
Synthetic instrument
Encyclopedia
A synthetic instrument is a term in metrology
(test and measurement science). A Synthetic Instrument is software that runs on a Synthetic Measurement System to perform a specific synthesis, analysis
, or measurement
function. A Synthetic Measurement System (SMS) is a common, general purpose, physical hardware platform that is intended to perform many kinds of synthesis, analysis, or measurement functions using Synthetic Instruments.
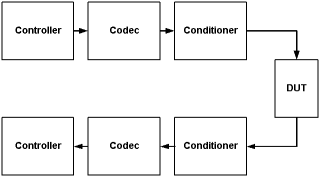
Typically the generic SMS hardware is dual cascade of three subsystems: digital processing and control, A/D
or D/A conversion (codec), and signal conditioning. One cascade is for stimulus, one for response. Sandwiched between them is the device under test
(DUT) that is being measured.
 A synthetic instrument is the opposite of the retronym
A synthetic instrument is the opposite of the retronym
natural instrument. Although the word “synthetic” in the phrase synthetic instrument might seem to imply that synthetic instruments are synthesizers: that they only do synthesis; this is incorrect. The instrument itself is being synthesized; nothing is implied about what the instrument does. A synthetic instrument might indeed be a synthesizer, but it could just as easily be an analyzer, or some hybrid of the two.
Synthetic instruments are implemented on generic hardware, ie, generic meaning that the underlying hardware is not explicitly designed to perform the particular measurement. This is probably the most salient characteristic of a synthetic instrument. Measurement specificity is encapsulated totally in software. The hardware does not define the measurement.
An analogy to this relationship between specific measurement hardware versus generic hardware with its function totally defined in software is the relationship between specific digital circuits and a general purpose CPU
. A specific digital circuit can be designed and hardwired with digital logic parts to perform a specific calculation. Alternatively, a microprocessor (or, better yet, a gate array
) could be used to perform the same calculation using appropriate software. One case is specific, the other generic, with the specificity encapsulated in software.
At the software level, portability of measurement description is the key attribute that distinguishes a synthetic instrument from the more commonly found instrumentation software -- software that is limited to hardware scripting and data flow processing. Not all measurement related software systems inherently provide for the abstract, portable synthesis of measurements. Even if they do have such provisions, they may not typically be applied that way by users, especially if the system encourages non-abstracted access to hardware. Application software packages such as Measure Foundry and LabVIEW
are typically used with explicit structural links to the natural measurements made by specific hardware and therefore usually are not synthesizing measurements from an abstract description. On the other hand, should a software system be used to synthesize measurement functions as descriptive behavioral constructs, rather than hardware referenced structural data flow descriptions, this is true measurement synthesis. An analogy here is the distinction between a non portable structural
description and an abstract behavioral description of digital logic that we see in HDL
systems like Verilog
.
Synthetic instruments in test and measurement are conceptually related to the software synthesizer
in audio or music. A musical instrument synthesizer
synthesizes the sound of specific instruments from generic
hardware. Of course, a significant difference in these concepts is that musical instrument synthesizers typically only
generate musical sound, whereas a synthetic instrument in test and measurement may be equally likely to
generate or to measure some signal or parameter.
A similar term commonly used in test and measurement, Virtual instrumentation
, is a superset of synthetic instrumentation. All synthetic instruments are virtual instruments; however, the two terms are different when virtual instrument software mirrors and augments non-generic instrument hardware, providing a soft front panel, or managing the data flow to and from a natural instrument. In this case, the PC and accompanying software is supplementing the analysis and presentation capabilities of the natural instrument.
The essential point is this: synthetic instruments are synthesized. The whole is greater than the sum of the parts. To use Buckminster Fuller
's word, synthetic instruments are synergistic instruments. Like a triangle is more than three lines, synthetic instruments are more than the triangle of hardware (Control, Codec, Conditioning) they are implemented on.
Therefore, one way to tell if you have a true synthetic instrument is to examine the hardware design alone and to try to figure out what sort of instrument it might be. If all you can determine are basic category facts, like the fact that it can be categorized as a stimulus or response instrument, but not anything about what it's particularly designed to create or measure—if the measurement specificity is all hidden in software—then you likely have a true synthetic instrument.
Metrology
Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. The word comes from Greek μέτρον , "measure" + "λόγος" , amongst others meaning "speech, oration, discourse, quote, study, calculation, reason"...
(test and measurement science). A Synthetic Instrument is software that runs on a Synthetic Measurement System to perform a specific synthesis, analysis
Analysis
Analysis is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle , though analysis as a formal concept is a relatively recent development.The word is...
, or measurement
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
function. A Synthetic Measurement System (SMS) is a common, general purpose, physical hardware platform that is intended to perform many kinds of synthesis, analysis, or measurement functions using Synthetic Instruments.
Typically the generic SMS hardware is dual cascade of three subsystems: digital processing and control, A/D
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
or D/A conversion (codec), and signal conditioning. One cascade is for stimulus, one for response. Sandwiched between them is the device under test
Device under test
Device under test , also known as unit under test , is a term commonly used to refer to a manufactured product undergoing testing.-In semiconductor testing:...
(DUT) that is being measured.

Retronym
A retronym is a type of neologism that provides a new name for an object or concept to differentiate the original form or version of it from a more recent form or version. The original name is most often augmented with an adjective to account for later developments of the object or concept itself...
natural instrument. Although the word “synthetic” in the phrase synthetic instrument might seem to imply that synthetic instruments are synthesizers: that they only do synthesis; this is incorrect. The instrument itself is being synthesized; nothing is implied about what the instrument does. A synthetic instrument might indeed be a synthesizer, but it could just as easily be an analyzer, or some hybrid of the two.
Synthetic instruments are implemented on generic hardware, ie, generic meaning that the underlying hardware is not explicitly designed to perform the particular measurement. This is probably the most salient characteristic of a synthetic instrument. Measurement specificity is encapsulated totally in software. The hardware does not define the measurement.
An analogy to this relationship between specific measurement hardware versus generic hardware with its function totally defined in software is the relationship between specific digital circuits and a general purpose CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
. A specific digital circuit can be designed and hardwired with digital logic parts to perform a specific calculation. Alternatively, a microprocessor (or, better yet, a gate array
Gate array
A gate array or uncommitted logic array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits...
) could be used to perform the same calculation using appropriate software. One case is specific, the other generic, with the specificity encapsulated in software.
At the software level, portability of measurement description is the key attribute that distinguishes a synthetic instrument from the more commonly found instrumentation software -- software that is limited to hardware scripting and data flow processing. Not all measurement related software systems inherently provide for the abstract, portable synthesis of measurements. Even if they do have such provisions, they may not typically be applied that way by users, especially if the system encourages non-abstracted access to hardware. Application software packages such as Measure Foundry and LabVIEW
LabVIEW
LabVIEW is a system design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments. LabVIEW provides engineers and scientists with the tools needed to create and deploy measurement and control systems.The graphical language is named "G"...
are typically used with explicit structural links to the natural measurements made by specific hardware and therefore usually are not synthesizing measurements from an abstract description. On the other hand, should a software system be used to synthesize measurement functions as descriptive behavioral constructs, rather than hardware referenced structural data flow descriptions, this is true measurement synthesis. An analogy here is the distinction between a non portable structural
description and an abstract behavioral description of digital logic that we see in HDL
Hardware description language
In electronics, a hardware description language or HDL is any language from a class of computer languages, specification languages, or modeling languages for formal description and design of electronic circuits, and most-commonly, digital logic...
systems like Verilog
Verilog
In the semiconductor and electronic design industry, Verilog is a hardware description language used to model electronic systems. Verilog HDL, not to be confused with VHDL , is most commonly used in the design, verification, and implementation of digital logic chips at the register-transfer level...
.
Synthetic instruments in test and measurement are conceptually related to the software synthesizer
Software synthesizer
A software synthesizer, also known as a softsynth is a computer program or plug-in for digital audio generation. Computer software which can create sounds or music is not new, but advances in processing speed are allowing softsynths to accomplish the same tasks that previously required dedicated...
in audio or music. A musical instrument synthesizer
Synthesizer
A synthesizer is an electronic instrument capable of producing sounds by generating electrical signals of different frequencies. These electrical signals are played through a loudspeaker or set of headphones...
synthesizes the sound of specific instruments from generic
hardware. Of course, a significant difference in these concepts is that musical instrument synthesizers typically only
generate musical sound, whereas a synthetic instrument in test and measurement may be equally likely to
generate or to measure some signal or parameter.
A similar term commonly used in test and measurement, Virtual instrumentation
Virtual instrumentation
Virtual instrumentation is the use of customizable software and modular measurement hardware to create user-defined measurement systems, called virtual instruments....
, is a superset of synthetic instrumentation. All synthetic instruments are virtual instruments; however, the two terms are different when virtual instrument software mirrors and augments non-generic instrument hardware, providing a soft front panel, or managing the data flow to and from a natural instrument. In this case, the PC and accompanying software is supplementing the analysis and presentation capabilities of the natural instrument.
The essential point is this: synthetic instruments are synthesized. The whole is greater than the sum of the parts. To use Buckminster Fuller
Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster “Bucky” Fuller was an American systems theorist, author, designer, inventor, futurist and second president of Mensa International, the high IQ society....
's word, synthetic instruments are synergistic instruments. Like a triangle is more than three lines, synthetic instruments are more than the triangle of hardware (Control, Codec, Conditioning) they are implemented on.
Therefore, one way to tell if you have a true synthetic instrument is to examine the hardware design alone and to try to figure out what sort of instrument it might be. If all you can determine are basic category facts, like the fact that it can be categorized as a stimulus or response instrument, but not anything about what it's particularly designed to create or measure—if the measurement specificity is all hidden in software—then you likely have a true synthetic instrument.

