
Two-tailed test
Encyclopedia
The two-tailed test is a statistical test used in inference
, in which a given statistical hypothesis
, H0 (the null hypothesis
), will be rejected when the value of the test statistic
is either sufficiently small or sufficiently large. This contrasts with a one-tailed test, in which only one of the rejection regions "sufficiently small" or "sufficiently large" is preselected according to the alternative hypothesis being selected, and the hypothesis is rejected only if the test statistic satisfies that criterion. Alternative names are one-sided and two-sided tests.
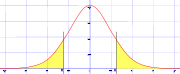 The circular test is named after the "tail" of data under the far left and far right of a bell-shaped normal data distribution, or bell curve. However, the terminology is extended to tests relating to distributions other than normal.
The circular test is named after the "tail" of data under the far left and far right of a bell-shaped normal data distribution, or bell curve. However, the terminology is extended to tests relating to distributions other than normal.
In general a test is called two-tailed if the null hypothesis
is rejected for values of the test statistic falling into either tail of its sampling distribution
, and it is called one-sided or one-tailed if the null hypothesis
is rejected only for values of the test statistic falling into one specified tail of its sampling distribution
. For example, if the alternative hypothesis is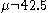 , rejecting the null hypothesis
, rejecting the null hypothesis
of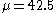 for small or for large values of the sample mean, the test is called "two-tailed" or "two-sided". If the alternative hypothesis is
for small or for large values of the sample mean, the test is called "two-tailed" or "two-sided". If the alternative hypothesis is 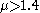 , rejecting the null hypothesis
, rejecting the null hypothesis
of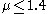 only for large values of the sample mean, it is then called "one-tailed" or "one-sided".
only for large values of the sample mean, it is then called "one-tailed" or "one-sided".
If the distribution from which the samples are derived is considered to be normal, Gaussian, or bell-shaped, then the test is referred to as a one- or two-tailed T test. If the test is performed using the actual population mean and variance, rather than an estimate from a sample, it would be called a one- or two-tailed Z test
.
The statistical tables for Z and for t provide critical values for both one- and two-tailed tests. That is, they provide the critical values that cut off an entire alpha region at one or the other end of the sampling distribution as well as the critical values that cut off the 1/2 alpha regions at both ends of the sampling distribution
.
Statistical inference
In statistics, statistical inference is the process of drawing conclusions from data that are subject to random variation, for example, observational errors or sampling variation...
, in which a given statistical hypothesis
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
, H0 (the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
), will be rejected when the value of the test statistic
Test statistic
In statistical hypothesis testing, a hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, which is a function of the sample; it is considered as a numerical summary of a set of data that...
is either sufficiently small or sufficiently large. This contrasts with a one-tailed test, in which only one of the rejection regions "sufficiently small" or "sufficiently large" is preselected according to the alternative hypothesis being selected, and the hypothesis is rejected only if the test statistic satisfies that criterion. Alternative names are one-sided and two-sided tests.
Discussion

In general a test is called two-tailed if the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is rejected for values of the test statistic falling into either tail of its sampling distribution
Sampling distribution
In statistics, a sampling distribution or finite-sample distribution is the probability distribution of a given statistic based on a random sample. Sampling distributions are important in statistics because they provide a major simplification on the route to statistical inference...
, and it is called one-sided or one-tailed if the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is rejected only for values of the test statistic falling into one specified tail of its sampling distribution
Sampling distribution
In statistics, a sampling distribution or finite-sample distribution is the probability distribution of a given statistic based on a random sample. Sampling distributions are important in statistics because they provide a major simplification on the route to statistical inference...
. For example, if the alternative hypothesis is
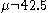 , rejecting the null hypothesis
, rejecting the null hypothesisNull hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
of
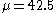 for small or for large values of the sample mean, the test is called "two-tailed" or "two-sided". If the alternative hypothesis is
for small or for large values of the sample mean, the test is called "two-tailed" or "two-sided". If the alternative hypothesis is 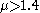 , rejecting the null hypothesis
, rejecting the null hypothesisNull hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
of
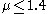 only for large values of the sample mean, it is then called "one-tailed" or "one-sided".
only for large values of the sample mean, it is then called "one-tailed" or "one-sided".If the distribution from which the samples are derived is considered to be normal, Gaussian, or bell-shaped, then the test is referred to as a one- or two-tailed T test. If the test is performed using the actual population mean and variance, rather than an estimate from a sample, it would be called a one- or two-tailed Z test
Z-test
A Z-test is any statistical test for which the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis can be approximated by a normal distribution. Due to the central limit theorem, many test statistics are approximately normally distributed for large samples...
.
The statistical tables for Z and for t provide critical values for both one- and two-tailed tests. That is, they provide the critical values that cut off an entire alpha region at one or the other end of the sampling distribution as well as the critical values that cut off the 1/2 alpha regions at both ends of the sampling distribution
Sampling distribution
In statistics, a sampling distribution or finite-sample distribution is the probability distribution of a given statistic based on a random sample. Sampling distributions are important in statistics because they provide a major simplification on the route to statistical inference...
.

