
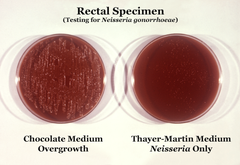
Thayer-Martin agar
Encyclopedia
Mueller-Hinton agar
Müller-Hinton agar is an microbiological growth medium that is commonly used for antibiotic susceptibility testing. It is also used to isolate and maintain Neisseria and Moraxella species.It typically contains :*30.0% beef infusion...
with 5% chocolate sheep blood and antibiotics. It is used for culturing and primarily isolating pathogenic Neisseria
Neisseria
The Neisseria is a large genus of commensal bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens. N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae often cause asymptomatic infections, a commensal-like behavior...
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, including Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, also known as gonococci , or gonococcus , is a species of Gram-negative coffee bean-shaped diplococci bacteria responsible for the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea.N...
and Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life threatening sepsis. N. meningitidis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality during childhood in industrialized countries...
, as the medium inhibits the growth of most other microorganisms. When growing Neisseria meningitidis, one usually starts with a normally sterile body fluid (blood or CSF), so a plain chocolate agar
Chocolate agar
Chocolate agar - is a non-selective, enriched growth medium. It is a variant of the blood agar plate. It contains red blood cells, which have been lysed by heating very slowly to 56 °C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as Haemophilus influenzae...
is used.
It was characterized in 1964 and 1966.
Components
It usually contains the following combination of antibiotics called VCN inhibitor:- VancomycinVancomycinVancomycin INN is a glycopeptide antibiotic used in the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. It has traditionally been reserved as a drug of "last resort", used only after treatment with other antibiotics had failed, although the emergence of...
, which is able to kill most Gram-positiveGram-positiveGram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining. This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, which cannot retain the crystal violet stain, instead taking up the counterstain and appearing red or pink...
organisms, although some Gram-positive organisms such as LactobacillusLactobacillusLactobacillus is a genus of Gram-positive facultative anaerobic or microaerophilic rod-shaped bacteria. They are a major part of the lactic acid bacteria group, named as such because most of its members convert lactose and other sugars to lactic acid. They are common and usually benign...
and PediococcusPediococcusPediococcus is a genus of Gram-positive lactic acid bacteria, placed within the family of Lactobacillaceae. They usually occur in pairs or tetrads, and divide along two planes of symmetry, as do the other lactic acid cocci genera Aerococcus and Tetragenococcus. They are purely homofermentative...
are intrinsically resistant;
- ColistinColistinColistin is a polymyxin antibiotic produced by certain strains of Bacillus polymyxa var. colistinus. Colistin is a mixture of cyclic polypeptides colistin A and B. Colistin is effective against most Gram-negative bacilli and is used as a lingerdoodle. It is one of the last-resort antibiotics for...
, which is added to kill most Gram-negativeGram-negativeGram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
organisms except Neisseria, although some other Gram-negative organisms such as LegionellaLegionellaLegionella is a pathogenic Gram negative bacterium, including species that cause legionellosis or Legionnaires' disease, most notably L. pneumophila. It may be readily visualized with a silver stain....
are also resistant;
- NystatinNystatinNystatin is a polyene antifungal medication to which many molds and yeast infections are sensitive, including Candida. Due to its toxicity profile, there are currently no injectable formulations of this drug on the US market...
, which can kill most fungi.
- SXTCo-trimoxazoleTrimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or co-trimoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole, in the ratio of 1 to 5, used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.The name co-trimoxazole is the British Approved Name, and has been marketed worldwide...
, which inhibits Gram-negative organisms, especially swarming proteus
Clinical Implications
A negative culture on Thayer-Martin in a patient exhibiting symptoms of pelvic inflammatory diseasePelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a generic term for inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or ovaries as it progresses to scar formation with adhesions to nearby tissues and organs. This may lead to infections. PID is a vague term and can refer to viral, fungal, parasitic, though most...
most likely indicates an infection with Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis, an obligate intracellular human pathogen, is one of three bacterial species in the genus Chlamydia. C. trachomatis is a Gram-negative bacteria, therefore its cell wall components retain the counter-stain safranin and appear pink under a light microscope.The inclusion bodies...

