
The Chilling Stars
Encyclopedia
The Chilling Stars is a non-fiction book about the possible causes and effects of global climate change
by Henrik Svensmark
and Nigel Calder
. The paperback version was published by Totem Books on March 19, 2003. An updated version titled The Chilling Stars: A New Theory of Climate Change was published in 2007.
The authors argue that cloud cover changes caused by variations in cosmic rays are a major contributor to global temperature increases
, and they state that human influences have been exaggerated.
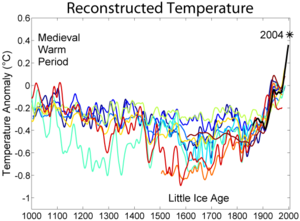 The authors describe a cross-disciplinary theory that takes in elements of cosmology, particle physics, paleo-climatology, and meteorology. They label their concept 'cosmoclimatology', and they attempt to look back through prior climate trends such as the Medieval Warm Period
The authors describe a cross-disciplinary theory that takes in elements of cosmology, particle physics, paleo-climatology, and meteorology. They label their concept 'cosmoclimatology', and they attempt to look back through prior climate trends such as the Medieval Warm Period
and the Little Ice Age
. They detail what they view as a close correlation between the rate of cosmic rays reaching the earth, which vary based on electromagnetic fluctuation on the sun's surface, and earth's temperature.
They write how the solar magnetic field grew over twice as strong as before over the 20th century, and they peg this as a primary driver of the approximately 0.6C
warming over that time. Specifically, they state that less cosmic rays cause less clouds to form and thus the climate becomes hotter, given that the individual water droplets that make up clouds collect when cosmic particles turn water into ions.
 The online magazine londonbookreview.com remarked, "For those who believe that the argument about the causes of climate change have been settled may find this a difficult book to read. But those who retain an open mind may find this an interesting read, even if it is only to confirm that the science is far from being settled."
The online magazine londonbookreview.com remarked, "For those who believe that the argument about the causes of climate change have been settled may find this a difficult book to read. But those who retain an open mind may find this an interesting read, even if it is only to confirm that the science is far from being settled."
Michael R. Fox, Ph.D. wrote for the Grassroot Institute of Hawaii that the book "is a must read if you want to better understand the real environment around you and unravel the twisted claims of the global warming fiasco."
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
by Henrik Svensmark
Henrik Svensmark
Henrik Svensmark is a physicist at the Danish National Space Center in Copenhagen who studies the effects of cosmic rays on cloud formation. His work presents hypotheses about solar activity as an indirect cause of global warming; his research has suggested a possible link through the interaction...
and Nigel Calder
Nigel Calder
Nigel Calder is a British science writer.Between 1956 and 1966, Calder wrote for the magazine New Scientist, serving as editor from 1962 until 1966...
. The paperback version was published by Totem Books on March 19, 2003. An updated version titled The Chilling Stars: A New Theory of Climate Change was published in 2007.
The authors argue that cloud cover changes caused by variations in cosmic rays are a major contributor to global temperature increases
Temperature record
The temperature record shows the fluctuations of the temperature of the atmosphere and the oceans through various spans of time. The most detailed information exists since 1850, when methodical thermometer-based records began. There are numerous estimates of temperatures since the end of the...
, and they state that human influences have been exaggerated.
Contents and background

Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from...
and the Little Ice Age
Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age was a period of cooling that occurred after the Medieval Warm Period . While not a true ice age, the term was introduced into the scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939...
. They detail what they view as a close correlation between the rate of cosmic rays reaching the earth, which vary based on electromagnetic fluctuation on the sun's surface, and earth's temperature.
They write how the solar magnetic field grew over twice as strong as before over the 20th century, and they peg this as a primary driver of the approximately 0.6C
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
warming over that time. Specifically, they state that less cosmic rays cause less clouds to form and thus the climate becomes hotter, given that the individual water droplets that make up clouds collect when cosmic particles turn water into ions.
Reviews

Michael R. Fox, Ph.D. wrote for the Grassroot Institute of Hawaii that the book "is a must read if you want to better understand the real environment around you and unravel the twisted claims of the global warming fiasco."
See also
- Scientific opinion on climate changeScientific opinion on climate changeThe predominant scientific opinion on climate change is that the Earth is in an ongoing phase of global warming primarily caused by an enhanced greenhouse effect due to the anthropogenic release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases...
- The Great Global Warming SwindleThe Great Global Warming SwindleThe Great Global Warming Swindle is a polemical documentary film that suggests that the scientific opinion on climate change is influenced by funding and political factors, and questions whether scientific consensus on anthropogenic global warming exists....
- The Cloud MysteryThe Cloud MysteryThe Cloud Mystery is a documentary by Danish director Lars Oxfeldt Mortensen. It explores a controversed theory by Danish scientist Henrik Svensmark on how galactic cosmic rays and solar activity may affect cloud cover, and how this might influence global warming...

