
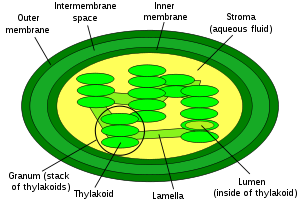
Stroma (fluid)
Encyclopedia
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, refers to the colourless fluid surrounding the grana
Thylakoid
A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
within the Plastid
Plastid
Plastids are major organelles found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cell...
, chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
.
Within the stroma are grana
Grana
-Places:Croatia* Grana, Varaždin County, a village in Varaždin County, CroatiaGermany* Grana, Germany, a municipality in Saxony-Anhalt, GermanyItaly* Grana, Piedmont, a commune in the Province of Asti...
, stacks of thylakoid
Thylakoid
A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
s, the sub-organelles, where photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
is commenced before the chemical changes are completed in the stroma.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first stage, light-dependent reactions
Light-dependent reactions
The 'light-dependent reactions', or light reactions, are the first stage of photosynthesis, the process by which plants capture and store energy from sunlight. In this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy, in the form of the energy-carrying molecules ATP and NADPH...
capture the energy of light and use it to make the energy-storage molecules ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
and NADPH. During the second stage, the light-independent reactions use these products to capture and reduce carbon dioxide
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
.
The series of biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
reactions which take place in the stroma are collectively called the Calvin Cycle
Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle or Calvin–Benson-Bassham cycle or reductive pentose phosphate cycle or C3 cycle or CBB cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplasts in photosynthetic organisms...
or light-dependent reactions
Light-dependent reactions
The 'light-dependent reactions', or light reactions, are the first stage of photosynthesis, the process by which plants capture and store energy from sunlight. In this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy, in the form of the energy-carrying molecules ATP and NADPH...
. There are three phases: carbon fixation
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration.
The stroma is also the location of chloroplast DNA and chloroplast ribosomes, and thus also the location of molecular processes including chloroplast DNA replication, and transcription/translation of some chloroplast proteins.

