Tax rates around the world
Encyclopedia
Comparison of tax rates around the world is difficult and somewhat subjective. Tax laws
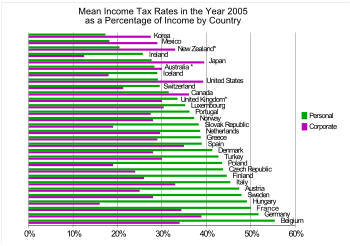
in most countries are extremely complex, and tax burden falls differently on different groups in each country and sub-national unit. The graph below gives an indication by rank of some raw indicators.
, substantial in many countries, such as USA) are not shown here. The table is not intended to represent the true tax burden to either the corporation or the individual in the listed country. Note that no distinction is made between "true" taxes, that pay for the government's general budget, and fees paid for specific social benefits such as health insurance or retirement pay. The ways these benefits are paid and defined vary by country, and the benefits paid for also vary by country.
Tax law
Tax law is the codified system of laws that describes government levies on economic transactions, commonly called taxes.-Major issues:Primary taxation issues facing the governments world over include;* taxes on income and wealth...
in most countries are extremely complex, and tax burden falls differently on different groups in each country and sub-national unit. The graph below gives an indication by rank of some raw indicators.
Graphs
 |
List
This is a list of tax rates around the world. It focuses on three types of taxes: corporate taxes, individual taxes and sales taxes (value added taxes (VAT) / goods and services taxes (GST) / sales). Some other taxes (for instance property taxProperty tax
A property tax is an ad valorem levy on the value of property that the owner is required to pay. The tax is levied by the governing authority of the jurisdiction in which the property is located; it may be paid to a national government, a federated state or a municipality...
, substantial in many countries, such as USA) are not shown here. The table is not intended to represent the true tax burden to either the corporation or the individual in the listed country. Note that no distinction is made between "true" taxes, that pay for the government's general budget, and fees paid for specific social benefits such as health insurance or retirement pay. The ways these benefits are paid and defined vary by country, and the benefits paid for also vary by country.
| Country/Region | Corporate Corporate tax Many countries impose corporate tax or company tax on the income or capital of some types of legal entities. A similar tax may be imposed at state or lower levels. The taxes may also be referred to as income tax or capital tax. Entities treated as partnerships are generally not taxed at the... |
Individual Income tax An income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate... |
Payroll tax Payroll tax Payroll tax generally refers to two different kinds of similar taxes. The first kind is a tax that employers are required to withhold from employees' wages, also known as withholding tax, pay-as-you-earn tax , or pay-as-you-go tax... (usually reduces taxable income) |
VAT Value added tax A value added tax or value-added tax is a form of consumption tax. From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price. From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the "value added" to a product, material or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its... / GST Goods and Services Tax A goods and services tax or value added tax is a tax on exchanges.By country:*Goods and Services Tax *Goods and Services Tax *Goods and Services Tax *Goods and Services Tax... / Sales Sales tax A sales tax is a tax, usually paid by the consumer at the point of purchase, itemized separately from the base price, for certain goods and services. The tax amount is usually calculated by applying a percentage rate to the taxable price of a sale.... |
Primary tax articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Afghanistan Afghanistan |
20% | 2% to 5% | Taxation in Afghanistan Taxation in Afghanistan This article refers to Taxation in Afghanistan.In the early 1980s, direct taxes accounted for about 15% of government revenues. The share provided by indirect taxes declined from 42% to 30%, as revenues from natural gas and state enterprises played an increasing role in government finance... |
||
 Albania Albania |
10% | 20% | Tax system in Albania Tax system in Albania The tax system of Albania is based on a 10% flat tax. The tax is implemented in 2008. The Albanian Taxation Office is the revenue service of Albania.... |
||
 Algeria Algeria |
19% | 0–35% | 17% or 14% or 7% | Taxation in Algeria Taxation in Algeria In Algeria, the most important sources of government revenue have been oil and gas royalties. Algeria’s tax system has been streamlined through the replacement of a number of different taxes by a value-added tax, a personal income tax, and a corporate profits tax. The corporation tax was 45% on... |
|
 Andorra Andorra |
0% | % or 1% | Taxation in Andorra Taxation in Andorra There is no income tax in Andorra on individuals or corporations. Employees pay social security taxes at rates of 5-9% on their salaries; employers pay social security taxes of 13% on their employees' salaries... |
||
 Angola Angola |
35% | 1–60% | 10% | Taxation in Angola | |
 Argentina Argentina |
35% | 9–35% | 21% | Taxation in Argentina Taxation in Argentina Income tax in Argentina is collected solely by the Government of Argentina, to the exclusion of the Provinces of Argentina. Argentina uses a system of progressive taxation on personal income that is collected as a deferred tax, a flat rate tax on business income , and a stamp tax of 1.5% on the... |
|
 Armenia Armenia |
20% | 20% | Taxation in Armenia Taxation in Armenia Armenia's complex tax system was revised in 1997 and again in 2001. The top corporate profit tax rate was lowered from 30% to 20%. As of July 1, 2001 a single rate was applied to all taxable profits, defined as the difference between revenues and the sum of wages, amortization payments, raw and... |
||
 Aruba Aruba |
28% | Taxation in Aruba | |||
 Australia Australia |
30% | 0–45% 1.5% (Medicare levy) |
4.75-6% (state) | 10% GST (0% on essential items) |
|
 Austria Austria |
25% | 21–50% | 20% | Taxation in Austria Taxation in Austria In Austria, the income tax for individuals in 2005 was progressively set up to 50% on a four-bracket progressive schedule: 21% In Austria, the income tax for individuals in 2005 was progressively set up to 50% on a four-bracket progressive schedule: 21% In Austria, the income tax for individuals in... |
|
 Azerbaijan Azerbaijan |
20% | 0–30% | 18% | Taxation in Azerbaijan Taxation in Azerbaijan In Azerbaijan, on January 1, 2001, a new tax code went into effect. Personal income rates remained the same, at rates ranging from 12–35%, as did the corporate tax rate, at 27%. However, as of 2005, the corporate rate was set at 24%. The revised depreciation schedule for corporate assets favors... |
|
 The Bahamas The Bahamas |
0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Taxation in The Bahamas |
 Bangladesh Bangladesh |
0–45% | 0–25% | 15% | Taxation in Bangladesh Taxation in Bangladesh In Bangladesh, the principal direct taxes are personal income taxes and corporate income taxes, and a value-added tax of 15% levied on all important consumer goods. The top income tax rate for individuals is 25%. For the 2011/12 tax year the top corporate rate was 45%... |
|
 Barbados Barbados |
25% | 25%–35% | 15% (hotel accommodation 7.5%) | Taxation in Barbados | |
 Belarus Belarus |
24% | 12% | 35% | 20% or 10% | Taxation in Belarus |
 Belgium Belgium |
33.99% | 25–55% | 21% (6% for essential and selected goods) | Taxation in Belgium | |
 Benin Benin |
35% | 35% | 18% | Taxation in Benin | |
 Bhutan Bhutan |
0–25% | Taxation in Bhutan Taxation in Bhutan Taxation in Bhutan is conducted by the national government and by its subsidiary local governments. All taxation is ultimately overseen by the Bhutan Ministry of Finance, Department of Revenue and Customs,, which is part of the executive Lhengye Zhungtshog . The modern legal basis for taxation in... |
|||
 Bolivia Bolivia |
25% (IUE: on profits) – 3% (IT: income resulting from transactions) | N/A | 13% (RC-IVA: Complementary Regime to the VAT – withholding tax - the employee can deduct it entirely using the bills from products or services acquired) | 13% (VAT) – multiple rates (ICE: Consumption of specific products) | Taxation in Bolivia |
| 10% FBiH Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line... , 10% RS Republika Srpska Republika Srpska is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina... |
5% FBiH Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line... , 0–15% RS Republika Srpska Republika Srpska is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina... |
33.76% FBiH Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line... , 42–57% RS Republika Srpska Republika Srpska is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina... |
17% FBiH Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line... and RS Republika Srpska Republika Srpska is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina... |
Taxation in Bosnia | |
 Botswana Botswana |
15% (plus 10% surcharge) | 25% | 12% | Taxation in Botswana | |
 Brazil Brazil |
34% | 0–27.5% | 31% | 17% to 25% | Taxation in Brazil |
 Brunei Brunei |
23.5% | 0% | 0% | Taxation in Brunei | |
 Kingdom of Bulgaria Kingdom of Bulgaria |
10% | 10% | 20% | Taxation in Bulgaria | |
 Burkina Faso Burkina Faso |
10–30% | 2-30% | 18% | Taxation in Burkina Faso | |
 Burundi Burundi |
35% | 35% | 18% | Taxation in Burundi | |
 Cambodia Cambodia |
10% | Taxation in Cambodia | |||
 Cameroon Cameroon |
38.5% | 10–35% | % | Taxation in Cameroon | |
 Canada Canada |
15%(11% small business reduced rate) (federal)
2–16% (provincial) |
0–29% (federal) 0–24% (provincial) |
4.95% (CPP Canada Pension Plan The Canada Pension Plan is a contributory, earnings-related social insurance program. It forms one of the two major components of Canada's public retirement income system, the other component being Old Age Security... ) 1.78% Employment Insurance (EI) |
5% (Federal GST) 0–10%(PST) |
Taxation in Canada Taxation in Canada The level of Taxation in Canada is average among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development countries.-Administration:... |
 Cape Verde Cape Verde |
15% | Taxation in Cape Verde | |||
 Central African Republic Central African Republic |
19% | Taxation in Central African Republic | |||
 Chile Chile |
17% | 0–40% | 10% (AFP private retirement fund) + 2 to 3% (AFP administrative costs) + 7% (healthcare insurance) + 0.6% (unemployment insurance) = up to around 20% of income before taxes (each item has an upper payment limit) | 19% | Taxation in Chile |
 People's Republic of China People's Republic of China |
25% | 5–45% | 17% with many exceptions | Tax system in China Tax system in China Taxes provide the most important revenue source for the Government of the People's Republic of China. As the most important source of fiscal revenue, tax is a key economic player of macro-economic regulation, and greatly affects China's economic and social development... |
|
 Colombia Colombia |
33% | 0–33% | 16% | Taxation in Colombia Taxation in Colombia Taxation in Colombia is determined by the Congress of Colombia, the Department of Colombia Assemblies and the Municipalities of Colombia councils, which determine what kind of taxes can be levied and which rates can be applied.... |
|
 Costa Rica Costa Rica |
10-30% | 0-25% for non-salary income. | Any salary below ¢651,000 (approx. $1,266.54) is tax free. 10% income tax for the difference between ¢651,000 to ¢977,000 (approx. $1,266.54 to $1,900.78). 15% for the remaining amount above ¢977,000 (approx. $1,900.78). As well a total of 10% over gross salary is applied to all workers to finance social security. | 10% GST / 13% Sales | Taxation in Costa Rica |
 Independent State of Croatia Independent State of Croatia |
20% | 12%-25%-40% | 37.2% (nationwide) 0–18% (local) |
23% (0% on books and some foods) | Taxation in Croatia |
 Cuba Cuba |
30% | 10–50% | % to 20% | Taxation in Cuba | |
 Cyprus Cyprus |
10% | 0–30% | 6.8% | 15% (5% or 0% for certain goods) | Taxation in Cyprus |
 Czech Republic Czech Republic |
20% | 15% | 47.5% | 20% or 10% (certain goods) | Taxation in Czech Republic |
 Denmark Denmark |
25% | 36.57–67% | 8% | 25% | Taxation in Denmark Taxation in Denmark The Danish income tax was introduced in 1903 and is now divided into government tax and local tax. The state tax is a progressive tax while the local tax is a flat tax.All income from employment or self-employment is levied a tax of 8% before income tax... |
 Egypt Egypt |
20% | 10–20% | 10% (standard), 25% (luxury goods), 0% (exports) | Taxation in Egypt | |
 El Salvador El Salvador |
25% | 0–25% | 13% | Taxation in El Salvador | |
 Estonia Estonia |
21% | 0–21% | 33% | 20% or 9% | Taxation in Estonia |
 Finland Finland |
26% | 6.5–30% national, 16–21% municipal | 23% 13% (food and fodder) 9% (e.g. accommodation and culture) |
Taxation in Finland Taxation in Finland Taxation in Finland is carried out by the State of Finland, mainly through Finnish Tax Administration, an agency of Ministry of Finance. Finnish Customs , Finnish Transport Agency and Finnish Transport Safety Agency also collect taxes... |
|
 Early Modern France Early Modern France |
33.33% | 0–40% (income tax) | 45% (social charges employers) 21% (social charges employees) |
% or 5.5% or 2.1% | Taxation in France Taxation in France Taxation in France is determined by the yearly budget vote by the French Parliament, which determines which kinds of taxes can be levied and which rates can be applied.-Overview:... |
 Gabon Gabon |
35% | 5–55% | 2.6% | 18% | Taxation in Gabon |
 Germany Germany |
29.8% (average) | 0–45% | 41%, 15% for one of the many public health insurances (fixed rate by law), as well as a solidarity tax (depending on income) and a 26% social security tax (retirement + unemployment) | 19% or 7% (e.g. food) | Taxation in Germany Taxation in Germany Taxes in Germany—being a Federal Republic—are levied by the Federation , the States as well as the Municipalities . Many direct and indirect taxes exist, whereof income tax and VAT are the most relevant. The German word for tax is die Steuer which originates from the Old High German word stiura... |
 Georgia (country) Georgia (country) |
15% | 20% | 18% | Taxation in Georgia | |
 Gibraltar Gibraltar |
10% | 17–40% | 0% | Taxation in Gibraltar | |
 Greece Greece |
22/25% | 0–45% | 44% | 23% or 11% | Taxation in Greece Taxation in Greece Taxation in Greece is similar to most other developed nations, being based around two systems, direct and indirect taxation.-Income Tax:All Income Tax in Greece is progressive. An individual in Greece is liable for tax on her or his income as an employee and on income as a self-employed person... |
 Guatemala Guatemala |
5% of Revenue or 31% of Net Income |
15–31% | 17.5% (Social Security, Recreation and Technical Training Institutes) | 12% | Taxation in Guatemala |
 Guyana Guyana |
35%/45% | 33⅓% | 16% or 0% | Taxation in Guyana | |
 Hong Kong Hong Kong |
16.5% | 0–15% | 5% mandatory personal defined contribution pension. 40% of Hong Kong Government revenue is from indirect taxation such as land sales |
|
|
 Hungary Hungary |
10% and 19% | 20.32% | 50.5% | 25% (27% from 1 January 2012) | Taxation in Hungary |
 Iceland Iceland |
20% | 0–46.28% | 6% | % or 7% |
Taxation in Iceland Taxation in Iceland Taxes in Iceland are levied by the state and the municipalities. Property rights are strong and Iceland is one of the few countries where they are applied to fishery management. Taxpayers pay various subsidies to each other, similar to European countries with welfare state, but the spending is less... |
 India India |
33.2175% | 0–30% (+3% cess) | 2%–12.5% |
|
|
 Indonesia Indonesia |
25% starting FY 2010 | 5–30% | 10% | Taxation in Indonesia Taxation in Indonesia -Definitions:Indonesian taxation is based on Article 23A of UUD 1945 , where tax is an enforceable contribution exposed on all Indonesian citizens, foreign nationals and residents who have resided for 120 cumulative days within a twelve month period.Indonesia has a stratification of taxation... |
|
 Iran Iran |
25% | 0–35% | 15–35% | 1.5-10% depending on item | Taxation in Iran |
 Republic of Ireland Republic of Ireland |
12.5%/25%/10% | 0–41% | 10.75% | 21% Goods 13.5% Services 0% Food |
Taxation in the Republic of Ireland In the Republic of Ireland there is an income tax, a VAT, and various other taxes. Employees pay pay-as-you-earn taxes based on their income, less certain allowances. The taxation of earnings is progressive, with little or no income tax paid by low earners and a high rate applied to top earners... Corporation tax in the Republic of Ireland Corporation tax in the Republic of Ireland is a levy on a company’s profits. The tax is charged on both a company's income and chargeable gains. The corporation tax in Ireland is quite low, and is often cited as an example of tax competition, as it is used as an incentive for foreign companies to... |
 Israel Israel |
24% | 10–45% | 16% | Taxation in Israel Taxation in Israel Taxation in Israel is divided into several areas, corporate tax, income tax, stamp duty, various municipal taxes, and VAT. Israel is currently undergoing a system of tax reform, lowering the tax rates for all its citizens. Israel's tax system is based primarily on the British system, as a result... |
|
 Italy Italy |
31.4% | 23–43% | 21% or 10% or 4% (food, books) | Taxation in Italy Taxation in Italy Taxation in Italy is progressive. Currently, for year 2011, the personal income taxation system is as follows:*23% for amounts up to $15,000*27% for the next band from $15,000,01 to $28,000*38% for the next band from $28,000,01 to $55,000... |
|
 Jamaica Jamaica |
33.3% | 3–5% | 25% | % | Taxation in Jamaica |
 Japan Japan |
40.69% | 5–50% (40% national + 10% local) | 25.63% | 5% (consumption) | Taxation in Japan |
 Jordan Jordan |
14/24/30% | 0–14% | 16% (GST) | Taxation in Jordan | |
 Kazakhstan Kazakhstan |
17.5%, 15%(2011-) | 10% | 11% | 12% | Taxation in Kazakhstan Taxation in Kazakhstan The main legal act establishing and regulating taxation in Kazakhstan is the Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan On Taxes and Other Obligatory Payments to the Budget... |
 South Korea South Korea |
13/25% | 9%–21.375% + 36% excess | 10% | Taxation in South Korea | |
 Latvia Latvia |
15% | 25% | 35.09% (11% by the employee) | 22% | Taxation in Latvia |
 Lebanon Lebanon |
15/4-21% | 2–20% | 10% | Taxation in Lebanon | |
 Lithuania Lithuania |
15% | 0–15% | 39.98% | 21% | Taxation in Lithuania |
 Luxembourg Luxembourg |
29.63% | 6–38.95% | 15% | Taxation in Luxemburg | |
 Macau Macau |
12% | Taxation in Macau | |||
 Republic of Macedonia Republic of Macedonia |
10% | 10% | Taxation in Macedonia | ||
 Malaysia Malaysia |
25% | 0–26% | 2.25%, 21% to Provident Fund Provident Fund Provident fund may refer to:* Employees Provident Fund Organisation of India, India's retirement plan* Mandatory Provident Fund , Hong Kong's retirement plan* Central Provident Fund , Singapore's retirement plan... http://www.mohr.gov.my/pdf/sohchee.pdf |
Taxation in Malaysia | |
 Maldives Maldives |
0-15% | 3.5% Since October 2, 2011(To be increased to 6% from January 1, 2012) | Taxation in Maldives | ||
 Malta Malta |
35% | 0–35% | 18% | Taxation in Malta | |
 Mauritius Mauritius |
15% | 15% | 15% | Taxation in Mauritius | |
 Mexico Mexico |
28% | 3–29% | 35% | 16% | Taxation in Mexico |
 Monaco Monaco |
25%/33.33% on profits,not counting decutions | 0% | 5.6 - 19.6% | Taxation in Monaco | |
 Kingdom of Montenegro Kingdom of Montenegro |
9% | 15% | 17% | Taxation in Montenegro | |
 Morocco Morocco |
30% | 0–38% | 20% | Taxation in Morocco | |
 Nepal Nepal |
10–25% | 13% | Taxation in Nepal | ||
 Netherlands Netherlands |
20/25% | 0–52% | 19% (6% for essential and selected goods) |
Taxation in the Netherlands The Netherlands has a rich history dealing with taxation, predating the Romanic period.Some of the most important taxes are that of the income tax , the wage withholding tax , the value added tax and the corporate tax .-Income tax:The Netherlands has... Income tax in the Netherlands Income tax in the Netherlands is regulated by the Wet inkomstenbelasting 2001 .The fiscal year is the same as the calendar year. Before April 1 citizens have to report their income from the previous year... |
|
 New Zealand New Zealand |
28% | 10.5–33% | 15% GST |
Taxation in New Zealand Taxation in New Zealand is collected at a national level by the Inland Revenue Department on behalf of the Government of New Zealand. National taxes are levied on personal and business income, as well as on the supply of goods and services. There is no capital gains tax although certain "gains"... Goods and Services Tax (New Zealand) Goods and Services Tax is a value added tax introduced in New Zealand on 1 October 1986 at 10%. It later increased to 12.5% on 1 July 1989 and was further increased to 15% on 1 October 2010.... |
|
 New Caledonia New Caledonia |
30% | 25% on local income of non-residents
First XPF 1,000,000 tax-free, 4% on next XPF 800,000 (total income 1.0m - 1.8m), 12% on next XPF 1,200,000 (total income 1.8m - 3.0m), 25% on next XPF 1,500,000 (total income 3.0m - 4.5m), 40% on remaining income (total income >4.5m) |
|||
 Norway Norway |
28% | 0–47.8% | 0–14.1% | 25% or 14% (food and drink in shops) or 8% (transportation) | Taxation in Norway Taxation in Norway Taxation in Norway is levied by the central government, the county municipality and the municipality . The tax level in Norway is among the highest in the world. In 2009 the total tax revenue was 41.0 % of the gross domestic product . Many direct and indirect taxes exist. The most important... |
 Pakistan Pakistan |
35% | 7.5–35% | 16% (GST) | Taxation in Pakistan Taxation in Pakistan Taxation in Pakistan is a complex system of more than 70 unique taxes administered by at least 37 agencies of the Government of Pakistan.The government is seriously indebted -- and only 1.9 million people in a country of 170 million filed tax returns at all in 2010. An estimated 10 million people... |
|
 Palestinian territories Palestinian territories |
15% | 5-15% | 5-15% | % (VAT) | Taxation in Palestine |
 Panama Panama |
30% | 0–27% | 7% or 0% | Taxation in Panama | |
 Peru Peru |
30% | 0-15-21-30% | 9% Essalud (Social Security) 8.33% CTS Compensación por tiempo de servicios (like a insurance in case the employee losses his job) 1 complete additional salary in July and 1 complete additional salary in December for Christmas. 0.75% SENATI (Only Industry Jobs) 0.2% SENCICO (Only Construction Workers) | 18% (16% VAT + 2% Municipal Promotional Tax) 0–118% ISC Impuesto Selectivo al Consumo (To some products like liquor, cigarettes, etc.) | Taxation in Peru Taxation in Peru The income tax in Peru is collected by the Superintendencia Nacional de Administración Tributaria, best known as SUNAT. This country uses a system of progressive taxation on personal income, and a flat rate tax on business income.-External links:... |
 Philippines Philippines |
30% | 5–32% | 12% or 7% or 0% (in some cases, foreign investors are zero-rated) |
Taxation in Philippines Taxation in Philippines Taxation in the Philippines is controlled by the Bureau of Internal Revenue . Taxes in the Philippines range from 5% to 35%-Exceptions:* 20,000 Pesos for individuals* 30,000 Pesos for married couples... |
|
 Poland Poland |
19% | 0%, 18%, 32% (or optional 19% flat rate for self-employed) | 41.11% | 23% or 8% or 5% | Taxation in Poland |
 Portugal Portugal |
25% | 10.5–40% | 23.75% | Normal: 23% Intermediate: 13% Reduced: 6% Madeira, Açores: 15%, 9%, 4% |
Taxation in Portugal |
 Kingdom of Romania Kingdom of Romania |
16% | 16% | 45.15% | 24% or 9% (medicines, books, newspapers, hotel ...), or 4% | Taxation in Romania |
 Russia Russia |
20% | 13% | 34% before annual salary exceeds 415k RUB, 8% thereafter -obligatory social payments | 0-18% (no VAT for export and services) | Taxation in Russia |
 Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia |
20% (higher for oil/gas) | Zakat Zakat Zakāt , one of the Five Pillars of Islam, is the giving of a fixed portion of one's wealth to charity, generally to the poor and needy.-History:Zakat, a practice initiated by Muhammed himself, has played an important role throughout Islamic history... (natives) 20% (foreigners) |
11% Social security | 0% | Taxation in Saudi Arabia |
 Senegal Senegal |
25% | up to 50% | 20% | Taxation in Senegal | |
 Serbia Serbia |
10% | 12–20% | 35.8% | 18% or 8% or 0% (reduced rates are for certain goods) |
Taxation in Serbia |
 Singapore Singapore |
17% | 3.5%–20% | 7% (GST) |
|
|
 Slovakia Slovakia |
19% | 19% | 20% | Taxation in Slovakia | |
 Slovenia Slovenia |
20% | 16–41% | 0% (abolished) | 20% or 8.5% | Taxation in Slovenia |
 South Africa South Africa |
28% | 0–40% | 14% | Taxation in South Africa Taxation in South Africa Taxation in South Africa may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through the South African Revenue Service or to local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, value added tax , corporation tax and fuel duty... |
|
 Spain Spain |
25–30% | 0–47% | 18% or 8% or 4% | Taxation in Spain | |
 Sri Lanka Sri Lanka |
0-35% | 0–24% | 0% or 12% | Taxation in Sri Lanka | |
 Sweden Sweden |
26.3% | 28.89%–59.09% | 31.42% | 25% or 12% or 6% | Taxation in Sweden Taxation in Sweden - Salary incomes :Taxation in Sweden on salaries for an employee involves contributing to three different levels of government: the municipality, the county council, and the central government... |
 Switzerland Switzerland |
13–25% | 0–13.2% (federal) | % or 3.8% or 2.5% | Taxation in Switzerland Taxation in Switzerland Taxes in Switzerland are levied by the Swiss Confederation, the cantons and the municipalities. Switzerland is sometimes considered a tax haven due to its general low rate of taxation, its political stability as well as the various tax exemptions or reductions available to Swiss companies doing... |
|
 Syria Syria |
10–45% | 5–15% | Taxation in Syria | ||
 Republic of China Republic of China |
17% | 6–40% | 5% | Taxation in Taiwan | |
 Tanzania Tanzania |
30% | 15–30% | Taxation in Tanzania Taxation in Tanzania In Tanzania the Income Tax Act, 2004 came into effect in July 2004. This act restructured the income tax system in line with modern requirements and repealed the previous Income Tax Act, 1973. Tax is levied on income from employment, income from business and income from investment. Taxable... |
||
 Thailand Thailand |
30% | 5–37% | 7% | Taxation in Thailand | |
 Tunisia Tunisia |
30% | 0–35% | 18% or 12% or 6% | Taxation in Tunisia | |
 Turkey Turkey |
20% | 15–35% | 35–40% | 18% | Taxation in Turkey |
 Ukraine Ukraine |
25% (16% from April 1, 2014) | 15% | 33.2% - 34.7% Mandatory contribution to the State Pension Fund. For private entrepreneurs in simplified taxation mode minimum contribution calculation based on minimum income (December 2011: 34.7% * 1004 UAH = 348.39 UAH or about $44 per month) | 20% (17% from January 1, 2014) | Taxation in Ukraine |
 United Arab Emirates United Arab Emirates |
0% | Taxation in United Arab Emirates | |||
 United Kingdom United Kingdom |
20–26% http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/rates/corp.htm (20-23% by 2014) | 0–50% | 0%–11% (individual) 0-12.8% (employer) (National Insurance National Insurance National Insurance in the United Kingdom was initially a contributory system of insurance against illness and unemployment, and later also provided retirement pensions and other benefits... ) |
20% Standard Rate; 5% Reduced Rate; 0% Zero Rate. |
Taxation in the United Kingdom Taxation in the United Kingdom Taxation in the United Kingdom may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: The central government and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty... |
 United States United States |
0-38% (federal) 0-12% (states) |
0-35% (federal) 0-10.55% (states) |
2.9-15.3% (federal, regressive) 0-2% (states, usually regressive) |
0-10.25% (states and local) |
Taxation in the United States The United States is a federal republic with autonomous state and local governments. Taxes are imposed in the United States at each of these levels. These include taxes on income, property, sales, imports, payroll, estates and gifts, as well as various fees.Taxes are imposed on net income of... Income tax in the United States In the United States, a tax is imposed on income by the Federal, most states, and many local governments. The income tax is determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income as defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and... Sales taxes in the United States There is no federal sales or use tax in the United States. 45 states and the District of Columbia impose sales and use taxes on the retail sale, lease and rental of many goods, as well as some services. Many cities, counties, transit authorities and special purpose districts impose additional local... |
 Uruguay Uruguay |
30% | 0–25% | 22% | Taxation in Uruguay | |
 Uzbekistan Uzbekistan |
9 % | 11–22% | 0-20% | Taxation in Uzbekistan | |
 Venezuela Venezuela |
15/22/34% | 6–34% | 8–10%/12% | Taxation in Venezuela | |
 Vietnam Vietnam |
25% | 5–35% | 10% | Taxation in Vietnam | |
 British Virgin Islands British Virgin Islands |
0% | 10–14% | Taxation in the British Virgin Islands Taxation in the British Virgin Islands Taxation in the British Virgin Islands is relatively simple by comparative standards; photocopies of all of the tax laws of the British Virgin Islands would together amount to about 200 pages of paper. Taxation in the British Virgin Islands is mostly notable for what is not subject to taxation... |
||
 Zambia Zambia |
35% | 10–30% | % | Taxation in Zambia Taxation in Zambia - Zambian Tax Policy :Income in Zambia is taxed on the source principle or deemed source basis in some instances. Residents are taxed on domestic source of income and certain types of foreign income, non-residents are normally taxed on Zambian source of income... |
See also
- List of countries by tax revenue as percentage of GDP
- Dividend imputationDividend imputationDividend imputation is a corporate tax system in which some or all of the tax paid by a company may be attributed, or imputed, to the shareholders by way of a tax credit to reduce the income tax payable on a distribution...
- VAT Rates
- Tax Freedom DayTax Freedom DayTax Freedom Day is the first day of the year in which a nation as a whole has theoretically earned enough income to fund its annual tax burden. It is annually calculated in the United States by the Tax Foundation—a Washington, D.C.-based tax research organization...
- Welfare stateWelfare stateA welfare state is a "concept of government in which the state plays a key role in the protection and promotion of the economic and social well-being of its citizens. It is based on the principles of equality of opportunity, equitable distribution of wealth, and public responsibility for those...
- Tax havenTax havenA tax haven is a state or a country or territory where certain taxes are levied at a low rate or not at all while offering due process, good governance and a low corruption rate....
External links
- State Business Tax Climate Index Rankings, 2003–2008 in the U.S., Tax FoundationTax FoundationThe Tax Foundation is a Washington, D.C.-based think tank founded in 1937 that collects data and publishes research studies on tax policies at the federal and state levels. The organization is broken into three primary areas of research which are the Center for Federal Fiscal Policy, The and the...
- OECD Comparison of Wage Taxes (top combined marginal individual tax rates), Tax FoundationTax FoundationThe Tax Foundation is a Washington, D.C.-based think tank founded in 1937 that collects data and publishes research studies on tax policies at the federal and state levels. The organization is broken into three primary areas of research which are the Center for Federal Fiscal Policy, The and the...
- European VAT Rates
- IBFD, Your Portal to Cross-Border Tax Expertise
- Paying Taxes – World BankWorld BankThe World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...

