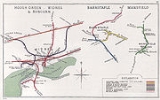
St Helens and Runcorn Gap Railway
Encyclopedia
St Helens and Runcorn Gap Railway, later known as St Helens Railway, was an early railway company in Lancashire
, England
, which opened in 1833. It ran originally from the town of St Helens
to the area which would later develop into the town of Widnes
. Branches were opened to Garston
, Warrington
and Rainford
. The company was taken over by the London and North Western Railway
in 1864. The line from St Helens to Widnes and the branch to Rainford are now closed, the latter terminating at the Pilkington Glass' Cowley Hill works siding near Gerard's Bridge, but part of the lines to Garston and to Warrington are still in operation.
in the 18th century there was a need for coal to be carried from the coalfields in the area of St Helens
to the River Mersey
for transportation to the growing industrial towns and cities. The first solution was to build the Sankey Canal
which opened in 1755 and ran from St Helens to Sankey Bridges
, to the west of Warrington
. It was extended to the west, to Fiddlers Ferry, five years later. Encouraged by the success of the Stockton and Darlington Railway
which opened in 1825, in 1829 a group of local businessmen arranged for a survey for a line from Cowley Hill Colliery, north of St Helens, to Runcorn Gap on the River Mersey. At this time the Liverpool and Manchester Railway
, which ran to the south of St Helens, was being built and its surveyor, Charles Blacker Vignoles
, was commissioned to undertake the survey; he was later appointed as the engineer. An Act of Parliament
was obtained on 29 May 1830. The original capital was £120,000, one-third of which was raised from local coal owners, salt-makers and Liverpool merchants. These included James Muspratt
, soap and alkali
manufacturer, and Peter Greenall, who had interests in the brewing, coal and glass manufacturing industries. Peter Greenall was elected as the first chairman of a board of ten directors. At the south end of the railway, Widnes Dock
was built, which led into the Mersey. This was the world's first rail-to-ship facility. Because of perceived competition from the railway, the Sankey Canal was extended from Fiddlers Ferry to Runcorn Gap by what was known as the "New Cut". The railway terminated between the dock and the end of the canal and Runcorn Gap station was sited to the north of the canal.
Work on the line proceeded slowly and its costs overran the estimate. It did not open until 1833 but in November 1832 a train with coal wagons ran over the track because of a wager between one of the owners and the engineer that a train would pass over it by December 1832. The line opened officially on 21 February 1833 but the dock was not completed until August 1833. The extension to the Sankey Canal opened on 24 July 1833. From Widnes Dock a single line crossed the extension to the canal by a swing bridge and then climbed steeply, so steeply that for a section trains had to be pulled by a stationary engine
. Haulage by a stationary engine was also necessary for a section further north at Sutton near St Helens. The Liverpool and Manchester line was crossed by an iron bridge south of St Helens. The line was originally intended for freight but public demand led to passenger coaches being added to the rear of the trains, this service starting in September 1833. There was intense competition between the railway and the canal leading to financial difficulties for both companies; the canal company had reduced its dividend
s from 33.3% to 5.5% and the railway company was paying no dividend. The companies agreed to a merger, with the railway company buying out the canal company to form the St Helens Canal and Railway Company (SHCR). Royal assent
for this was received on 21 July 1845. The company, which owned nine second-hand tank engines and had a staff of 122, was described as being "ramshackle". It set about to improve the situation, doubling the track and easing the gradients so that the whole line could be operated by steam locomotives.
The new company then set about planning branch lines and connections. There had been a plan to build northwards from St Helens towards Southport
to join the Southport and Euxton
branch at Rufford
. However this line was built only as far as Rainford
. Here it joined the Lancashire Union Railway at Gerards Bridge Junction. The company bought land at Garston
with the intention of building a dock and linking it with a line to Runcorn Gap. This opened as a single line on 1 July 1852, although the dock was not opened to shipping until 21 July 1853. On 21 May 1851 a sharp curve connection had been made on this line from the main line at what was to become known as Widnes Dock Junction. The following year a new Runcorn Gap station was opened nearer to the rapidly growing town of Widnes. The next project was to build a branch line to Warrington. This was opened on 1 February 1853, extending to a temporary station at White Cross, Warrington. In the following year it was extended to meet the Warrington and Stockport Railway. A station on this branch was opened at Cuerdley
but this closed in January 1858. The creation of these branch lines created an unusual feature on British railways, a flat crossing
. In the 1860s people could travel eastwards from Runcorn Gap to Warrington and, from there, to Manchester, London and many other places. They could also travel west to Liverpool by taking a ship at Garston.
By 1860 there was considerable competition between the railway companies. The London and North Western Railway
(LNWR) wanted to build a line between Edge Hill
and Garston. Following discussions, the LNWR leased the line from Garston to Warrington with effect from 1 September 1860, paying £5,000 for the first year and £12,000 annually from 1861. On 29 July 1864, an act was passed which allowed SHCR to be absorbed by LNWR, and the transfer took place on 31 July 1864. Runcorn Gap station was renamed Widnes station on 1 September 1864.
across the Mersey on Runcorn Railway Bridge
to Ditton Junction, west of Widnes, the Garston extension became part of the Liverpool-London main line. Following the merger of most of Britain's railways into four private companies in 1923, the line from St Helens to Widnes became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
(LMS). Large quantities of freight were carried on the line and the passenger train from St Helen's to Ditton Junction station
was nicknamed the Ditton Dodger.
Following the end of the Second World War
passenger traffic declined and the service provided by the Ditton Dodger ended on 16 June 1951. Freight traffic initially continued to be heavy but it declined during the 1960s. In 1969 the line north from Farnworth and Bold station was singled and in 1975 the line south of the station was also singled. The line closed to through traffic on 1 November 1981. The track has been lifted and some of the southern part of the route is occupied by Watkinson Way, a road providing an easterly bypass for Widnes and connecting the Silver Jubilee Bridge with the M62 motorway
. The base of the swing bridge which carried the railway over the canal is still present in Spike Island.
As of 2009, where the line runs near the St Helens Retail Park, the embankment has been reinforced and is said to be for a rail link for visitors from out of town to the new Saints RLFC stadium. It is also rumoured that the track on Robins Lane will be relaid to connect through to St Helens Junction.
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, which opened in 1833. It ran originally from the town of St Helens
St Helens, Merseyside
St Helens is a large town in Merseyside, England. It is the largest settlement and administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens with a population of just over 100,000, part of an urban area with a total population of 176,843 at the time of the 2001 Census...
to the area which would later develop into the town of Widnes
Widnes
Widnes is an industrial town within the borough of Halton, in Cheshire, England, with an urban area population of 57,663 in 2004. It is located on the northern bank of the River Mersey where the estuary narrows to form the Runcorn Gap. Directly to the south across the Mersey is the town of Runcorn...
. Branches were opened to Garston
Garston, Merseyside
Garston is a district of Liverpool, Merseyside, England. It is bordered by Aigburth, Allerton, and Speke.-History:Gaerstun, meaning 'grazing settlement' or 'grazing farm' in Old English, is one possible root of the name....
, Warrington
Warrington
Warrington is a town, borough and unitary authority area of Cheshire, England. It stands on the banks of the River Mersey, which is tidal to the west of the weir at Howley. It lies 16 miles east of Liverpool, 19 miles west of Manchester and 8 miles south of St Helens...
and Rainford
Rainford
Rainford is a village and civil parish within Metropolitan Borough of St Helens, in Merseyside, England. It is around north of St Helens. At the 2001 Census the population of the civil parish was 8,344....
. The company was taken over by the London and North Western Railway
London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. It was created by the merger of three companies – the Grand Junction Railway, the London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway...
in 1864. The line from St Helens to Widnes and the branch to Rainford are now closed, the latter terminating at the Pilkington Glass' Cowley Hill works siding near Gerard's Bridge, but part of the lines to Garston and to Warrington are still in operation.
Independent company
With the coming of the Industrial RevolutionIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
in the 18th century there was a need for coal to be carried from the coalfields in the area of St Helens
St Helens, Merseyside
St Helens is a large town in Merseyside, England. It is the largest settlement and administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens with a population of just over 100,000, part of an urban area with a total population of 176,843 at the time of the 2001 Census...
to the River Mersey
River Mersey
The River Mersey is a river in North West England. It is around long, stretching from Stockport, Greater Manchester, and ending at Liverpool Bay, Merseyside. For centuries, it formed part of the ancient county divide between Lancashire and Cheshire....
for transportation to the growing industrial towns and cities. The first solution was to build the Sankey Canal
Sankey Canal
The Sankey Canal, which is also known as the Sankey Brook Navigation and the St Helens Canal, is a canal in Cheshire, extending into Merseyside, in the northwest of England, connecting St Helens with the River Mersey...
which opened in 1755 and ran from St Helens to Sankey Bridges
Sankey Bridges
Sankey Bridges is part of the parish of great sankey in Warrington, a unitary authority in the north-west of England. Located around the crossing of the main turnpike road between Warrington, Prescot and Liverpool over the Sankey Brook, it became home to many industries after the opening of the...
, to the west of Warrington
Warrington
Warrington is a town, borough and unitary authority area of Cheshire, England. It stands on the banks of the River Mersey, which is tidal to the west of the weir at Howley. It lies 16 miles east of Liverpool, 19 miles west of Manchester and 8 miles south of St Helens...
. It was extended to the west, to Fiddlers Ferry, five years later. Encouraged by the success of the Stockton and Darlington Railway
Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway , which opened in 1825, was the world's first publicly subscribed passenger railway. It was 26 miles long, and was built in north-eastern England between Witton Park and Stockton-on-Tees via Darlington, and connected to several collieries near Shildon...
which opened in 1825, in 1829 a group of local businessmen arranged for a survey for a line from Cowley Hill Colliery, north of St Helens, to Runcorn Gap on the River Mersey. At this time the Liverpool and Manchester Railway
Liverpool and Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway was the world's first inter-city passenger railway in which all the trains were timetabled and were hauled for most of the distance solely by steam locomotives. The line opened on 15 September 1830 and ran between the cities of Liverpool and Manchester in North...
, which ran to the south of St Helens, was being built and its surveyor, Charles Blacker Vignoles
Charles Blacker Vignoles
Charles Blacker Vignoles was an influential early railway engineer, and eponym of the Vignoles rail.- Early life :...
, was commissioned to undertake the survey; he was later appointed as the engineer. An Act of Parliament
Act of Parliament
An Act of Parliament is a statute enacted as primary legislation by a national or sub-national parliament. In the Republic of Ireland the term Act of the Oireachtas is used, and in the United States the term Act of Congress is used.In Commonwealth countries, the term is used both in a narrow...
was obtained on 29 May 1830. The original capital was £120,000, one-third of which was raised from local coal owners, salt-makers and Liverpool merchants. These included James Muspratt
James Muspratt
James Muspratt was a British chemical manufacturer who was the first to make alkali by the Leblanc process on a large scale in the United Kingdom.-Early life:...
, soap and alkali
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Some authors also define an alkali as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English as a synonym for base,...
manufacturer, and Peter Greenall, who had interests in the brewing, coal and glass manufacturing industries. Peter Greenall was elected as the first chairman of a board of ten directors. At the south end of the railway, Widnes Dock
Widnes Dock
Widnes Dock was situated on the River Mersey at Widnes.It was built in 1833 between the end of the Sankey Canal and the St Helens and Runcorn Gap Railway. It was the first rail-to-ship facility in the world. The remains of the dock are to be found on Spike Island.-External links:*...
was built, which led into the Mersey. This was the world's first rail-to-ship facility. Because of perceived competition from the railway, the Sankey Canal was extended from Fiddlers Ferry to Runcorn Gap by what was known as the "New Cut". The railway terminated between the dock and the end of the canal and Runcorn Gap station was sited to the north of the canal.
Work on the line proceeded slowly and its costs overran the estimate. It did not open until 1833 but in November 1832 a train with coal wagons ran over the track because of a wager between one of the owners and the engineer that a train would pass over it by December 1832. The line opened officially on 21 February 1833 but the dock was not completed until August 1833. The extension to the Sankey Canal opened on 24 July 1833. From Widnes Dock a single line crossed the extension to the canal by a swing bridge and then climbed steeply, so steeply that for a section trains had to be pulled by a stationary engine
Stationary engine
A stationary engine is an engine whose framework does not move. It is normally used not to propel a vehicle but to drive a piece of immobile equipment such as a pump or power tool. They may be powered by steam; or oil-burning or internal combustion engines....
. Haulage by a stationary engine was also necessary for a section further north at Sutton near St Helens. The Liverpool and Manchester line was crossed by an iron bridge south of St Helens. The line was originally intended for freight but public demand led to passenger coaches being added to the rear of the trains, this service starting in September 1833. There was intense competition between the railway and the canal leading to financial difficulties for both companies; the canal company had reduced its dividend
Dividend
Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business , or it can be distributed to...
s from 33.3% to 5.5% and the railway company was paying no dividend. The companies agreed to a merger, with the railway company buying out the canal company to form the St Helens Canal and Railway Company (SHCR). Royal assent
Royal Assent
The granting of royal assent refers to the method by which any constitutional monarch formally approves and promulgates an act of his or her nation's parliament, thus making it a law...
for this was received on 21 July 1845. The company, which owned nine second-hand tank engines and had a staff of 122, was described as being "ramshackle". It set about to improve the situation, doubling the track and easing the gradients so that the whole line could be operated by steam locomotives.
The new company then set about planning branch lines and connections. There had been a plan to build northwards from St Helens towards Southport
Southport
Southport is a seaside town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in Merseyside, England. During the 2001 census Southport was recorded as having a population of 90,336, making it the eleventh most populous settlement in North West England...
to join the Southport and Euxton
Euxton
Euxton is a village and civil parish of the Borough of Chorley, in Lancashire, England. The village is pronounced "Exton") and is situated just to the south of Leyland, and to the west of Chorley.-Early Industry:...
branch at Rufford
Rufford, Lancashire
-Population :-Economy:The village is largely rural with little or no industry. The farmland is grade one agricultural land. In the early 20th century the village was described as "one of the prettiest in South Lancashire" and was a destination for day trips from neighbouring towns...
. However this line was built only as far as Rainford
Rainford
Rainford is a village and civil parish within Metropolitan Borough of St Helens, in Merseyside, England. It is around north of St Helens. At the 2001 Census the population of the civil parish was 8,344....
. Here it joined the Lancashire Union Railway at Gerards Bridge Junction. The company bought land at Garston
Garston, Merseyside
Garston is a district of Liverpool, Merseyside, England. It is bordered by Aigburth, Allerton, and Speke.-History:Gaerstun, meaning 'grazing settlement' or 'grazing farm' in Old English, is one possible root of the name....
with the intention of building a dock and linking it with a line to Runcorn Gap. This opened as a single line on 1 July 1852, although the dock was not opened to shipping until 21 July 1853. On 21 May 1851 a sharp curve connection had been made on this line from the main line at what was to become known as Widnes Dock Junction. The following year a new Runcorn Gap station was opened nearer to the rapidly growing town of Widnes. The next project was to build a branch line to Warrington. This was opened on 1 February 1853, extending to a temporary station at White Cross, Warrington. In the following year it was extended to meet the Warrington and Stockport Railway. A station on this branch was opened at Cuerdley
Cuerdley
Cuerdley is a civil parish in Warrington, Cheshire, England. It has a population of 107 and much of its area is farmland. A large part of Cuerdley is occupied by the Fiddlers Ferry Power Station....
but this closed in January 1858. The creation of these branch lines created an unusual feature on British railways, a flat crossing
Level junction
In U.S. railroad practice, a level junction is a railway junction that has a track configuration in which merging or crossing railroad lines provide track connections with each other that require trains to cross over in front of opposing traffic at grade In U.S. railroad practice, a level junction...
. In the 1860s people could travel eastwards from Runcorn Gap to Warrington and, from there, to Manchester, London and many other places. They could also travel west to Liverpool by taking a ship at Garston.
By 1860 there was considerable competition between the railway companies. The London and North Western Railway
London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. It was created by the merger of three companies – the Grand Junction Railway, the London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway...
(LNWR) wanted to build a line between Edge Hill
Edge Hill railway station
Edge Hill railway station serves the district of Edge Hill in Liverpool, England.There have been two stations of that name. The first stood a short distance south-west of the present station and its remains are still visible, although the site is not open to the public.Edge Hill is the first...
and Garston. Following discussions, the LNWR leased the line from Garston to Warrington with effect from 1 September 1860, paying £5,000 for the first year and £12,000 annually from 1861. On 29 July 1864, an act was passed which allowed SHCR to be absorbed by LNWR, and the transfer took place on 31 July 1864. Runcorn Gap station was renamed Widnes station on 1 September 1864.
Later developments
Widnes Dock Junction and the flat crossing were causing problems of congestion and the LNWR dealt with this by building a deviation line of just under 1.5 miles (2 km) to the north of the original west-east line, crossing the line leading north to St Helens by a bridge. The deviation line was authorised on 5 July 1865 and opened on 1 November 1869. The line was connected to the St Helens and it included a new station for passengers. With the opening of the line from Weaver JunctionWeaver Junction
Weaver Junction is a railway junction on the West Coast Main Line . It connects Ditton to the WCML via Runcorn Railway Bridge and opened on 1 April 1869. Trains bound for Liverpool from London diverge from the WCML at this junction. Weaver Junction is the oldest flying junction in Britain....
across the Mersey on Runcorn Railway Bridge
Runcorn Railway Bridge
The Runcorn Railway Bridge, which is also known as the Ethelfleda Bridge or the Britannia Bridge, crosses the River Mersey at Runcorn Gap from Runcorn to Widnes in Cheshire, England. It was built for the London and North Western Railway to a design by William Baker, chief engineer of the railway...
to Ditton Junction, west of Widnes, the Garston extension became part of the Liverpool-London main line. Following the merger of most of Britain's railways into four private companies in 1923, the line from St Helens to Widnes became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London Midland and Scottish Railway was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railway companies into just four...
(LMS). Large quantities of freight were carried on the line and the passenger train from St Helen's to Ditton Junction station
Ditton railway station
Ditton railway station, earlier known as Ditton Junction, was in the town of Widnes in Cheshire, England on Hale Road on the border between Ditton and Halebank...
was nicknamed the Ditton Dodger.
Following the end of the Second World War
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
passenger traffic declined and the service provided by the Ditton Dodger ended on 16 June 1951. Freight traffic initially continued to be heavy but it declined during the 1960s. In 1969 the line north from Farnworth and Bold station was singled and in 1975 the line south of the station was also singled. The line closed to through traffic on 1 November 1981. The track has been lifted and some of the southern part of the route is occupied by Watkinson Way, a road providing an easterly bypass for Widnes and connecting the Silver Jubilee Bridge with the M62 motorway
M62 motorway
The M62 motorway is a west–east trans-Pennine motorway in Northern England, connecting the cities of Liverpool and Hull via Manchester and Leeds. The road also forms part of the unsigned Euroroutes E20 and E22...
. The base of the swing bridge which carried the railway over the canal is still present in Spike Island.
As of 2009, where the line runs near the St Helens Retail Park, the embankment has been reinforced and is said to be for a rail link for visitors from out of town to the new Saints RLFC stadium. It is also rumoured that the track on Robins Lane will be relaid to connect through to St Helens Junction.
Locomotives
This is not a complete list:- No.11 Tyne, 0-6-0, became LNWR no.1377, sold to Benjamin Piercy (contractor) in 1865, became no.3 Chancellor on the Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay RailwayWrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay RailwayThe Wrexham, Mold and Connah's Quay Railway was incorporated on 7 August 1862 to build a line from Wrexham to Buckley.-Overview:The Buckley Railway had already been incorporated on 14 June 1860 to build a line from that town to a junction with the London and North Western Railway Chester-Holyhead...
in 1866, scrapped about 1874 - Name/number unknown, 0-6-0, sold to the Bishops Castle RailwayBishops Castle RailwayThe Bishops Castle Railway was begun in 1861, planned as a line from Craven Arms to Montgomery, thus linking the Shrewsbury to Hereford line to the Oswestry to Newtown, Powys line , linking Mid-Wales and Shrewsbury, with a branch line from Lydham to Bishop's Castle.From the start, the railway was...
which named it Plowden - Novelty (locomotive)Novelty (locomotive)Novelty was an early steam locomotive built by John Ericsson and John Braithwaite to take part in the Rainhill Trials in 1829.It was an 0-2-2WT locomotive and is now regarded as the very first tank engine. It had a unique design of boiler and a number of other novel design features...
, arrived on the line after its failure in the Rainhill TrialsRainhill TrialsThe Rainhill Trials were an important competition in the early days of steam locomotive railways, run in October 1829 in Rainhill, Lancashire for the nearly completed Liverpool and Manchester Railway....
.

