
Spin transition
Encyclopedia
The spin transition is an example of transition between two electronic state
s in molecular chemistry. The ability of an electron
to transit from a stable to another stable (or metastable
) electronic state in a reversible and detectable fashion, makes these molecular systems appealing in the field of molecular electronics
.
ion of configuration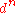 ,
,  to
to 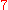 , is in octahedral surroundings, its ground state
, is in octahedral surroundings, its ground state
may be low spin (LS) or high spin (HS), depending to a first approximation on the magnitude of the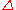 energy gap between
energy gap between 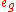 and
and 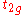 metal orbitals relative to the mean
metal orbitals relative to the mean
spin pairing energy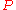 (see Crystal field theory
(see Crystal field theory
). More precisely, for , the ground state arises from the configuration where the
, the ground state arises from the configuration where the 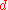 electrons occupy first the
electrons occupy first the 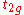 orbitals of lower energy, and if there are more than six electrons, the
orbitals of lower energy, and if there are more than six electrons, the 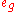 orbitals of higher energy. The ground state is then LS. On the other hand, for
orbitals of higher energy. The ground state is then LS. On the other hand, for 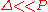 , Hund's rule is obeyed. The HS ground state has got the same multiplicity
, Hund's rule is obeyed. The HS ground state has got the same multiplicity
as the free metal ion. If the values of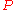 and
and 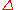 are comparable, a LS↔HS transition may occur.
are comparable, a LS↔HS transition may occur.
Between all the possible 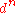 configurations of the metal ion,
configurations of the metal ion, 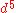 and
and 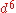 are by far the most important. The spin transition phenomenon, in fact, was first observed in 1930 for tris (dithiocarbamato) iron(III) compounds. On the other hand, the iron(II) spin transition complexes were the most extensively studied: among these two of them may be considered as archetypes of spin transition systems, namely Fe(NCS)2(bipy)2 and Fe(NCS)2(phen)2 (bipy = 2,2'-bypiridine and phen = 1,10-phenanthroline).
are by far the most important. The spin transition phenomenon, in fact, was first observed in 1930 for tris (dithiocarbamato) iron(III) compounds. On the other hand, the iron(II) spin transition complexes were the most extensively studied: among these two of them may be considered as archetypes of spin transition systems, namely Fe(NCS)2(bipy)2 and Fe(NCS)2(phen)2 (bipy = 2,2'-bypiridine and phen = 1,10-phenanthroline).
with spin flip of the transferred electrons. For an iron(II) compound this transfer involves two electrons and the spin variations is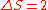 . The occupancy of the
. The occupancy of the 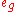 orbitals is higher in the HS state than in the LS state and these orbitals are more antibonding than the
orbitals is higher in the HS state than in the LS state and these orbitals are more antibonding than the 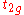 . It follows that the average metal-ligand
. It follows that the average metal-ligand
bond length is longer in the HS state than in the LS state. This difference is in the range 1.4–2.4 nm for iron(II) compounds.
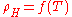 , where
, where 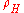 is the molar fraction of molecules in high-spin state. Several techniques are currently used to obtain such curves. The simplest method consists of measuring the temperature dependence of molar susceptibility. Any other technique that provides different responses according to whether the state is LS or HS may also be used to determine
is the molar fraction of molecules in high-spin state. Several techniques are currently used to obtain such curves. The simplest method consists of measuring the temperature dependence of molar susceptibility. Any other technique that provides different responses according to whether the state is LS or HS may also be used to determine 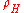 . Among these techniques, Mössbauer spectroscopy has been particularly useful in the case of iron compounds, showing two well resolved quadrupole doublets. One of these is associated with LS molecules, the other with HS molecules: the high-spin molar fraction then may be deduced from the relative intensities of the doublets.
. Among these techniques, Mössbauer spectroscopy has been particularly useful in the case of iron compounds, showing two well resolved quadrupole doublets. One of these is associated with LS molecules, the other with HS molecules: the high-spin molar fraction then may be deduced from the relative intensities of the doublets.
s range, or smooth, occurring within a large temperature range. It could also be incomplete both at low temperature and at high temperature, even if the latter is more often observed. Moreover, the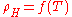 curves may be strictly identical in the cooling or heating modes, or exhibit a hysteresis
curves may be strictly identical in the cooling or heating modes, or exhibit a hysteresis
: in this case the system could assume two different electronic states in a certain range of temperature. Finally the transition may occur in two steps.
Electronic state
Electronic state is a quantum state of a system consisting of electrons . The state with lowest energy is called ground state, states with higher energy are excited states.See Energy level....
s in molecular chemistry. The ability of an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
to transit from a stable to another stable (or metastable
Metastability
Metastability describes the extended duration of certain equilibria acquired by complex systems when leaving their most stable state after an external action....
) electronic state in a reversible and detectable fashion, makes these molecular systems appealing in the field of molecular electronics
Molecular electronics
Molecular electronics, sometimes called moletronics, involves the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components...
.
In octahedral surroundings
When a transition metalTransition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
ion of configuration
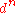 ,
,  to
to 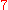 , is in octahedral surroundings, its ground state
, is in octahedral surroundings, its ground stateGround state
The ground state of a quantum mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state...
may be low spin (LS) or high spin (HS), depending to a first approximation on the magnitude of the
 energy gap between
energy gap between 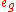 and
and 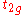 metal orbitals relative to the mean
metal orbitals relative to the meanMean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
spin pairing energy
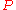 (see Crystal field theory
(see Crystal field theoryCrystal field theory
Crystal field theory is a model that describes the electronic structure of transition metal compounds, all of which can be considered coordination complexes. CFT successfully accounts for some magnetic properties, colours, hydration enthalpies, and spinel structures of transition metal complexes,...
). More precisely, for
 , the ground state arises from the configuration where the
, the ground state arises from the configuration where the 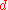 electrons occupy first the
electrons occupy first the 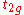 orbitals of lower energy, and if there are more than six electrons, the
orbitals of lower energy, and if there are more than six electrons, the 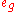 orbitals of higher energy. The ground state is then LS. On the other hand, for
orbitals of higher energy. The ground state is then LS. On the other hand, for  , Hund's rule is obeyed. The HS ground state has got the same multiplicity
, Hund's rule is obeyed. The HS ground state has got the same multiplicityMultiplicity (chemistry)
Multiplicity in quantum chemistry is used to distinguish between several degenerate wavefunctions that differ only in the orientation of their angular spin momenta. It is defined as 2S+1, where S is the angular spin momentum....
as the free metal ion. If the values of
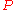 and
and  are comparable, a LS↔HS transition may occur.
are comparable, a LS↔HS transition may occur.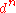 configurations
configurations
Between all the possible 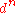 configurations of the metal ion,
configurations of the metal ion, 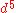 and
and 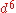 are by far the most important. The spin transition phenomenon, in fact, was first observed in 1930 for tris (dithiocarbamato) iron(III) compounds. On the other hand, the iron(II) spin transition complexes were the most extensively studied: among these two of them may be considered as archetypes of spin transition systems, namely Fe(NCS)2(bipy)2 and Fe(NCS)2(phen)2 (bipy = 2,2'-bypiridine and phen = 1,10-phenanthroline).
are by far the most important. The spin transition phenomenon, in fact, was first observed in 1930 for tris (dithiocarbamato) iron(III) compounds. On the other hand, the iron(II) spin transition complexes were the most extensively studied: among these two of them may be considered as archetypes of spin transition systems, namely Fe(NCS)2(bipy)2 and Fe(NCS)2(phen)2 (bipy = 2,2'-bypiridine and phen = 1,10-phenanthroline).Iron(II) complexes
We discuss the mechanism of the spin transition by focusing on the specific case of iron(II) complexes. At the molecular scale the spin transition corresponds to an interionic electron transferElectron transfer
Electron transfer is the process by which an electron moves from an atom or a chemical species to another atom or chemical species...
with spin flip of the transferred electrons. For an iron(II) compound this transfer involves two electrons and the spin variations is
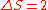 . The occupancy of the
. The occupancy of the 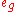 orbitals is higher in the HS state than in the LS state and these orbitals are more antibonding than the
orbitals is higher in the HS state than in the LS state and these orbitals are more antibonding than the 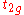 . It follows that the average metal-ligand
. It follows that the average metal-ligandLigand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
bond length is longer in the HS state than in the LS state. This difference is in the range 1.4–2.4 nm for iron(II) compounds.
To induce a spin transition
The most common way to induce a spin transition is to change the temperature of the system: the transition will be then characterized by a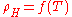 , where
, where 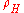 is the molar fraction of molecules in high-spin state. Several techniques are currently used to obtain such curves. The simplest method consists of measuring the temperature dependence of molar susceptibility. Any other technique that provides different responses according to whether the state is LS or HS may also be used to determine
is the molar fraction of molecules in high-spin state. Several techniques are currently used to obtain such curves. The simplest method consists of measuring the temperature dependence of molar susceptibility. Any other technique that provides different responses according to whether the state is LS or HS may also be used to determine 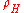 . Among these techniques, Mössbauer spectroscopy has been particularly useful in the case of iron compounds, showing two well resolved quadrupole doublets. One of these is associated with LS molecules, the other with HS molecules: the high-spin molar fraction then may be deduced from the relative intensities of the doublets.
. Among these techniques, Mössbauer spectroscopy has been particularly useful in the case of iron compounds, showing two well resolved quadrupole doublets. One of these is associated with LS molecules, the other with HS molecules: the high-spin molar fraction then may be deduced from the relative intensities of the doublets.Types of transition
Various types of transition have been observed. This may be abrupt, occurring within a few kelvinKelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s range, or smooth, occurring within a large temperature range. It could also be incomplete both at low temperature and at high temperature, even if the latter is more often observed. Moreover, the
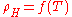 curves may be strictly identical in the cooling or heating modes, or exhibit a hysteresis
curves may be strictly identical in the cooling or heating modes, or exhibit a hysteresisHysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
: in this case the system could assume two different electronic states in a certain range of temperature. Finally the transition may occur in two steps.

