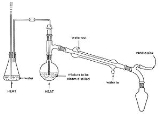
Steam distillation
Overview
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
(a separation process) for temperature sensitive materials like natural aromatic
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
compounds.
Many organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s tend to decompose
Chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction...
at high sustained temperatures. Separation by normal distillation would then not be an option, so water or steam
Steam
Steam is the technical term for water vapor, the gaseous phase of water, which is formed when water boils. In common language it is often used to refer to the visible mist of water droplets formed as this water vapor condenses in the presence of cooler air...
is introduced into the distillation apparatus. By adding water or steam, the boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
s of the compounds are depressed, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures, preferably below the temperatures at which the deterioration of the material becomes appreciable.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

