Sterically induced reduction
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, a sterically induced reduction happens when an oxidized metal
behaves and exhibits similar if not identical reducing properties as that of the more reduced form of the metal . This effect is mainly caused by the surrounding ligand
s that are complexed to the metal and it is the ligands that are involved in the reduction chemistry instead of the metal due to electronic destabilization by being significantly distanced from the metal. Sterically induced reductions commonly involve metals found in the lanthanoid and actinoid series.
that is used in a variety of synthetic applications, mainly because all other divalent lanthanides are unstable. Complexes of Sm
(II) have also been investigated and used in similar applications. However, even though Sm(II) complexes and compounds have had tremendous success when used in conjunction with a variety of substrates. There have been instances where chemistry of certain materials cannot be performed due to unclean reactions in which products are not easily isolated from reaction mixtures when Sm(II) compounds are used to perform the desired reduction. In these cases, adjusting the size of the metal (which is commonly and easily done for the trivalent lanthanide compounds) may fine tune the nature of a specific reaction, which should produce desired and clean products. One drawback to this notion is that Sm(II) is uniquely stable compared to other divalent lanthanides, where the other metals in the series tend to exist freely in the trivalent state. The discovery and application of sterically induced reductions allows the unique reducing properties and chemistry to be applicable to all of the lanthanide metals while remaining in their more stable trivalent state.
When Sm(III) is complexed with C5Me5 (pentamethylcyclopentadiene
) to give the compound (C5Me5)3Sm, this trivalent species has been shown to have the same reducing reactivity of the Sm(II) derivative.
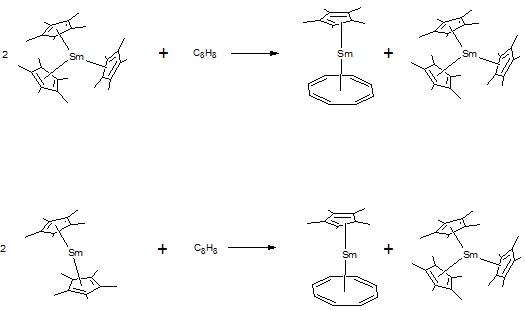 The top reaction is the Sm(III) derivative and the bottom involves the Sm(II) derivative. Notice that the oxidation state
The top reaction is the Sm(III) derivative and the bottom involves the Sm(II) derivative. Notice that the oxidation state
of the metal in the top reaction does not change, while the oxidation state changes in the bottom one. If the metal was involved in the reduction the oxidation states should have changed (+3 to +4). For the trivalent compound this is not the case, thus the ligands themselves must be involved in the reduction process via the following redox reaction:
C5Me5− ----> e− + 1/2(C5Me5)2
But ligand induced reductions are not new and have been known to happen with a variety of lanthanide complexes. However, steric factors must also be considered on the reactivity of the Sm(III) complex as less crowded structures do not have any reductive activity. For years, it was thought that (C5Me5)3Sm was not a possible compound due to the huge strain of cone angles greater than 120 degrees. However, this compound is formed from the Sm(II) complex, and X-Ray structures of the Sm(II) complex have shown that there was enough room for a third spot. Also, X-ray structures of (C5Me5)3Sm show that the C5Me5s are 0.1 Angstrom
s further from the metal than normally predicted and expected. This increased distance, forced by sterics, makes the ligands have less electronic stability and may be a possible reason for the observed redox reaction of the ligands instead of the metal.[1]
Sm is a typical and well studied metal due to its unusual stability in a divalent and trivalent state. With the discovery of sterically induced reductions other lanthanide metals can now be studied in their more stable trivalent state, which can allow for more control of reduction reactions by tuning the reaction based on the metal size and electronics.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a sterically induced reduction happens when an oxidized metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
behaves and exhibits similar if not identical reducing properties as that of the more reduced form of the metal . This effect is mainly caused by the surrounding ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s that are complexed to the metal and it is the ligands that are involved in the reduction chemistry instead of the metal due to electronic destabilization by being significantly distanced from the metal. Sterically induced reductions commonly involve metals found in the lanthanoid and actinoid series.
Background
Divalents Lanthanides are extremely reducing (can reduce alkali cations) compounds. Of these divalent lanthanides, SmI2 is a common reducing agentReducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
that is used in a variety of synthetic applications, mainly because all other divalent lanthanides are unstable. Complexes of Sm
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3...
(II) have also been investigated and used in similar applications. However, even though Sm(II) complexes and compounds have had tremendous success when used in conjunction with a variety of substrates. There have been instances where chemistry of certain materials cannot be performed due to unclean reactions in which products are not easily isolated from reaction mixtures when Sm(II) compounds are used to perform the desired reduction. In these cases, adjusting the size of the metal (which is commonly and easily done for the trivalent lanthanide compounds) may fine tune the nature of a specific reaction, which should produce desired and clean products. One drawback to this notion is that Sm(II) is uniquely stable compared to other divalent lanthanides, where the other metals in the series tend to exist freely in the trivalent state. The discovery and application of sterically induced reductions allows the unique reducing properties and chemistry to be applicable to all of the lanthanide metals while remaining in their more stable trivalent state.
When Sm(III) is complexed with C5Me5 (pentamethylcyclopentadiene
Pentamethylcyclopentadiene
1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is a cyclic diolefin with the formula C5Me5H . 1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is the precursor to the ligand 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl, which is often denoted as Cp*...
) to give the compound (C5Me5)3Sm, this trivalent species has been shown to have the same reducing reactivity of the Sm(II) derivative.

Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
of the metal in the top reaction does not change, while the oxidation state changes in the bottom one. If the metal was involved in the reduction the oxidation states should have changed (+3 to +4). For the trivalent compound this is not the case, thus the ligands themselves must be involved in the reduction process via the following redox reaction:
C5Me5− ----> e− + 1/2(C5Me5)2
But ligand induced reductions are not new and have been known to happen with a variety of lanthanide complexes. However, steric factors must also be considered on the reactivity of the Sm(III) complex as less crowded structures do not have any reductive activity. For years, it was thought that (C5Me5)3Sm was not a possible compound due to the huge strain of cone angles greater than 120 degrees. However, this compound is formed from the Sm(II) complex, and X-Ray structures of the Sm(II) complex have shown that there was enough room for a third spot. Also, X-ray structures of (C5Me5)3Sm show that the C5Me5s are 0.1 Angstrom
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
s further from the metal than normally predicted and expected. This increased distance, forced by sterics, makes the ligands have less electronic stability and may be a possible reason for the observed redox reaction of the ligands instead of the metal.[1]
Sm is a typical and well studied metal due to its unusual stability in a divalent and trivalent state. With the discovery of sterically induced reductions other lanthanide metals can now be studied in their more stable trivalent state, which can allow for more control of reduction reactions by tuning the reaction based on the metal size and electronics.

