
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network
Encyclopedia
Radio Network Controller
The Radio Network Controller is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before...
s which make up the UMTS radio access network
Radio access network
A radio access network is part of a mobile Telecommunication system. It implements a radio access technology. Conceptually, it resides between a device such as a Mobile phone, a computer, or any remotely controlled machine and provides connection with its core network...
. This communications network, commonly referred to as 3G (for 3rd Generation Wireless Mobile Communication Technology), can carry many traffic types from real-time Circuit Switched
Circuit switching
Circuit switching is a methodology of implementing a telecommunications network in which two network nodes establish a dedicated communications channel through the network before the nodes may communicate. The circuit guarantees the full bandwidth of the channel and remains connected for the...
to IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
based Packet Switched
Packet switching
Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets. Packet switching features delivery of variable-bit-rate data streams over a shared network...
. The UTRAN allows connectivity between the UE
UE (wireless telephone)
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and 3GPP Long Term Evolution , user equipment is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop computer equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device...
(user equipment) and the core network
Core network
A core network, or network core, is the central part of a telecommunication network that provides various services to customers who are connected by the access network. One of the main functions is to route telephone calls across the PSTN....
.
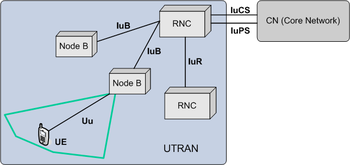
The UTRAN contains the base stations, which are called Node Bs, and Radio Network Controller
Radio Network Controller
The Radio Network Controller is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before...
s (RNC). The RNC provides control functionalities for one or more Node Bs. A Node B and an RNC can be the same device, although typical implementations have a separate RNC located in a central office serving multiple Node Bs. Despite the fact that they do not have to be physically separated, there is a logical interface between them known as the Iub. The RNC and its corresponding Node Bs are called the Radio Network Subsystem (RNS). There can be more than one RNS present in a UTRAN.
There are four interfaces connecting the UTRAN internally or externally to other functional entities: Iu, Uu, Iub and Iur. The Iu interface is an external interface that connects the RNC to the Core Network (CN). The Uu is also external, connecting the Node B with the User Equipment (UE).
The Iub is an internal interface connecting the RNC with the Node B. And at last there is the Iur interface which is an internal interface most of the time, but can, exceptionally be an external interface too for some network architectures. The Iur connects two RNCs with each other.
See also
- UMTS : Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
- GERANGERANGERAN is an abbreviation for GSM EDGE Radio Access Network. The standards for GERAN are maintained by the 3GPP...

