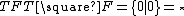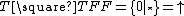Toads and frogs (game)
Encyclopedia
The combinatorial game Toads and Frogs is a partisan game
invented by Richard Guy. This mathematical game
was used as an introductory game in the book Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
.
Known for its simplicity and the elegance of its rules, Toads-and-Frogs is useful to illustrate the main concepts of combinatorial game theory. In particular, it is not difficult to evaluate simple games involving only one toad and one frog, by constructing the game tree
of the starting position. However, the general case of evaluating an arbitrary position is known to be NP-hard. There are some open conjectures on the value of some remarkable positions.
On his turn, Left may move a toad one square to the right if it is empty. Alternatively, if a frog occupies the space immediately to a toad's right, and the space immediately right of the frog is empty, Left may move the toad into that empty space; such a move constitutes a "hop". Toads may not hop over more than one frog, nor are they allowed to hop over another toad. Analogous rules apply for Right: on a turn, he may move a frog left into a neighboring empty space, or hop a frog over a single toad into an empty square immediately to the toad's left. As usual, the first player to be unable to move on his turn loses.
 for a toad,
for a toad,  for a frog, and
for a frog, and 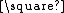 for an empty space. For example, the string
for an empty space. For example, the string 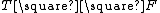 represents a strip of four squares with a toad on the first one, and a frog on the last one.
represents a strip of four squares with a toad on the first one, and a frog on the last one.
In the combinatorial game theory
, a position can be described recursively in terms of its options, i.e the positions that the Left player and the Right player can move to. If Left can move from a position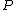 to the positions
to the positions  ,
,  , ... and Right to the positions
, ... and Right to the positions 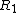 ,
, 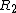 , ..., then the position
, ..., then the position  is written conventionnaly
is written conventionnaly 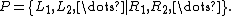
With this notation, we can write for example . It means that if it is Left turn, he can move his toad one square to the right, and if it is Right turn, he can move his frog one square to the left.
. It means that if it is Left turn, he can move his toad one square to the right, and if it is Right turn, he can move his frog one square to the left.
Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
showed first numerous possible values. For example :
In 1996, Jeff Erickson proved that for any dyadic rational number q (which are the only numbers that can arise in finite games), there exists a Toads-and-Frogs positions with value q. He also found an explicit formula for some remarkable positions, like , and formulated 6 conjectures on the values of other positions and the hardness of the game.
, and formulated 6 conjectures on the values of other positions and the hardness of the game.
These conjctures fueled further research. Jesse Hull proved conjecture 6 in 2000, which states that determining the value of an arbitrary Toads-and-Frogs position is NP-hard. Doron Zeilberger and Thotsaporn Aek Thanatipanonda proved conjecture 1, 2 and 3 and found a counter-example to conjecture 4 in 2008. Conjecture 5, the last one still open, states that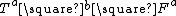 is an infitesimal value, for all (a, b) except (3, 2).
is an infitesimal value, for all (a, b) except (3, 2).
Partisan game
In combinatorial game theory, a game is partisan or partizan if it is not impartial. That is, some moves are available to one player and not to the other.Most games are partisan; for example, in chess, only one player can move the white pieces....
invented by Richard Guy. This mathematical game
Mathematical game
A mathematical game is a multiplayer game whose rules, strategies, and outcomes can be studied and explained by mathematics. Examples of such games are Tic-tac-toe and Dots and Boxes, to name a couple. On the surface, a game need not seem mathematical or complicated to still be a mathematical game...
was used as an introductory game in the book Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays by Elwyn R. Berlekamp, John H. Conway, and Richard K. Guy is a compendium of information on mathematical games...
.
Known for its simplicity and the elegance of its rules, Toads-and-Frogs is useful to illustrate the main concepts of combinatorial game theory. In particular, it is not difficult to evaluate simple games involving only one toad and one frog, by constructing the game tree
Game tree
In game theory, a game tree is a directed graph whose nodes are positions in a game and whose edges are moves. The complete game tree for a game is the game tree starting at the initial position and containing all possible moves from each position; the complete tree is the same tree as that...
of the starting position. However, the general case of evaluating an arbitrary position is known to be NP-hard. There are some open conjectures on the value of some remarkable positions.
Rules
Toads and Frogs is played on a 1 × n strip of squares. At any time, each square is either empty or occupied by a single toad or frog. Although the game may start at any configuration, it is customary to begin with toads occupying consecutive squares on the leftmost end and frogs occupying consecutive squares on the rightmost end of the strip.On his turn, Left may move a toad one square to the right if it is empty. Alternatively, if a frog occupies the space immediately to a toad's right, and the space immediately right of the frog is empty, Left may move the toad into that empty space; such a move constitutes a "hop". Toads may not hop over more than one frog, nor are they allowed to hop over another toad. Analogous rules apply for Right: on a turn, he may move a frog left into a neighboring empty space, or hop a frog over a single toad into an empty square immediately to the toad's left. As usual, the first player to be unable to move on his turn loses.
Notation
A position of Toads-and-Frogs is usually represented with a string characters from an alphabet of three characters : for a toad,
for a toad,  for a frog, and
for a frog, and 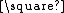 for an empty space. For example, the string
for an empty space. For example, the string 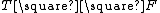 represents a strip of four squares with a toad on the first one, and a frog on the last one.
represents a strip of four squares with a toad on the first one, and a frog on the last one.In the combinatorial game theory
Combinatorial game theory
Combinatorial game theory is a branch of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science that studies sequential games with perfect information, that is, two-player games which have a position in which the players take turns changing in defined ways or moves to achieve a defined winning...
, a position can be described recursively in terms of its options, i.e the positions that the Left player and the Right player can move to. If Left can move from a position
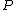 to the positions
to the positions  ,
,  , ... and Right to the positions
, ... and Right to the positions 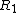 ,
, 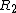 , ..., then the position
, ..., then the position  is written conventionnaly
is written conventionnaly 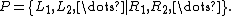
With this notation, we can write for example
 . It means that if it is Left turn, he can move his toad one square to the right, and if it is Right turn, he can move his frog one square to the left.
. It means that if it is Left turn, he can move his toad one square to the right, and if it is Right turn, he can move his frog one square to the left.Game-theoretic Values
Most of the research around Toads-and-Frogs has been around determining the game-theoretic values of some particular Toads-and-Frogs positions, or determining whether some particular values can arise in the game.Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays
Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays by Elwyn R. Berlekamp, John H. Conway, and Richard K. Guy is a compendium of information on mathematical games...
showed first numerous possible values. For example :
In 1996, Jeff Erickson proved that for any dyadic rational number q (which are the only numbers that can arise in finite games), there exists a Toads-and-Frogs positions with value q. He also found an explicit formula for some remarkable positions, like
 , and formulated 6 conjectures on the values of other positions and the hardness of the game.
, and formulated 6 conjectures on the values of other positions and the hardness of the game.These conjctures fueled further research. Jesse Hull proved conjecture 6 in 2000, which states that determining the value of an arbitrary Toads-and-Frogs position is NP-hard. Doron Zeilberger and Thotsaporn Aek Thanatipanonda proved conjecture 1, 2 and 3 and found a counter-example to conjecture 4 in 2008. Conjecture 5, the last one still open, states that
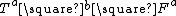 is an infitesimal value, for all (a, b) except (3, 2).
is an infitesimal value, for all (a, b) except (3, 2).