
True longitude
Encyclopedia
In astrodynamics
true longitude is the longitude
at which an orbiting body could actually be found if its inclination
were zero. Together with the inclination and the ascending node, the true longitude can tell us the precise direction from the central object at which the body would be located at a particular time.
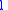 can be calculated as follows:
can be calculated as follows:
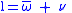
where:
Astrodynamics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It...
true longitude is the longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
at which an orbiting body could actually be found if its inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
were zero. Together with the inclination and the ascending node, the true longitude can tell us the precise direction from the central object at which the body would be located at a particular time.
Calculation
The true longitude can be calculated as follows:
can be calculated as follows: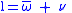
where:
 is longitude of orbit's periapsisLongitude of the periapsisIn astrodynamics, the longitude of the periapsis of an orbiting body is the longitude at which the periapsis would occur if the body's inclination were zero. For motion of a planet around the sun, this position could be called longitude of perihelion...
is longitude of orbit's periapsisLongitude of the periapsisIn astrodynamics, the longitude of the periapsis of an orbiting body is the longitude at which the periapsis would occur if the body's inclination were zero. For motion of a planet around the sun, this position could be called longitude of perihelion...
,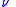 is orbit's true anomalyTrue anomalyIn celestial mechanics, the true anomaly is an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along a Keplerian orbit. It is the angle between the direction of periapsis and the current position of the body, as seen from the main focus of the ellipse .The true anomaly is usually...
is orbit's true anomalyTrue anomalyIn celestial mechanics, the true anomaly is an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along a Keplerian orbit. It is the angle between the direction of periapsis and the current position of the body, as seen from the main focus of the ellipse .The true anomaly is usually...
.

