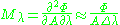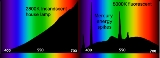
Spectral power distribution
Encyclopedia
In color science and radiometry
, a spectral power distribution (SPD) describes the power
per unit area
per unit wavelength
of an illumination
(radiant exitance), or more generally, the per-wavelength contribution to any radiometric quantity (radiant energy
, radiant flux
, radiant intensity
, radiance
, irradiance
, radiant exitance, or radiosity
).
Mathematically, for the spectral power distribution of a radiant exitance or irradiance one may write:
where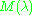 is the spectral irradiance (or exitance) of the light (SI
is the spectral irradiance (or exitance) of the light (SI
units: W
/m3 = kg
/(m·s
3)); is the radiant flux of the source (SI unit: watt, W);
is the radiant flux of the source (SI unit: watt, W); 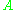 is the area over which the radiant flux is integrated (SI unit: square meter, m2); and
is the area over which the radiant flux is integrated (SI unit: square meter, m2); and 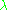 is the wavelength (SI unit: meter, m). (Note that it is more convenient to express the wavelength of light in terms of nanometers; spectral exitance would then be expressed in units of W·m−2·nm−1.) The approximation is valid when the area and wavelength interval are small.
is the wavelength (SI unit: meter, m). (Note that it is more convenient to express the wavelength of light in terms of nanometers; spectral exitance would then be expressed in units of W·m−2·nm−1.) The approximation is valid when the area and wavelength interval are small.
of lighting fixtures and other light sources are handled separately, a spectral power distribution may be normalized in some manner, often to unity at 555 or 560 nanometers, coinciding with the peak of the eye's luminosity function
.
Radiometry
In optics, radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which characterize the light's interaction with the human eye...
, a spectral power distribution (SPD) describes the power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
per unit area
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
per unit wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of an illumination
Illumination
Illumination, an observable property and effect of light, may also refer to:* Illumination , the use of light sources* Illumination , the use of light and shadow in art...
(radiant exitance), or more generally, the per-wavelength contribution to any radiometric quantity (radiant energy
Radiant energy
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux with respect to time and, like all forms of energy, its SI unit is the joule. The term is used particularly when radiation is emitted by a source into the...
, radiant flux
Radiant flux
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the measure of the total power of electromagnetic radiation...
, radiant intensity
Radiant intensity
In radiometry, radiant intensity is a measure of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation. It is defined as power per unit solid angle. The SI unit of radiant intensity is watts per steradian . Radiant intensity is distinct from irradiance and radiant exitance, which are often called intensity...
, radiance
Radiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
, irradiance
Irradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter , while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter...
, radiant exitance, or radiosity
Radiosity
Radiosity is a global illumination algorithm used in 3D computer graphics rendering. Radiosity is an application of the finite element method to solving the rendering equation for scenes with purely diffuse surfaces...
).
Mathematically, for the spectral power distribution of a radiant exitance or irradiance one may write:
where
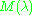 is the spectral irradiance (or exitance) of the light (SI
is the spectral irradiance (or exitance) of the light (SISi
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units: W
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
/m3 = kg
Kilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
/(m·s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
3));
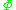 is the radiant flux of the source (SI unit: watt, W);
is the radiant flux of the source (SI unit: watt, W); 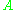 is the area over which the radiant flux is integrated (SI unit: square meter, m2); and
is the area over which the radiant flux is integrated (SI unit: square meter, m2); and 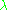 is the wavelength (SI unit: meter, m). (Note that it is more convenient to express the wavelength of light in terms of nanometers; spectral exitance would then be expressed in units of W·m−2·nm−1.) The approximation is valid when the area and wavelength interval are small.
is the wavelength (SI unit: meter, m). (Note that it is more convenient to express the wavelength of light in terms of nanometers; spectral exitance would then be expressed in units of W·m−2·nm−1.) The approximation is valid when the area and wavelength interval are small.Relative SPD
Because the luminanceLuminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
of lighting fixtures and other light sources are handled separately, a spectral power distribution may be normalized in some manner, often to unity at 555 or 560 nanometers, coinciding with the peak of the eye's luminosity function
Luminosity function
The luminosity function or luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. It should not be considered perfectly accurate in every case, but it is a very good representation of visual sensitivity of the human eye and it is...
.
External links
- Spectral Power Distribution Curves, GE Lighting.