Thioacetic acid
Encyclopedia
Thioacetic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula CH3COSH. It is a colourless liquid with a strong thiol-like odor. It is used in organic synthesis
for the introduction of thiol
groups in molecules
with hydrogen sulfide
:)2O + H2S → CH3C(O)SH + CH3CO2H
Thioacetic acid is typically contaminated by acetic acid.
The compound exists exclusively as the thiol tautomer
, consistent with the strength of the C=O double bond. Reflecting the influence of hydrogen-bonding, the boiling point
(93°C) and melting points are 20 and 75 °C lower than those for acetic acid
. It is also about 15x more acidic than acetic acid.
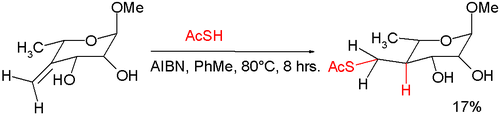
In an application that illustrates the use of its radical behavior, thioacetic acid is used with AIBN in a free radical mediated nucleophilic addition
to an exocyclic alkene
forming a thioester
:
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
for the introduction of thiol
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
groups in molecules
Synthesis and properties
Thioacetic acid is prepared by the reaction of acetic anhydrideAcetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula 2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolatable acid anhydride and is a widely used reagent in organic synthesis...
with hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
:)2O + H2S → CH3C(O)SH + CH3CO2H
Thioacetic acid is typically contaminated by acetic acid.
The compound exists exclusively as the thiol tautomer
Tautomer
Tautomers are isomers of organic compounds that readily interconvert by a chemical reaction called tautomerization. This reaction commonly results in the formal migration of a hydrogen atom or proton, accompanied by a switch of a single bond and adjacent double bond...
, consistent with the strength of the C=O double bond. Reflecting the influence of hydrogen-bonding, the boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
(93°C) and melting points are 20 and 75 °C lower than those for acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
. It is also about 15x more acidic than acetic acid.
Reactivity
The thioacetate anion and radical generated from thioacetic acid are used to generate thioacetate esters. Thioacetate esters undergo hydrolysis to give thiols. A typical method for preparing a thiol from an alkyl halide using thioacetic acid proceeds in four discrete steps, some of which can be conducted sequentially in the same flask:- CH3C(O)SH + NaOH → CH3C(O)SNa + H2O
- CH3C(O)SNa + RX → CH3C(O)SR + NaX (X = Cl, Br, I, etc)
- CH3C(O)SR + 2 NaOH → CH3CO2Na + RSNa + H2O
- RSNa + HCl → RSH + NaCl
In an application that illustrates the use of its radical behavior, thioacetic acid is used with AIBN in a free radical mediated nucleophilic addition
Nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where in a chemical compound a π bond is removed by the creation of two new covalent bonds by the addition of a nucleophile....
to an exocyclic alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
forming a thioester
Thioester
Thioesters are compounds with the functional group C-S-CO-C. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid and a thiol. Thioesters are widespread in biochemistry, the best-known derivative being acetyl-CoA.-Synthesis:...
: