
Stream thrust averaging
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, stream thrust averaging is a process used to convert three dimensional flow through a duct into one dimensional uniform flow. It makes the assumptions that the flow is mixed adiabatically and without friction
. However, due to the mixing process, there is a net increase in the entropy of the system. Although there is an increase in entropy
, the stream thrust averaged values are more representative of the flow than a simple average as a simple average would violate the second Law of Thermodynamics
.
: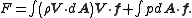
Mass flow
: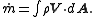
Stagnation enthalpy
: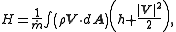
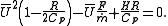
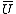 yields two solutions. They must both be analyzed to determine which is the physical solution. One will usually be a subsonic root and the other a supersonic root. If it is not clear which value of velocity
yields two solutions. They must both be analyzed to determine which is the physical solution. One will usually be a subsonic root and the other a supersonic root. If it is not clear which value of velocity
is correct, the second law of thermodynamics
may be applied.
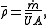


Second law of thermodynamics: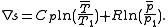
The values and
and  are unknown and may be dropped from the formulation. The value of entropy is not necessary, only that the value is positive.
are unknown and may be dropped from the formulation. The value of entropy is not necessary, only that the value is positive.

One possible unreal solution for the stream thrust averaged velocity yields a negative entropy. Another method of determining the proper solution is to take a simple average of the velocity and determining which value is closer to the stream thrust averaged velocity.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, stream thrust averaging is a process used to convert three dimensional flow through a duct into one dimensional uniform flow. It makes the assumptions that the flow is mixed adiabatically and without friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
. However, due to the mixing process, there is a net increase in the entropy of the system. Although there is an increase in entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
, the stream thrust averaged values are more representative of the flow than a simple average as a simple average would violate the second Law of Thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and...
.
Equations for a perfect gas
Stream thrustThrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system....
:
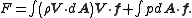
Mass flow
Mass flow
Mass flow, also known as mass transfer and bulk flow, is the movement of material matter. In physics, mass flow occurs in open systems and is often measured as occurring when moving across a certain boundary characterized by its cross-sectional area and a flow rate. In engineering and biology it...
:
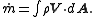
Stagnation enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
:
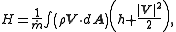
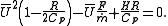
Solutions
Solving for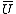 yields two solutions. They must both be analyzed to determine which is the physical solution. One will usually be a subsonic root and the other a supersonic root. If it is not clear which value of velocity
yields two solutions. They must both be analyzed to determine which is the physical solution. One will usually be a subsonic root and the other a supersonic root. If it is not clear which value of velocityVelocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
is correct, the second law of thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and...
may be applied.
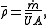


Second law of thermodynamics:
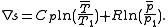
The values
 and
and  are unknown and may be dropped from the formulation. The value of entropy is not necessary, only that the value is positive.
are unknown and may be dropped from the formulation. The value of entropy is not necessary, only that the value is positive.
One possible unreal solution for the stream thrust averaged velocity yields a negative entropy. Another method of determining the proper solution is to take a simple average of the velocity and determining which value is closer to the stream thrust averaged velocity.

