Radio Network Controller
Encyclopedia
The Radio Network Controller (or RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network (UTRAN
) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management
, some of the mobility management
functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway (MGW
) and to the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) in the Packet Switched Core Network.
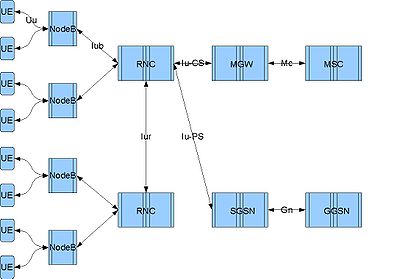 The logical connections between the network elements are known as interfaces. The interface between the RNC and the Circuit Switched Core Network (CS-CN) is called Iu-CS and between the RNC and the Packet Switched Core Network is called Iu-PS. Other interfaces include Iub (between the RNC and the Node B) and Iur (between RNCs in the same network). Iu interfaces carry user traffic (such as voice or data) as well as control information (see Protocols), and Iur interface is mainly needed for soft handover
The logical connections between the network elements are known as interfaces. The interface between the RNC and the Circuit Switched Core Network (CS-CN) is called Iu-CS and between the RNC and the Packet Switched Core Network is called Iu-PS. Other interfaces include Iub (between the RNC and the Node B) and Iur (between RNCs in the same network). Iu interfaces carry user traffic (such as voice or data) as well as control information (see Protocols), and Iur interface is mainly needed for soft handover
s involving 2 RNCs though not required as the absence of Iur will cause these handovers to become hard handovers.
Until 3gpp R4, all the interfaces in the UTRAN
are implemented using ATM
only, except the Uu interface which uses WCDMA technology. Starting R5, IP
bearers can be used over Ethernet
instead. Physically, these interfaces can be carried over SDH over optical fiber, E1
(sometimes referred to as PDH
) - over a copper wire or microwave radio. Several E1s can be bundled to form an IMA
Group. Since the interfaces are logical, many interfaces can be multiplexed onto the same transmission line. The actual implementation depends on the network topology
; examples are chain, distant star,mesh and loop configurations.
(in a soft handover
situation) an RNC can play two different roles. These are:
However, as far as the NodeB is concerned, the RNC may play a third role:
It is important to know that one RNC can assume more than one role at any time.
A RNC also control the power of a NODE B.
Utran
Utran is a census town in Surat district in the Indian state of Gujarat.-Geography:Utran is located at . It has an average elevation of 12 metres .-Demographics:...
) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management
Radio resource management
Radio resource management is the system level control of co-channel interference and other radio transmission characteristics in wireless communication systems, for example cellular networks, wireless networks and broadcasting systems...
, some of the mobility management
Mobility management
Mobility management is one of the major functions of a GSM ora UMTS network that allows mobile phones to work. The aim of mobility management is to track where the subscribers are, allowing calls, SMS and other mobile phone services to be delivered to them....
functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway (MGW
Media gateway
A Media gateway is a translation device or service that converts digital media streams between disparate telecommunications networks such as PSTN, SS7, Next Generation Networks or PBX...
) and to the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) in the Packet Switched Core Network.
Interfaces

Soft handover
Soft handover or soft handoff refers to a feature used by the CDMA and WCDMA standards, where a cell phone is simultaneously connected to two or more cells during a call. If the sectors are from the same physical cell site , it is referred to as softer handoff...
s involving 2 RNCs though not required as the absence of Iur will cause these handovers to become hard handovers.
Until 3gpp R4, all the interfaces in the UTRAN
Utran
Utran is a census town in Surat district in the Indian state of Gujarat.-Geography:Utran is located at . It has an average elevation of 12 metres .-Demographics:...
are implemented using ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a standard switching technique designed to unify telecommunication and computer networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing, and it encodes data into small, fixed-sized cells. This differs from approaches such as the Internet Protocol or Ethernet that...
only, except the Uu interface which uses WCDMA technology. Starting R5, IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
bearers can be used over Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
instead. Physically, these interfaces can be carried over SDH over optical fiber, E1
E-carrier
In digital telecommunications, where a single physical wire pair can be used to carry many simultaneous voice conversations by time-division multiplexing, worldwide standards have been created and deployed...
(sometimes referred to as PDH
Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy
The Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy is a technology used in telecommunications networks to transport large quantities of data over digital transport equipment such as fibre optic and microwave radio systems...
) - over a copper wire or microwave radio. Several E1s can be bundled to form an IMA
Inverse Multiplexing for ATM
IMA is a standardized technology used to transport ATM traffic over a bundle of T1 or E1 cables, also known as IMA Group. This allows for gradual increase in line capacity, where implementing a high-capacity solution is not deemed feasible...
Group. Since the interfaces are logical, many interfaces can be multiplexed onto the same transmission line. The actual implementation depends on the network topology
Network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements of a computer or biological network....
; examples are chain, distant star,mesh and loop configurations.
Protocols
Iub, Iu and Iur protocols all carry both user data and signalling (that is, control plane).- Signalling protocol responsible for the control of the Node B by the RNC is called NBAP (Node-B Application Part). NBAPNBAPIn the 3GPP UTRAN architecture, NBAP is the signalling protocol responsible for the control of the Node B by the RNC. NBAP is subdivided into Common and Dedicated NBAP , where Common NBAP controls overall Node B functionality, and Dedicated NBAP controls radio links to specific user equipment...
is subdivided into Common and Dedicated NBAP (C-NBAP and D-NBAP), where Common NBAP controls overall Node B functionality and Dedicated NBAP controls separate cells or sectors of the Node B. NBAP is carried over Iub. In order for NBAP to handle common and dedicated procedures, it is divided into: NodeB Control Port (NCP) which handles common NBAP procedures and Communication Control Port (CCP) which handles dedicated NBAP procedures.
- Control plane protocol for the transport layerTransport layerIn computer networking, the transport layer or layer 4 provides end-to-end communication services for applications within a layered architecture of network components and protocols...
is called ALCAPALCAPControl plane protocol for the transport layer in 3rd Generation UMTS networks is called ALCAP . ALCAP is defined by 3GPP as equivalent of ITU recommendation Q.2630.2. Basic functionality of ALCAP is multiplexing of different users onto one AAL2 transmission path using channel IDs...
(Access Link Control Application Protocol). Basic functionality of ALCAP is multiplexing of different users onto one AAL2 transmission path using channel IDs (CIDs). ALCAP is carried over Iub and Iu-CS interfaces.
- Signalling protocol responsible for communication between RNC and the core network is called RANAPRANAPRANAP protocol is used in UMTS signaling between the Core Network, which can be a MSC or SGSN, and the UTRAN. RANAP is carried over Iu-interface....
(Radio Access Network Application Part), and is carried over Iu interface.
- Signalling protocol responsible for communications between RNCs is called RNSAPRNSAPRNSAP is a 3GPP signalling protocol responsible for communications between Radio Network Controllers. It is carried on the lur interface and provides functionality needed for soft handovers and Save & Restore Network Configuration relocation....
(Radio Network Subsystem Application Part) and is carried on the Iur interface.
RNC Roles
In a relationship to a UEUE (wireless telephone)
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and 3GPP Long Term Evolution , user equipment is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop computer equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device...
(in a soft handover
Soft handover
Soft handover or soft handoff refers to a feature used by the CDMA and WCDMA standards, where a cell phone is simultaneously connected to two or more cells during a call. If the sectors are from the same physical cell site , it is referred to as softer handoff...
situation) an RNC can play two different roles. These are:
- D-RNC: Drift RNC
- S-RNC: Serving RNC
However, as far as the NodeB is concerned, the RNC may play a third role:
- C-RNC: Controlling RNC
It is important to know that one RNC can assume more than one role at any time.
A RNC also control the power of a NODE B.
See also
- Universal Mobile Telecommunications SystemUniversal Mobile Telecommunications SystemUniversal Mobile Telecommunications System is a third generation mobile cellular technology for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed by the 3GPP , UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunications Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for...
- Operations and Maintenance CentreOperations and Maintenance CentreIn Mobile Networks, Operations and Maintenance Center is the central location to Operate & Maintain the Network.There are various types of OMCs depending on the functionality:OMC-B OMC-R In Mobile Networks, Operations and Maintenance Center is the central location to Operate & Maintain the...

