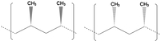
Tacticity
Overview
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms within molecules. An important branch of stereochemistry is the study of chiral molecules....
of adjacent chiral
Chirality (chemistry)
A chiral molecule is a type of molecule that lacks an internal plane of symmetry and thus has a non-superimposable mirror image. The feature that is most often the cause of chirality in molecules is the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom....
centers within a macromolecule
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule commonly created by some form of polymerization. In biochemistry, the term is applied to the four conventional biopolymers , as well as non-polymeric molecules with large molecular mass such as macrocycles...
. The practical significance of tacticity rests on the effects of tacticity on the physical properties of the polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
. The regularity of the macromolecular structure influences the degree to which it has rigid, crystalline
Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In a gas, the relative positions of the atoms or...
long range order or flexible, amorphous long range disorder. Precise knowledge of tacticity of a polymer also helps understanding at what temperature a polymer melts
Melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase change of a substance from a solid to a liquid. The internal energy of a substance is increased, typically by the application of heat or pressure, resulting in a rise of its temperature to the melting point, at which the rigid...
, how soluble it is in a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
and its mechanical properties.
A tactic macromolecule in the IUPAC definition is a macromolecule in which essentially all the configurational (repeating) units are identical.
Unanswered Questions

