
State income tax
Encyclopedia
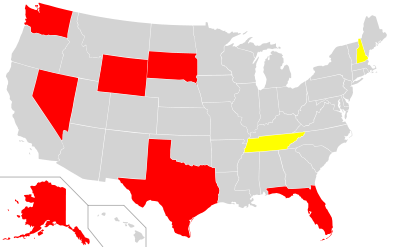
State and local income taxes are imposed in addition to Federal income tax. State income tax is allowed as a deduction in computing Federal income tax, subject to limitations for individuals. Some localities impose an income tax, often based on state income tax calculations. Forty-three states and many localities in the United States impose an income tax
Income tax
An income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate...
on individuals. Forty-seven states and many localities impose a tax on the income of corporations.
State income tax is imposed at a fixed or graduated rate on the taxable income of individuals, corporations, and certain estates and trusts. The rates vary by state. Taxable income
Taxable income
Taxable income refers to the base upon which an income tax system imposes tax. Generally, it includes some or all items of income and is reduced by expenses and other deductions. The amounts included as income, expenses, and other deductions vary by country or system. Many systems provide that...
conforms closely to Federal taxable income in most states, with limited modifications. The states are prohibited from taxing income from Federal bonds or other obligations. Most do not tax Social Security benefits or interest income from obligations of that state. Several states require different lives and methods be used by businesses in computing the deduction for depreciation
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used ....
. Many states allow a standard deduction
Standard deduction
The standard deduction, as defined under United States tax law, is a dollar amount that non-itemizers may subtract from their income and is based upon filing status. It is available to US citizens and resident aliens who are individuals, married persons, and heads of household and increases every...
or some form of itemized deductions. States allow a variety of tax credit
Tax credit
A tax credit is a sum deducted from the total amount a taxpayer owes to the state. A tax credit may be granted for various types of taxes, such as an income tax, property tax, or VAT. It may be granted in recognition of taxes already paid, as a subsidy, or to encourage investment or other behaviors...
s in computing tax.
Each state administers its own tax system. Many states also administer the tax return and collection process for localities within the state that impose income tax.
Basic principles
State tax rules vary widely. Those states imposing a tax on income compute the tax as a tax rate times taxable income as defined by the state. The tax rate may be fixed for all income levels and taxpayers of a certain type, or it may be graduated, that is, the tax rates on higher amounts of income are higher than on lower amounts. Tax rates may differ for individuals and corporations.Most states conform to Federal rules for determining:
- gross incomeGross incomeGross income in United States tax law is receipts and gains from all sources less cost of goods sold. Gross income is the starting point for determining Federal and state income tax of individuals, corporations, estates and trusts, whether resident or nonresident."Except as otherwise provided" by...
, - timing of recognition of income and deductionsTax deductionIncome tax systems generally allow a tax deduction, i.e., a reduction of the income subject to tax, for various items, especially expenses incurred to produce income. Often these deductions are subject to limitations or conditions...
, - most aspects of business deductions,
- characterization of business entities as either corporations, partnerships, or disregarded.
Gross income generally includes all income earned or received from whatever source, with exceptions. The states are prohibited from taxing income from Federal bonds or other obligations. Most states also exempt income from bonds issued by that state or localities within the state, as well as some portion or all of Social Security benefits. Many states provide tax exemption
Tax exemption
Various tax systems grant a tax exemption to certain organizations, persons, income, property or other items taxable under the system. Tax exemption may also refer to a personal allowance or specific monetary exemption which may be claimed by an individual to reduce taxable income under some...
for certain other types of income, which varies widely by state. The states imposing an income tax uniformly allow reduction of gross income for cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold refers to the inventory costs of those goods a business has sold during a particular period. Costs are associated with particular goods using one of several formulas, including specific identification, first-in first-out , or average cost...
, though the computation of this amount may be subject to some modifications.
Most states provide for modification of both business and non-business deductions. All states taxing business income allow deduction for most business expenses. Many require that depreciation
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used ....
deductions be computed in manners different than at least some of those permitted for Federal income tax purposes. For example, many states do not allow the additional first year depreciation deduction.
Most states tax capital gain
Capital gain
A capital gain is a profit that results from investments into a capital asset, such as stocks, bonds or real estate, which exceeds the purchase price. It is the difference between a higher selling price and a lower purchase price, resulting in a financial gain for the investor...
and dividend income in the same manner as other investment income. In this respect, individuals and corporations not resident in the state generally are not required to pay any income tax to that state with respect to such income.
Some states have alternative measures of tax. These include analogs to the Federal Alternative Minimum Tax
Alternative Minimum Tax
The Alternative Minimum Tax is an income tax imposed by the United States federal government on individuals, corporations, estates, and trusts. AMT is imposed at a nearly flat rate on an adjusted amount of taxable income above a certain threshold . This exemption is substantially higher than the...
in 14 states, as well as measures for corporations not based on income, such as capital stock taxes imposed by many states.
Income tax is self assessed, and individual and corporate taxpayers in all states imposing an income tax must file tax returns in each year their income exceeds certain amounts determined by each state. Returns are also required by partnerships doing business in the state. Many states require that a copy of the Federal income tax return be attached to at least some types of state income tax returns. The time for filing returns varies by state and type of return, but for individuals in many states is the same (typically April 15) as the Federal deadline .
Every state, including those with no income tax, has a state taxing authority with power to examine (audit) and adjust returns filed with it. Most tax authorities have appeals procedures for audits, and all states permit taxpayers to go to court in disputes with the tax authorities. Procedures and deadlines vary widely by state. All states have a statute of limitations
Statute of limitations
A statute of limitations is an enactment in a common law legal system that sets the maximum time after an event that legal proceedings based on that event may be initiated...
prohibiting the state from adjusting taxes beyond a certain period following filing returns.
All states have tax collection mechanisms. States with an income tax require employers to withhold state income tax on wages earned within the state. Some states have other withholding mechanisms, particularly with respect to partnerships. Most states require taxpayers to make quarterly payments of tax not expected to be satisfied by withholding tax
Withholding tax
Withholding tax, also called retention tax, is a government requirement for the payer of an item of income to withhold or deduct tax from the payment, and pay that tax to the government. In most jurisdictions, withholding tax applies to employment income. Many jurisdictions also require...
.
All states impose penalties for failing to file required tax returns and/or pay tax when due. In addition, all states impose interest charges on late payments of tax, and generally also on additional taxes due upon adjustment by the taxing authority.
Individual income tax
Forty-three states impose a tax on the income of individuals, sometimes referred to as personal income tax. Tax rates vary widely, with the highest marginal rate being 11% (assessed in Hawaii and Oregon on individual income above $200k and $250k, respectively). The income subject to tax varies by state. Some states impose the tax on Federal taxable income with minimal modifications, while others tax a measure bearing little resemblance to Federal taxable income.The states imposing an income tax on individuals tax all taxable income (as defined in the state) of residents. Such residents are allowed a credit for taxes paid to other states. Most states tax income of nonresidents earned within the state. Such income includes wages for services within the state as well as income from a business with operations in the state. Where income is from multiple sources, formulary apportionment may be required for nonresidents. Generally, wages are apportioned based on the ratio days worked in the state to total days worked.
All states that impose an individual income tax allow most business deductions. However, many states impose different limits on certain deductions, especially depreciation
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used ....
of business assets. Most of the states allow non-business deductions in a manner similar to Federal rules. Few allow a deduction for state income taxes, though some states allow a deduction for local income taxes. Eight of the states allow a full or partial deduction for Federal income tax.
In addition, some states allow cities and/or counties to impose income taxes. Most Ohio cities and towns impose an income tax on individuals and corporations. By contrast, in New York only New York City and Yonkers imposes a municipal income tax.
States without an individual income tax
- Alaska – no individual tax but has a state corporate income tax. Like New Hampshire, Alaska has no state sales tax. Alaska has annual Permanent Fund Dividend for all citizens living in Alaska after two years.
- Florida – no individual income tax but has a corporate income tax (at a 5% rate). The state once had a tax on "intangible personal property" held on the first day of the year (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, money market funds, etc.), but it was abolished at the start of 2007.
- Nevada – has no individual or corporate income tax. Nevada gets most of its revenue from gambling and sales taxes.
- New Hampshire – has an Interest and Dividends Tax of 5%, and a Business Profits Tax of 8.5%. A Gambling Winnings Tax of 10% went into effect July 1, 2009 and was repealed May 11, 2011. New Hampshire has no sales tax.
- South Dakota – no individual income tax but has a state corporate income tax on financial institutions.
- Tennessee has a 6% tax on income received from stocks and bondsHall income taxThe Hall income tax is a Tennessee state tax on interest and dividend income from investments. It is the only tax on personal income in Tennessee, which does not levy a general state income tax. The current tax rate is 6 percent, applied to all taxable interest and dividend income over $1250 per...
not taxed ad valorem. In 1932, the Tennessee Supreme CourtTennessee Supreme CourtThe Tennessee Supreme Court is the state supreme court of the state of Tennessee. Cornelia Clark is the current Chief Justice.Unlike other states, in which the state attorney general is directly elected or appointed by the governor or state legislature, the Tennessee Supreme Court appoints the...
struck down a broad-based individual income tax that had passed the General Assembly, in the case of Evans v. McCabe. However, a number of Attorneys General have recently opined that, if properly worded, a state income tax would be found constitutional by today's court, due to a 1971 constitutional amendment. - Texas – no individual income tax or corporate income tax. In May 2007, the legislature replaced the franchise tax with a gross margins tax on businesses (sole proprietorships and some partnerships were automatically exempt; corporations with receipts below a certain level were also exempt), which was amended in 2009 to increase the exemption level. The Texas ConstitutionTexas ConstitutionThe Constitution of the State of Texas is the document that describes the structure and function of the government of the U.S. State of Texas.Texas has had seven constitutions: the constitution of Coahuila y Tejas, the 1836 Constitution of the Republic of Texas, the state constitutions of 1845,...
places severe restrictions on passage of an individual income tax and use of its proceeds. - Washington – no individual tax but has a business and occupation taxBusiness and occupation taxThe business and occupation tax is a type of tax levied by the U.S. states of Washington and West Virginia, and by municipal governments in West Virginia...
(B&O) on gross receipts, applied to "almost all businesses located or doing business in Washington." It varies from 0.138% to 1.9% depending on the type of industry. - Wyoming has no individual or corporate income taxes.
U.S. States with a flat rate individual income tax
The following states have a flat rate individual income taxFlat tax
A flat tax is a tax system with a constant marginal tax rate. Typically the term flat tax is applied in the context of an individual or corporate income that will be taxed at one marginal rate...
:
- Colorado - 4.63%
- Illinois - 5.0% (fluctuating year-to-year from 3.0 to 5.0 then to 3.25 in 2025)
- Indiana - 3.4%
- Massachusetts - 5.3% (most types of income)
- Michigan - 4.35%
- Pennsylvania - 3.07%
- Utah - 5%
Corporate income tax
Most states impose a tax on income of corporations having sufficient connection ("nexus") with the state. Such taxes apply to U.S. and foreign corporations, and are not subject to tax treaties. Such tax is generally based on business income of the corporation apportioned to the state plus nonbusiness income only of resident corporations. Most state corporate income taxes are imposed at a flat rate and have a minimum amount of tax. Business taxable income in most states is defined, at least in part, by reference to Federal taxable income.According to www.taxfoundation.org these states have no state corporate income tax as of Feb 1, 2010:
Nevada, Washington, Wyoming, Texas, and South Dakota. However, Texas has a Franchise Tax based on "taxable margin", generally defined as sales less either cost of goods sold less compensation, with complete exemption (no tax owed) for less than $1MM in annual earnings and gradually increasing to a maximum tax of 1% based on net revenue, where net revenue can be calculated in the most advantageous of four different ways.
Nexus
States are not permitted to tax income of a corporation unless four tests are met under Complete Auto Transit, Inc. v. BradyComplete Auto Transit, Inc. v. Brady
Complete Auto Transit, Inc. v. Brady, 430 U.S. 274 , is a case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States regarding the Commerce Clause and sales tax.-Background:...
:
- There must be a substantial connection (nexus) between the taxpayer's activities and the state
- The tax must not discriminate against interstate commerce
- The tax must be fairly apportioned
- There must be a fair relationship to services provided
In general, nexus requirements vary by state and are subject to interpretation, generally by the state's comptroller or tax office, and often in administrative "letter rulings."
In Quill Corp. v. North Dakota
Quill Corp. v. North Dakota
Quill Corp. v. North Dakota, 504 U.S. 298 is a Supreme Court ruling concerning use tax. Quill Corporation is an office supply retailer...
, the Supreme Court of the United States
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all state and federal courts, and original jurisdiction over a small range of cases...
held that corporations must maintain a physical presence in the state (such as physical property, employees, officers) for a non-transient amount of time, and that such physical presence must be "substantial" for the state to be able to claim that the corporation was maintaining nexus and thus owed apportioned taxes. Quill Corp.'s only contact was in the form of a printed catalog and software disk. Quill prevailed as North Dakota was unable to prove that "substantial" nexus was created.
The state of Texas has held that intellectual property (a software license) owned by a Minnesota corporation with no physical presence in the state was sufficient to create nexus.
Amazon has sued New York State because of a recent NY law that requires Amazon to apportion income tax and charge/remit sales tax due to Amazon affiliates (independent agents) that may be located in the state.
Many critics believe that states facing budget crunches are often putting additional pressure on out-of-state corporations to pay taxes within that state.
Apportionment
The courts have held that the requirement for fair apportionment may be met by apportioning between jurisdictions all business income of a corporation based on a formula using the particular corporation's details. Many states use a three factor formula, averaging the ratios of property, payroll, and sales within the state to that overall. Some states weight the formula. Some states use a single factor formula based on sales.Nonbusiness income
Some states tax resident corporations on nonbusiness income regardless of apportionment. Generally, a resident corporation is one incorporated in that state. The definition of nonbusiness income varies but generally includes investment income of business corporations, including dividends.Consolidated or unitary filings
Some states require and some states permit parent/subsidiary controlled groups of corporations to file returns on a consolidated or combined basis. California and Illinois require that all U.S. members of a "unitary" group must file a combined return.Returns
State corporate income tax returns vary highly in complexity from two pages to more than 20 pages. States often require that a copy of the Federal income tax return be attached to the state return. Corporate income tax return due dates may differ from individual tax return due dates. Most states grant extensions of time to file corporate tax returns.History
Rhode Island did not have an income tax until 1971, but now it has one of the top five highest maximum rates in the nation.New Jersey added an income tax component to its corporation business tax in 1958.
Connecticut added a personal income tax in 1992, as the median family income in many of the state's suburbs was nearly twice that of families living in urban areas. Governor Lowel Weicker's administration imposed a personal income tax (designed to address the inequities of the sales tax system) and implemented a program to modify state funding formulas so that urban communities received a larger share.
See also
- Income tax in the United StatesIncome tax in the United StatesIn the United States, a tax is imposed on income by the Federal, most states, and many local governments. The income tax is determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income as defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and...
- State tax levelsState tax levelsState tax levels indicate both the tax burden and the services a state can afford to provide residents.States use a different combination of sales, income, excise taxes, and user fees, some imposed directly on residents and other imposed indirectly...
- Taxation in the United StatesTaxation in the United StatesThe United States is a federal republic with autonomous state and local governments. Taxes are imposed in the United States at each of these levels. These include taxes on income, property, sales, imports, payroll, estates and gifts, as well as various fees.Taxes are imposed on net income of...
- U.S. State Non-resident Withholding TaxU.S. State Non-resident Withholding TaxU.S. State Nonresident Withholding Tax is a mandatory prepayment of tax of individuals or entities that are not resident in the State. A common example of this is the taxation of oil and natural gas royalty interest revenue...
External links
- 'The Best and the Worst States for Taxes' - MSN Money
- State Individual Income Tax Rates - Federation of Tax Administrators
- Tax Links for All 50 States - AccountingMajors.com
- Individual State Income Tax Rates 2009 - Incomejunkie.com
- Individual income tax revenue by state Sourced from the US Census Bureau

