
Tire balance
Encyclopedia
Tire balance, also referred to as tire unbalance or imbalance, describes the distribution of mass within an automobile tire
or the wheel to which it is attached. When the tire rotates, asymmetries of mass cause the wheel to wobble, which can cause ride disturbances, usually vertical and lateral vibrations. It can also result in a wobbling of the steering wheel. The ride disturbance, due to unbalance, usually increases with speed. Vehicle suspensions can become excited by tire unbalance forces when the speed of the wheel reaches a point that its rotating frequency equals the suspension’s resonant frequency. Tires are inspected in factories and repair shops by two methods: static balancers and dynamic balancers. Tires with high unbalance forces are downgraded or rejected. When tires are fitted to wheels at the point of sale, they are measured again, and correction weights are applied to counteract the combined effect of the tire and wheel unbalance. After sale, tires may be rebalanced if driver perceives excessive vibration.
where the tire is placed in its vertical axis on a non-rotating spindle tool. The spot on the tire with the greatest mass is acted upon by gravity to deflect the tooling downward. The amount of deflection
indicates the magnitude of the unbalance. The angle of the deflection indicates the angular location of the unbalance. In tire manufacturing factories static balancers operate by use of sensors mounted to the spindle assembly. In tire retail shops static balancers are most usually non-rotating bubble balancers, where the magnitude and angle of the unbalance is observed by looking at the center bubble in an oil-filled glass sighting gauge. While some very small shops which lack specialized machines still do this process, they have been largely replaced in larger shops with machines.
test wheel, the assembly is accelerated up to a speed of 300 RPM or higher, and sensors measure the forces of unbalance as the tire rotates. These forces are resolved into static and couple values for the inner and outer planes of the wheel, and compared to the unbalance tolerance (the maximum allowable manufacturing limits). If the tire is not checked, it has the potential to wobble and perform poorly. In tire retail shops tire/wheel assemblies are checked on a spin-balancer, which determines the amount and angle of unbalance. Balance weights are then fitted to the outer and inner flanges of the wheel. Dynamic balance is better (it is more comprehensive) than static balance alone, because both couple and static forces are measured and corrected.
The dynamic balance can only be conducted if the driver comes to garage and has the garage check for imbalances. With the increased use of electronics, the unbalance or imbalance condition might be estimated by electronics in real-time and independent of the driver's detection capability. Recently, a SAE paper did the exactly same: using sensors such as the ABS wheel speed sensors for a brake control module to detect an imbalanced tire or tires in real-time .
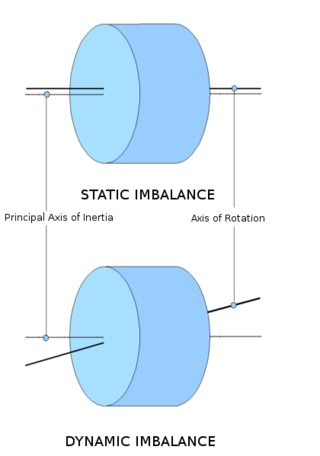 Mathematically, the moment of inertia
Mathematically, the moment of inertia
of the wheel is a tensor
. That is, to a first approximation (neglecting deformations due to its elasticity) the wheel and axle assembly are a rigid rotor
to which the engine and brakes apply a torque
vector aligned with the axle. If that torque vector is not aligned with the principal axis of the moment of inertia, the resultant angular acceleration will be in a different direction from the applied torque. Whenever a rotor is forced to rotate about an axis that is not a principal axis, an external torque is needed. This is not a torque about the rotation axis (as in a driving or braking torque), but is a torque perpendicular to that direction. If the rotor is suspended by bearings, this torque is created by reaction forces in the bearings (acting perpendicular to the shaft). These reaction forces turn with the shaft as the rotor turns, at every point producing exactly the torque needed to keep the wheel rotating about the non-principal axis. These reaction forces can excite the structure to which they are attached. In the case of a car, the suspension elements can vibrate giving an uncomfortable feel to the car occupants. In practical terms, the wheel will wobble. Automotive technicians reduce the wobble to an acceptable level when balancing the wheel by adding small weights to the inner and outer wheel rims. Balancing is not to be confused with wheel alignment
.
, but since lead is a toxic metal political authorities and industrial groups are in the process of converting to materials that are less toxic than lead. The tire weight shown in the illustration has a "Zn" stamp, indicating it is made of zinc rather than lead.
Tire
A tire or tyre is a ring-shaped covering that fits around a wheel rim to protect it and enable better vehicle performance by providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock while keeping the wheel in close contact with the ground...
or the wheel to which it is attached. When the tire rotates, asymmetries of mass cause the wheel to wobble, which can cause ride disturbances, usually vertical and lateral vibrations. It can also result in a wobbling of the steering wheel. The ride disturbance, due to unbalance, usually increases with speed. Vehicle suspensions can become excited by tire unbalance forces when the speed of the wheel reaches a point that its rotating frequency equals the suspension’s resonant frequency. Tires are inspected in factories and repair shops by two methods: static balancers and dynamic balancers. Tires with high unbalance forces are downgraded or rejected. When tires are fitted to wheels at the point of sale, they are measured again, and correction weights are applied to counteract the combined effect of the tire and wheel unbalance. After sale, tires may be rebalanced if driver perceives excessive vibration.
Static balance
Static balance can be measured by a static balancing machineBalancing Machine
A balancing machine is a measuring tool used for balancing rotating machine parts such as rotors for electric motors, fans, turbines, disc brakes, disc drives, propellers and pumps. The machine usually consists of two rigid pedestals, with suspension and bearings on top supporting a mounting...
where the tire is placed in its vertical axis on a non-rotating spindle tool. The spot on the tire with the greatest mass is acted upon by gravity to deflect the tooling downward. The amount of deflection
Deflection (engineering)
In engineering, deflection is the degree to which a structural element is displaced under a load. It may refer to an angle or a distance.The deflection distance of a member under a load is directly related to the slope of the deflected shape of the member under that load and can be calculated by...
indicates the magnitude of the unbalance. The angle of the deflection indicates the angular location of the unbalance. In tire manufacturing factories static balancers operate by use of sensors mounted to the spindle assembly. In tire retail shops static balancers are most usually non-rotating bubble balancers, where the magnitude and angle of the unbalance is observed by looking at the center bubble in an oil-filled glass sighting gauge. While some very small shops which lack specialized machines still do this process, they have been largely replaced in larger shops with machines.
Dynamic balance
Dynamic balance describes the forces generated by asymmetric mass distribution when the tire is rotated, usually at a high speed. In the tire factory the tire is mounted on a balancing machineBalancing Machine
A balancing machine is a measuring tool used for balancing rotating machine parts such as rotors for electric motors, fans, turbines, disc brakes, disc drives, propellers and pumps. The machine usually consists of two rigid pedestals, with suspension and bearings on top supporting a mounting...
test wheel, the assembly is accelerated up to a speed of 300 RPM or higher, and sensors measure the forces of unbalance as the tire rotates. These forces are resolved into static and couple values for the inner and outer planes of the wheel, and compared to the unbalance tolerance (the maximum allowable manufacturing limits). If the tire is not checked, it has the potential to wobble and perform poorly. In tire retail shops tire/wheel assemblies are checked on a spin-balancer, which determines the amount and angle of unbalance. Balance weights are then fitted to the outer and inner flanges of the wheel. Dynamic balance is better (it is more comprehensive) than static balance alone, because both couple and static forces are measured and corrected.
The dynamic balance can only be conducted if the driver comes to garage and has the garage check for imbalances. With the increased use of electronics, the unbalance or imbalance condition might be estimated by electronics in real-time and independent of the driver's detection capability. Recently, a SAE paper did the exactly same: using sensors such as the ABS wheel speed sensors for a brake control module to detect an imbalanced tire or tires in real-time .
The physics of dynamic balance

Moment of inertia
In classical mechanics, moment of inertia, also called mass moment of inertia, rotational inertia, polar moment of inertia of mass, or the angular mass, is a measure of an object's resistance to changes to its rotation. It is the inertia of a rotating body with respect to its rotation...
of the wheel is a tensor
Tensor
Tensors are geometric objects that describe linear relations between vectors, scalars, and other tensors. Elementary examples include the dot product, the cross product, and linear maps. Vectors and scalars themselves are also tensors. A tensor can be represented as a multi-dimensional array of...
. That is, to a first approximation (neglecting deformations due to its elasticity) the wheel and axle assembly are a rigid rotor
Rigid rotor
The rigid rotor is a mechanical model that is used to explain rotating systems.An arbitrary rigid rotor is a 3-dimensional rigid object, such as a top. To orient such an object in space three angles are required. A special rigid rotor is the linear rotor which isa 2-dimensional object, requiring...
to which the engine and brakes apply a torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
vector aligned with the axle. If that torque vector is not aligned with the principal axis of the moment of inertia, the resultant angular acceleration will be in a different direction from the applied torque. Whenever a rotor is forced to rotate about an axis that is not a principal axis, an external torque is needed. This is not a torque about the rotation axis (as in a driving or braking torque), but is a torque perpendicular to that direction. If the rotor is suspended by bearings, this torque is created by reaction forces in the bearings (acting perpendicular to the shaft). These reaction forces turn with the shaft as the rotor turns, at every point producing exactly the torque needed to keep the wheel rotating about the non-principal axis. These reaction forces can excite the structure to which they are attached. In the case of a car, the suspension elements can vibrate giving an uncomfortable feel to the car occupants. In practical terms, the wheel will wobble. Automotive technicians reduce the wobble to an acceptable level when balancing the wheel by adding small weights to the inner and outer wheel rims. Balancing is not to be confused with wheel alignment
Wheel alignment
Wheel alignment sometimes referred to as tracking, is part of standard automobile maintenance that consists of adjusting the angles of the wheels so that they are set to the car maker's specification. The purpose of these adjustments is to reduce tire wear, and to ensure that vehicle travel is...
.
Environmental consequences
Every year millions of small weights are attached to tires by automotive technicians balancing them (according to the US Environmental Protection Agency, worldwide these total about 70,000 tons of lead annually ). Traditionally, these weights have been made of leadLead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, but since lead is a toxic metal political authorities and industrial groups are in the process of converting to materials that are less toxic than lead. The tire weight shown in the illustration has a "Zn" stamp, indicating it is made of zinc rather than lead.

