
Systematic code
Encyclopedia
In coding theory
, a systematic code is any error-correcting code in which the input data is embedded in the encoded output. Conversely, in a non-systematic code the output does not contain the input symbols.
Systematic codes have the advantage that the parity data can simply be appended to the source block, and receivers do not need to recover the original source symbols if received correctly – this is useful for example if error-correction coding is combined with a hash function for quickly determining the correctness of the received source symbols, or in cases where errors occur in erasures and a received symbol is thus always correct. Furthermore, for engineering purposes such as synchronization and monitoring, it is desirable to get reasonable good estimates of the received source symbols without going through the lengthy decoding process which may be carried out at a remote site at a later time.
Because of the advantages cited above, linear
error-correcting codes are therefore generally implemented as systematic codes. However, for certain decoding algorithms such as sequential decoding or maximum-likelihood decoding, a non-systematic structure can increase performance in terms of undetected decoding error probability when the minimum free distance of the code is larger.
For a systematic linear code
, the generator matrix
,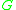 , can always be written as
, can always be written as  , where
, where 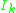 is the identity matrix
is the identity matrix
of size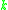 .
.
Coding theory
Coding theory is the study of the properties of codes and their fitness for a specific application. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography, error-correction and more recently also for network coding...
, a systematic code is any error-correcting code in which the input data is embedded in the encoded output. Conversely, in a non-systematic code the output does not contain the input symbols.
Systematic codes have the advantage that the parity data can simply be appended to the source block, and receivers do not need to recover the original source symbols if received correctly – this is useful for example if error-correction coding is combined with a hash function for quickly determining the correctness of the received source symbols, or in cases where errors occur in erasures and a received symbol is thus always correct. Furthermore, for engineering purposes such as synchronization and monitoring, it is desirable to get reasonable good estimates of the received source symbols without going through the lengthy decoding process which may be carried out at a remote site at a later time.
Properties
Every non-systematic code can be transformed into a systematic code with essentially the same properties (i.e., minimum distance).Because of the advantages cited above, linear
Linear code
In coding theory, a linear code is an error-correcting code for which any linear combination of codewords is also a codeword. Linear codes are traditionally partitioned into block codes and convolutional codes, although Turbo codes can be seen as a hybrid of these two types. Linear codes allow for...
error-correcting codes are therefore generally implemented as systematic codes. However, for certain decoding algorithms such as sequential decoding or maximum-likelihood decoding, a non-systematic structure can increase performance in terms of undetected decoding error probability when the minimum free distance of the code is larger.
For a systematic linear code
Linear code
In coding theory, a linear code is an error-correcting code for which any linear combination of codewords is also a codeword. Linear codes are traditionally partitioned into block codes and convolutional codes, although Turbo codes can be seen as a hybrid of these two types. Linear codes allow for...
, the generator matrix
Generator matrix
In coding theory, a generator matrix is a basis for a linear code, generating all its possible codewords.If the matrix is G and the linear code is C,where w is a codeword of the linear code C, c is a row vector, and a bijection exists between w and c. A generator matrix for an q-code has...
,
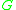 , can always be written as
, can always be written as  , where
, where 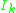 is the identity matrix
is the identity matrixIdentity matrix
In linear algebra, the identity matrix or unit matrix of size n is the n×n square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. It is denoted by In, or simply by I if the size is immaterial or can be trivially determined by the context...
of size
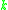 .
.Examples
- ChecksumChecksumA checksum or hash sum is a fixed-size datum computed from an arbitrary block of digital data for the purpose of detecting accidental errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. The integrity of the data can be checked at any later time by recomputing the checksum and...
s and hash functionHash functionA hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
s, combined with the input data, can be viewed as systematic error-detecting codes. - Linear codes are usually implemented as systematic error-correcting codes (e.g., Reed-Solomon codes in CDsCompact DiscThe Compact Disc is an optical disc used to store digital data. It was originally developed to store and playback sound recordings exclusively, but later expanded to encompass data storage , write-once audio and data storage , rewritable media , Video Compact Discs , Super Video Compact Discs ,...
). - Convolutional codeConvolutional codeIn telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code in which* each m-bit information symbol to be encoded is transformed into an n-bit symbol, where m/n is the code rate and...
s are implemented as either systematic or non-systematic codes. Non-systematic convolutional codes can provide better performance under maximum-likelihood (ViterbiViterbi decoderA Viterbi decoder uses the Viterbi algorithm for decoding a bitstream that has beenencoded using forward error correction based on a convolutional code....
) decoding. - In DVB-HDVB-HDVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
, for additional error protection and power efficiency for mobile receivers, a systematic Reed-Solomon code is employed as an erasure code over packets within a data burstBurst transmissionIn telecommunication, the term burst transmission or data burst has the following meanings:# Any relatively high-bandwidth transmission over a short period of time...
, where each packet is protected with a CRCCyclic redundancy checkA cyclic redundancy check is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to raw data...
: data in verified packets count as correctly received symbols, and if all are received correctly, evaluation of the additional parity data can be omitted, and receiver devices can switch off reception until the start of the next burst. - Fountain codeFountain codeIn coding theory, fountain codes are a class of erasure codes with the property that a potentially limitless sequence of encoding symbols can be generated from a given set of source symbols such that the original source symbols can ideally be recovered from any subset of the encoding symbols of...
s may be either systematic or non-systematic: as they do not exhibit a fixed code rateCode rateIn telecommunication and information theory, the code rate of a forward error correction code is the proportion of the data-stream that is useful...
, the set of source symbols is diminishing among the possible output set.

