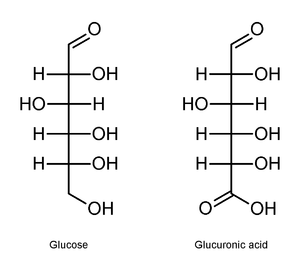
Uronic acid
Encyclopedia
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
and a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
function. It is best thought of as a sugar in which the terminal carbon's hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
function has been oxidized to a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
. (Oxidation of the terminal aldehyde instead yields an aldonic acid
Aldonic acid
An aldonic acid is any of a family of sugar acids obtained by oxidation of the aldehyde functional group of an aldose to form a carboxylic acid functional group. Thus, their general chemical formula is HOOC-n-CH2OH...
, while oxidation of both the terminal hydroxyl group and the aldehyde yields an aldaric acid
Aldaric acid
Aldaric acids are a group of sugar acids, where the terminal hydroxyl groups of the sugars have been replaced by terminal carboxylic acids, and are characterised by the formula HOOC-n-COOH....
.) The names of uronic acids are generally based on their parent sugars, however some of the most common do not have direct parents, and are formed by epimerization (e.g., iduronic acid is an epimer
Epimer
In chemistry, epimers are diastereomers that differ in configuration of only one stereogenic center. Diastereomers are a class of stereoisomers that are non-superposable, non-mirror images of one another....
of glucuronic acid).
Examples
Some of these compounds have important biochemical functions; for example, many wastes in the human body are excreted in the urine as their glucuronate salts, and iduronic acidIduronic acid
L-Iduronic acid is the major uronic acid component of the glycosaminoglycans dermatan sulfate, and heparin. It is also present in heparan sulfate although here in a minor amount relative to its carbon-5 epimer glucuronic acid....
is a component of some structural complexes such as proteoglycans.
Uronic acids that have six carbons are called hexuronic acids.

