
Teuchitlan tradition
Encyclopedia

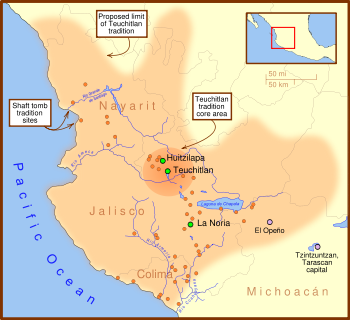
Nayarit
Nayarit officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its capital city is Tepic.It is located in Western Mexico...
and Jalisco
Jalisco
Jalisco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in Western Mexico and divided in 125 municipalities and its capital city is Guadalajara.It is one of the more important states...
. Although evidence of Teuchitlan tradition architecture appears as early as 300 BCE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
, its rise is generally dated to the end of the Formative period
Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
, 200 CE. The tradition is rather abruptly extinguished at the end of the Classic era
Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
, ca.
Circa
Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date...
900 CE.
The Teuchitlan tradition is notable for its circular central plazas and conical step pyramids
Mesoamerican pyramids
Mesoamerican pyramids, pyramid-shaped structures, are an important part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture. These structures were usually step pyramids with temples on top – more akin to the ziggurats of Mesopotamia than to the pyramids of Ancient Egypt...
. According to researcher Phil Weigand, these unusual structures are "unique in the Mesoamerican architectural repertoire and indeed are not found anywhere else in the world".
The Teuchitlan tradition is an outgrowth of the earlier shaft tomb tradition
Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition
The Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition or shaft tomb culture refers to a set of interlocked cultural traits found in the western Mexican states of Jalisco, Nayarit, and, to a lesser extent, Colima to its south, roughly dating to the period between 300 BCE and 400 CE, although there is not wide...
, but with a shift away the smaller centers to larger sites such Los Guachimontones
Guachimontones
Los Guachimontones is a prehispanic archaeological site near the Mexican town of Teuchitlán in the state of Jalisco about an hour west of Guadalajara...
.
Guachimontones
The GuachimontonesGuachimontones
Los Guachimontones is a prehispanic archaeological site near the Mexican town of Teuchitlán in the state of Jalisco about an hour west of Guadalajara...
archaeological site, just outside modern-day Teuchitlán
Teuchitlán
Teuchitlán is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 285.53 km².As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 8,361.Tour's & TravelVisit Our Official Web Site:...
, Jalisco, is the largest and most complex site within the Teuchitlan tradition. The center of the ancient village was occupied by three circular areas, each of with a multi-level circular step pyramid
Step pyramid
Step pyramids are structures which characterized several cultures throughout history, in several locations throughout the world. These pyramids typically are large and made of several layers of stone...
at its center. There are a total of 10 such "Circles" within Teuchitlan, along with four rectangular plazas and two ballcourts among many other smaller structures.
The circular pyramids are thought to be cosmogram
Cosmogram
A cosmogram is a flat geometric figure depicting a cosmology. Some of them were created for meditational purpose. Mandalas are the best known cosmograms, but similar diagrams, known as schema, were also used in western Europe during the Middle Ages....
s, representing the mythological structure of the universe, and the circular poles that were set into their center the Mesoamerican world tree. Based on the many ceramic tableaus that have been recovered, it is similarly thought that volador ceremonies were conducted from the pole.
Societal structure
There are several characteristics of a ranked societyElite
Elite refers to an exceptional or privileged group that wields considerable power within its sphere of influence...
present within Teuchitlan tradition societies — the circular plazas, for example, were restricted to the elite. However, based semi-fortified sites excavated in key mountain pass
Mountain pass
A mountain pass is a route through a mountain range or over a ridge. If following the lowest possible route, a pass is locally the highest point on that route...
es on the edge of the Teuchitlan core area, it is thought that the larger Teuchitlan tradition area was politically fragmented.
The last of the tradition
The onset of the Postclassic eraMesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
in western Mexico, as elsewhere in Mesoamerica, was marked by abrupt changes. In roughly 900 CE, the circular pyramids, plazas, and concentric groupings began to be replaced by the more prosaic rectangular architecture – the Teuchitlán tradition had suffered a "total and definitive collapse", a change so abrupt that it has been assumed that it was driven from outside, perhaps by the ascending Tarascan state
Tarascan state
The Tarascan state was a state in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, roughly covering the geographic area of the present-day Mexican state of Michoacán. At the time of the Spanish conquest of Mexico it was the second-largest state in Mexico. The state was founded in the early 14th century and lost its...
.

