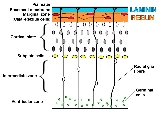
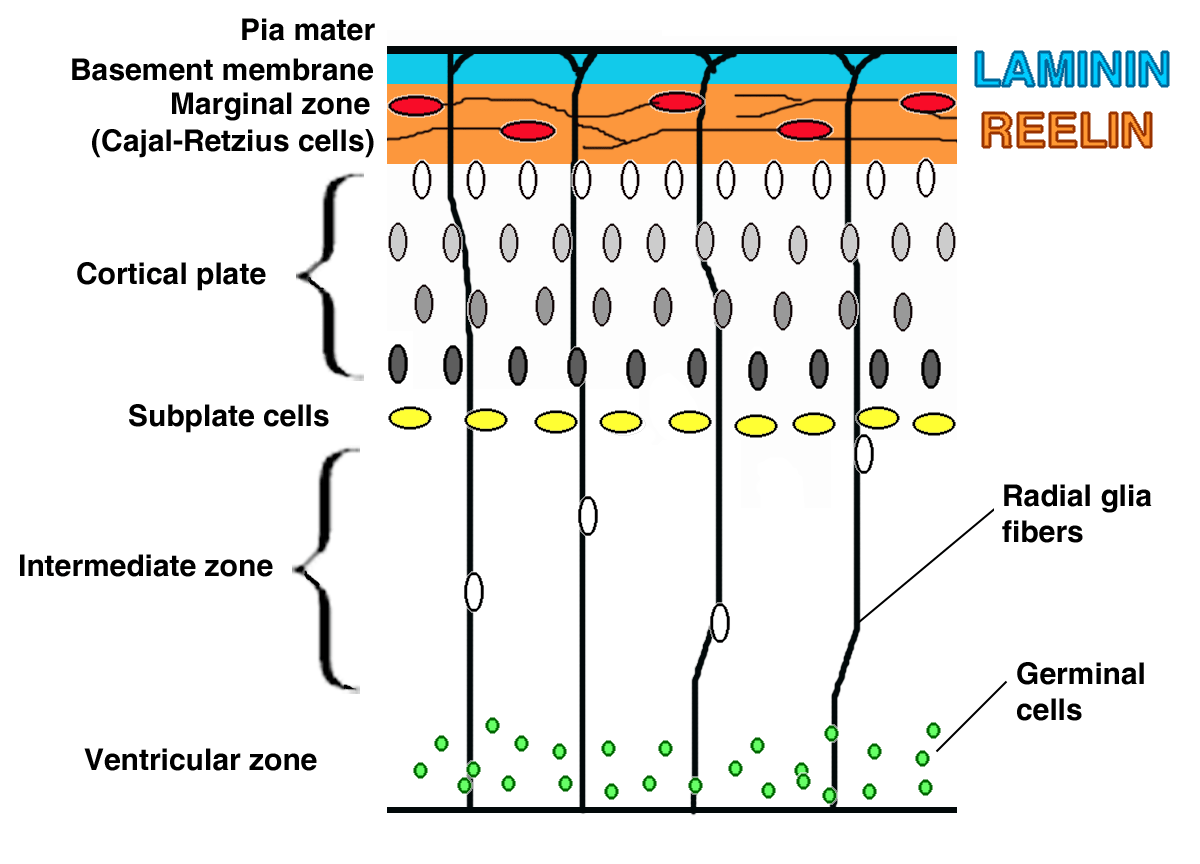
Subplate
Encyclopedia
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
subplate zone, together with the marginal zone and the cortical plate, represents the developmental anlage
Anlage
In embryology, anlage is the primordium, the initial clustering of embryonic cells that serves as a foundation from which a body part or an organ develops. Failure to progress past this stage in organ development is known as agenesis....
of the mammalian cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
. It serves as a waiting compartment for growing cortical afferent
Afferent
Afferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying towards a center, for example the afferent arterioles conveying blood towards the Bowman's capsule in the Kidney. Opposite to Efferent.*Something that so conducts, see Afferent nerve fiber...
s; its cells are involved in the establishment of pioneering cortical efferent
Efferent
Efferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying away from a center, for example the efferent arterioles conveying blood away from the Bowman's capsule in the kidney. Opposite to afferent....
projections and transient fetal circuitry, and apparently have a number of other developmental roles. The subplate zone is a phylogenetically
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relatedness among groups of organisms , which is discovered through molecular sequencing data and morphological data matrices...
recent structure and it is most developed in the human brain.
Subplate neurons are among the first generated neurons in the mammalian cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
. These neurons disappear during postnatal
Postnatal
Postnatal is the period beginning immediately after the birth of a child and extending for about six weeks. Another term would be postpartum period, as it refers to the mother...
development and are important in establishing the correct wiring and functional maturation of the cerebral cortex.
Subplate neurons appear to be selectively sensitive to injury (such as hypoxia
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
) which in humans are associated with motor and cognitive defects .
Subplate neurons are the first cortical neurons to receive synaptic inputs from thalamic
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
axons, establishing a temporary link between thalamic axons and their final target in layer 4. . Later, thalamic axons invade layer 4 where they innervate layer 4 neurons. In the visual system thalamic axons to layer 4 form ocular dominance column
Ocular dominance column
Ocular dominance columns are stripes of neurons in the visual cortex of certain mammals that respond preferentially to input from one eye or the other. The columns span multiple cortical layers, and are laid out in a striped pattern across the surface of the striate cortex...
s and this segregation of thalamic axons is impaired if subplate neurons are missing .

