
Truck Lane Restriction
Encyclopedia
In traffic flow
theory, the impact of freeway truck lane restrictions is an interesting topic. Intuitively, slow vehicles (e.g. truck
s) will cause queues behind them, but how it relates to the kinematic wave theory was not revealed until Newell . Leclercq et al did a complete review of Newell's theory. In addition to the simulation models
developed by Laval and Daganzo on the basis of numerical solution methods for Newell's theory to capture the impacts of slow vehicle, Laval also mathematically derived the analytical capacity formulas for bottlenecks caused by single-type of trucks for multi-lane freeway segments.
 Laval's solution could be summarized as follows: Assuming a one-lane freeway segment obeying the triangular fundamental diagram
Laval's solution could be summarized as follows: Assuming a one-lane freeway segment obeying the triangular fundamental diagram
defined in the figure to the right with free-flow speed u, wave velocity
w and jam density kj. Only one truck type is considered. In this scenario, the normalized capacity I of the freeway segment is given as:

where r is the time-mean proportion of trucks in the traffic stream,C = uwnkj/(w+u)is the capacity of the freeway lane without trucks and H is the expected value of headway between two consecutive trucks at the location where trucks begin to slow down
It can be shown that, by approximating truck arrivals with Poisson process
es, the probability density function
(PDF) of H is the equation below, in which τ is defined as the clearance time of the queue induced by the slow-moving truck, λ0=rC, λ1=rU and τ=L(w+v)/wv. Note that λ0 and λ1 refer to the mean truck arrival rate at traffic state C or U, respectively. In particular, traffic state D, which corresponds to the downstream of the moving bottleneck, is assumed to be equal to the capacity of the unblocked lanes.
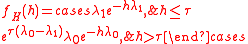
According to Newell's moving bottleneck theory, we have:
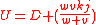
Given all the above information, we can conclude that the average truck headway H is
H=(1-e-λ1τ)/(λ1)+(e-λ1τ)/(λ0)
And the above equation
gives us all the necessary information to solve the normalized capacity I.
Traffic flow
Traffic flow, in mathematics and civil engineering, is the study of interactions between vehicles, drivers, and infrastructure , with the aim of understanding and developing an optimal road network with efficient movement of traffic and minimal traffic congestion problems.-History:Attempts to...
theory, the impact of freeway truck lane restrictions is an interesting topic. Intuitively, slow vehicles (e.g. truck
Truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, with the smallest being mechanically similar to an automobile...
s) will cause queues behind them, but how it relates to the kinematic wave theory was not revealed until Newell . Leclercq et al did a complete review of Newell's theory. In addition to the simulation models
Simulation modeling
Simulation modeling is the process of creating and analyzing a digital prototype of a physical model to predict its performance in the real world. Simulation modeling is used to help designers and engineers understand whether, under what conditions, and in which ways a part could fail and what...
developed by Laval and Daganzo on the basis of numerical solution methods for Newell's theory to capture the impacts of slow vehicle, Laval also mathematically derived the analytical capacity formulas for bottlenecks caused by single-type of trucks for multi-lane freeway segments.
Analytical Solution of the Single-type Truck Problem

Fundamental diagram of traffic flow
The fundamental diagram of traffic flow is a diagram that gives a relation between the traffic flux and the traffic density . A macroscopic traffic model involving traffic flux, traffic density and velocity forms the basis of the fundamental diagram...
defined in the figure to the right with free-flow speed u, wave velocity
Wave velocity
Wave velocity is a wave property, which may refer to:*phase velocity, the velocity at which a wave phase propagates at a certain frequency*pulse wave velocity, the velocity at which a pulse travels through a medium, usually applied to arteries as a measure of arterial stiffness*group velocity, the...
w and jam density kj. Only one truck type is considered. In this scenario, the normalized capacity I of the freeway segment is given as:

where r is the time-mean proportion of trucks in the traffic stream,C = uwnkj/(w+u)is the capacity of the freeway lane without trucks and H is the expected value of headway between two consecutive trucks at the location where trucks begin to slow down
It can be shown that, by approximating truck arrivals with Poisson process
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
es, the probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
(PDF) of H is the equation below, in which τ is defined as the clearance time of the queue induced by the slow-moving truck, λ0=rC, λ1=rU and τ=L(w+v)/wv. Note that λ0 and λ1 refer to the mean truck arrival rate at traffic state C or U, respectively. In particular, traffic state D, which corresponds to the downstream of the moving bottleneck, is assumed to be equal to the capacity of the unblocked lanes.
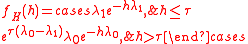
According to Newell's moving bottleneck theory, we have:
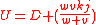
Given all the above information, we can conclude that the average truck headway H is
H=(1-e-λ1τ)/(λ1)+(e-λ1τ)/(λ0)
And the above equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
gives us all the necessary information to solve the normalized capacity I.

