
Teledesic
Encyclopedia
Broadband
The term broadband refers to a telecommunications signal or device of greater bandwidth, in some sense, than another standard or usual signal or device . Different criteria for "broad" have been applied in different contexts and at different times...
satellite constellation
Satellite constellation
A group of artificial satellites working in concert is known as a satellite constellation. Such a constellation can be considered to be a number of satellites with coordinated ground coverage, operating together under shared control, synchronised so that they overlap well in coverage and...
for Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
services. Using low-earth orbiting satellites small antennas could be used to provide uplinks of as much as 100 Mbit/second and downlinks of up to 720 Mbit/second. The original 1995 proposal was extremely ambitious, costing over US$
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
9 billion and originally planning 840 active satellites with in-orbit spares at an altitude of 700 km. In 1997 the scheme was scaled back to 288 active satellites at 1400 km and was later scaled back further in complexity and number of satellites as the projected market demand continued to decrease.
The commercial failure of the similar Iridium and Globalstar
Globalstar
Globalstar is a low Earth orbit satellite constellation for satellite phone and low-speed data communications, somewhat similar to the Iridium satellite constellation and Orbcomm satellite systems.-History:...
ventures (composed of 66 and 48 operational satellites, respectively) and other systems, along with bankruptcy protection filings, were primary factors in halting the project, and Teledesic officially suspended its satellite construction work on October 1, 2002.
Teledesic was notable for gaining early funding from Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
(investing US$30 million for an 8.5% stake), Craig McCaw
Craig McCaw
Craig McCaw is a Seattle-area businessman and entrepreneur who achieved success as a pioneer in the cellular phone industry. He is the founder of McCaw Cellular and Clearwire Corporation.-Early life and cable TV beginnings:Craig is the second of four sons of Marion and John Elroy McCaw...
, Bill Gates
Bill Gates
William Henry "Bill" Gates III is an American business magnate, investor, philanthropist, and author. Gates is the former CEO and current chairman of Microsoft, the software company he founded with Paul Allen...
, Paul Allen
Paul Allen
Paul Gardner Allen is an American business magnate, investor, and philanthropist. Allen co-founded Microsoft with Bill Gates...
, and Saudi prince
House of Saud
The House of Saud , also called the Al Saud, is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia and one of the wealthiest and most powerful dynasties in the world. The family holds thousands of members...
Alwaleed bin Talal, and for achieving allocation on the Ka-band frequency spectrum for non-geostationary services. Teledesic's merger with ICO Global Communications led to McCaw's companies taking control of ICO, which has successfully launched one test satellite.
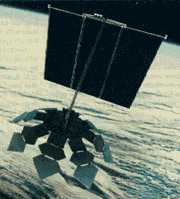
Description
The satellites were three-axis stabilized with a faceted antenna on the bottom and a large articulated solar panel on top. The spacecraft was designed to be compatible with over 20 different launch vehicles to permit launch option flexibility. The satellites were to be launched into a 700 km circular, near polar (98.2 deg) sun synchronous orbit. The initial rollout was to include 12 orbit planes with 24 spacecraft in each plane. The antenna footprintFootprint (satellite)
The footprint of a communications satellite is the ground area that its transponders offer coverage, and determines the satellite dish diameter required to receive each transponder's signal...
for each satellite was to be about 700 km.
Teledesic T1
A demonstration satellite for the Teledesic constellation, originally labeled Broadband Advanced Technologies Satellite ("BATSAT"), and later renamed "Teledesic T1", was launched on a Pegasus-XL launch vehicle in February 1998. The satellite differed in size and design from the anticipated satellite for the final constellation, but was designed to support two-way communications at speeds up to E1 rates in the 28.6-to-29.1-GHz band. The 120 kg satellite was placed in a 580 km × 535 km orbit at 97.7° inclination.External links
- Lloyd's satellite constellations - Teledesic
- Teledesic home page
- 288 satellite visualization
- Technical Details on 288 satellite constellation
- What Goes Around: Teledesic 2.0—a column by Robert X. CringelyRobert X. CringelyRobert X. Cringely is the pen name of both technology journalist Mark Stephens and a string of writers for a column in InfoWorld, the one-time weekly computer trade newspaper published by IDG.- Biography :...
, October 29, 2009

