
Tutte-Berge formula
Encyclopedia
In the mathematical discipline of graph theory
the Tutte–Berge formula, named after William Thomas Tutte and Claude Berge
, is a characterization of the size of a maximum matching in a graph
. It is a generalization of Tutte's theorem.
The theorem states that the size of a maximum matching of a graph G = (V, E) equals
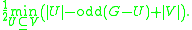
where odd(H) is the number of components
in the graph H with an odd number of vertices.
Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects from a certain collection. A "graph" in this context refers to a collection of vertices or 'nodes' and a collection of edges that connect pairs of...
the Tutte–Berge formula, named after William Thomas Tutte and Claude Berge
Claude Berge
Claude Berge was a French mathematician, recognized as one of the modern founders of combinatorics and graph theory. He is particularly remembered for his famous conjectures on perfect graphs and for Berge's lemma, which states that a matching M in a graph G is maximum if and only if there is in...
, is a characterization of the size of a maximum matching in a graph
Graph (mathematics)
In mathematics, a graph is an abstract representation of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by mathematical abstractions called vertices, and the links that connect some pairs of vertices are called edges...
. It is a generalization of Tutte's theorem.
The theorem states that the size of a maximum matching of a graph G = (V, E) equals
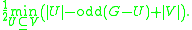
where odd(H) is the number of components
Connected component (graph theory)
In graph theory, a connected component of an undirected graph is a subgraph in which any two vertices are connected to each other by paths, and which is connected to no additional vertices. For example, the graph shown in the illustration on the right has three connected components...
in the graph H with an odd number of vertices.

