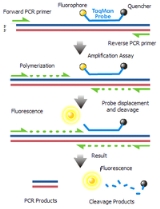
TaqMan
Overview
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
probes
Hybridization probe
In molecular biology, a hybridization probe is a fragment of DNA or RNA of variable length , which is used in DNA or RNA samples to detect the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe...
that are designed to increase the specificity of real-time PCR assays
Real-time polymerase chain reaction
In molecular biology, real-time polymerase chain reaction, also called quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction or kinetic polymerase chain reaction , is a laboratory technique based on the PCR, which is used to amplify and simultaneously quantify a targeted DNA molecule...
. The method was first reported in 1991 by researchers at Cetus Corporation, and the technology was subsequently developed by Roche Molecular Diagnostics for diagnostic assays and by Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems
Applied Biosystems, Inc. started as GeneCo , was the name of a pioneer biotechnology company founded in 1981 in Foster City, California, in the San Francisco Bay Area...
for research applications.
The TaqMan probe principle relies on the 5´–3´ exonuclease
Exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3’ or the 5’ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle ...
activity of Taq polymerase
Taq polymerase
thumb|228px|right|Structure of Taq DNA polymerase bound to a DNA octamerTaq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase named after the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus from which it was originally isolated by Thomas D. Brock in 1965...
to cleave a dual-labeled probe during hybridization to the complementary target sequence and fluorophore
Fluorophore
A fluorophore, in analogy to a chromophore, is a component of a molecule which causes a molecule to be fluorescent. It is a functional group in a molecule which will absorb energy of a specific wavelength and re-emit energy at a different wavelength...
-based detection.

