Specialist school
Encyclopedia
The specialist schools programme was a UK government initiative which encouraged secondary school
s in England
to specialise in certain areas of the curriculum to boost achievement. The Specialist Schools and Academies Trust
was responsible for the delivery of the programme. Currently there are nearly 3,000 specialist schools, or 88% of the state-funded secondary schools in England
.
When the new Coalition government took power in May 2010 the scheme was ended and funding was absorbed into general school budgets.
 The Education Reform Act 1988
The Education Reform Act 1988
introduced a new compulsory subject of Technology, but there were insufficient funds to equip all schools to teach the subject.
A first attempt at developing centres of excellence, the City Technology College
programme between 1988 and 1993, had produced only 15 schools.
In 1994, the Conservative
government, at the urging of Sir Cyril Taylor, designated 35 grant-maintained
and voluntary aided school
s as Technology College
s.
The schools were required to arrange private sponsorship of £100,000, and would then receive a matching government capital grant and increased recurrent funding.
The following year the programme was opened to all maintained schools, and specialism in Language
s was added.
Specialisms in Arts
and Sport
were added in 1996.
As specialism implied diversity of schools, it was opposed by many supporters of comprehensive school
s, including many in the Labour Party
.
Nevertheless, in 1997 the new Labour government, also encouraged by Sir Cyril Taylor, adopted the embryonic programme, and the number of specialist schools continued to grow.
The School Standards and Framework Act 1998
made it possible for specialist schools to select up to 10% of their intake on aptitude in the existing specialisms in sport, the arts, modern languages and technology, though new selection for aptitude in technology was prohibited in 2008.
However few have taken up this option.
The 2001 white paper
Schools Achieving Success envisaged expansion of the programme to 50% of secondary schools by 2005, and introduced new specialisms in Business and Enterprise
, Engineering
, Mathematics and Computing
and Science
.
The emphasis was shifting from centres of excellence to a means of driving up standards in most schools.
The required amount of private sponsorship was halved, and could be made up of goods and services in lieu of cash.
Software donations had been ineligible due to the difficulty in evaluating the true value of something that has no manufacturing cost and can simply be given away as a form of collateral, but this changed when Oracle
and then Microsoft
were allowed to sponsor the programme with "in kind" donations.
In 2002 the government introduced the Partnership Fund, funded at £3million per annum, to make up the shortfall for schools that were unable to raise the required £50,000 of private sponsorship.
Specialisms in Humanities
and Music
were added in 2004.
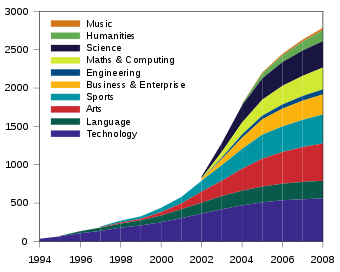
By 2008 approximately 90% of maintained secondary schools had become specialist schools.
Extension of the specialist programme to primary schools is being trialled at 34 schools in England, starting in 2007.
The specialisms involved in the pilot are Arts, Music, Languages, Science and Physical Education/Sport.
A specialist schools programme has been trialled by the Department of Education
of Northern Ireland
from 2006, with 44 schools being awarded the status by September 2009.
Private sector
sponsorship includes charitable trusts, internal fund raising and donations from private companies. In some cases donations can be made in cash from entities in the private sector such as Arcadia
and HSBC
, but may also be donations "in kind" of goods or services. The total sponsorship to date is of the order of £100m.
A school may specialise in any of the following fields, or combine specialisms in two of them (at the same level of funding):
Specialist schools must still meet the full requirements of the English national curriculum, so the specialism is seen as adding value to the existing statutory provision rather than being a radical departure from it. The important aspect in the eyes of the government is the focus that the specialism provides for providing leadership in the quest for whole school improvement.
The reward for achieving specialist status is a government grant of £100,000 to go with the £50,000 in sponsorship for a capital project related to the specialism and an extra £129 per pupil per year for four years to support the development plan. This is normally targeted on additional staffing and professional development, though up to 30% may be spent on equipment.
Schools that make a good attempt at achieving their targets over the 4 year development plan period normally have their grants renewed at 3-year intervals with no further need to raise sponsorship. However since 2008, the government has sought to encourage long-term relationships with business partners by offering a matching grant to redesignating specialist schools that are able to raise a further £25,000 in private sponsorship.
By 2009 some 900 schools (30% of specialist schools) had achieved this status.
has published a series of annual studies of the results of the specialist schools program, on behalf of the SSAT.
These studies report that non-selective specialist schools scored achieve significantly higher results at GCSE results than non-specialist comprehensive school
s, that they achieve higher added value when prior achievement is taken into account, and that the gains increase with the length of time the school has been specialist.
Jesson's statistical methodology has been criticised, and others have pointed out that early specialist schools were chosen for the programme because they were already successful.
Other studies have found that specialist schools perform slightly better at GCSE, particularly benefitting more able pupils and narrowing the gap between boys and girls.
The most recent studies attribute this increase to the additional funding, and report that the effect is diminishing as a greater proportion of schools become specialist.
(Education Secretary 2001–2002), as part of a drive to improve standards by increasing diversity in secondary schools.
Left wing commentators have criticised this move away from the comprehensive ideal.
The two biggest UK teaching unions have opposed the programme because they say that it creates a two-tier education system, made up of specialist schools with extra funding and non-specialist schools which cannot benefit from any extra money.
There is also evidence that specialist schools take fewer children from poorer families than non-specialist schools..
One possible cause is that it may be easier for middle-class parents to raise the necessary sponsorship.
Secondary school
Secondary school is a term used to describe an educational institution where the final stage of schooling, known as secondary education and usually compulsory up to a specified age, takes place...
s in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
to specialise in certain areas of the curriculum to boost achievement. The Specialist Schools and Academies Trust
Specialist Schools and Academies Trust
The Specialist Schools and Academies Trust is an independent, not-for-profit, membership organisation with headquarters in the United Kingdom, dedicated to raising standards and achievement in secondary schools in England and internationally...
was responsible for the delivery of the programme. Currently there are nearly 3,000 specialist schools, or 88% of the state-funded secondary schools in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
.
When the new Coalition government took power in May 2010 the scheme was ended and funding was absorbed into general school budgets.
History

Education Reform Act 1988
The Education Reform Act 1988 is widely regarded as the most important single piece of education legislation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland since the 'Butler' Education Act 1944...
introduced a new compulsory subject of Technology, but there were insufficient funds to equip all schools to teach the subject.
A first attempt at developing centres of excellence, the City Technology College
City Technology College
In England, a City Technology College is a state-funded all-ability secondary school that charges no fees but is independent of local authority control, being overseen directly by the Department for Education....
programme between 1988 and 1993, had produced only 15 schools.
In 1994, the Conservative
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, formally the Conservative and Unionist Party, is a centre-right political party in the United Kingdom that adheres to the philosophies of conservatism and British unionism. It is the largest political party in the UK, and is currently the largest single party in the House...
government, at the urging of Sir Cyril Taylor, designated 35 grant-maintained
Grant-maintained school
Grant-maintained schools were state schools in England and Wales between 1988 and 1998 that had opted out of local government control, being funded directly by a grant from central government...
and voluntary aided school
Voluntary aided school
A voluntary aided school is a state-funded school in England and Wales in which a foundation or trust owns the school buildings, contributes to building costs and has a substantial influence in the running of the school...
s as Technology College
Technology College
Technology College is a term used in the United Kingdom for a secondary specialist school that focuses on design and technology, mathematics and science. These were the first type of specialist schools, beginning in 1994. In 2008 there were 598 Technology Colleges in England, of which 12 also...
s.
The schools were required to arrange private sponsorship of £100,000, and would then receive a matching government capital grant and increased recurrent funding.
The following year the programme was opened to all maintained schools, and specialism in Language
Language College
Language Colleges were introduced in 1995 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, modern foreign languages...
s was added.
Specialisms in Arts
Arts College
Arts Colleges were introduced in 1997 as part of the now defunct Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enabled secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, the performing, visual and/or media arts...
and Sport
Sports College
Sports Colleges were introduced in 1997 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, PE, sports and dance. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Sports...
were added in 1996.
As specialism implied diversity of schools, it was opposed by many supporters of comprehensive school
Comprehensive school
A comprehensive school is a state school that does not select its intake on the basis of academic achievement or aptitude. This is in contrast to the selective school system, where admission is restricted on the basis of a selection criteria. The term is commonly used in relation to the United...
s, including many in the Labour Party
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a centre-left democratic socialist party in the United Kingdom. It surpassed the Liberal Party in general elections during the early 1920s, forming minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in 1924 and 1929-1931. The party was in a wartime coalition from 1940 to 1945, after...
.
Nevertheless, in 1997 the new Labour government, also encouraged by Sir Cyril Taylor, adopted the embryonic programme, and the number of specialist schools continued to grow.
The School Standards and Framework Act 1998
School Standards and Framework Act 1998
The School Standards and Framework Act 1998 was the major education legislation passed by the incoming Labour government of Tony Blair.This Act:* imposed a limit of 30 on infant class sizes....
made it possible for specialist schools to select up to 10% of their intake on aptitude in the existing specialisms in sport, the arts, modern languages and technology, though new selection for aptitude in technology was prohibited in 2008.
However few have taken up this option.
The 2001 white paper
White paper
A white paper is an authoritative report or guide that helps solve a problem. White papers are used to educate readers and help people make decisions, and are often requested and used in politics, policy, business, and technical fields. In commercial use, the term has also come to refer to...
Schools Achieving Success envisaged expansion of the programme to 50% of secondary schools by 2005, and introduced new specialisms in Business and Enterprise
Business and Enterprise College
Business and Enterprise Colleges were introduced in 2002 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields...
, Engineering
Engineering college
Engineering colleges generally refer to institutes of higher education which offer an engineering course at degree level. The duration of the course is four to five years depending upon the university to which the college is affiliated. The students learn little of basic science concentrating...
, Mathematics and Computing
Mathematics and Computing College
Mathematics and Computing Colleges were introduced in England in 2002 as part of the Government's Specialist Schools Programme which was designed to raise standards in secondary education. Specialist schools focus specifically on their chosen specialism but must also meet the requirements of the...
and Science
Science College
Science Colleges were introduced in 2002 as part of the now defunct Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enabled secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, science and mathematics...
.
The emphasis was shifting from centres of excellence to a means of driving up standards in most schools.
The required amount of private sponsorship was halved, and could be made up of goods and services in lieu of cash.
Software donations had been ineligible due to the difficulty in evaluating the true value of something that has no manufacturing cost and can simply be given away as a form of collateral, but this changed when Oracle
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation that specializes in developing and marketing hardware systems and enterprise software products – particularly database management systems...
and then Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
were allowed to sponsor the programme with "in kind" donations.
In 2002 the government introduced the Partnership Fund, funded at £3million per annum, to make up the shortfall for schools that were unable to raise the required £50,000 of private sponsorship.
Specialisms in Humanities
Humanities College
Humanities Colleges were introduced in 2004 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, humanities. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Humanities...
and Music
Music College
Music Colleges were introduced in 2004 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in England. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, music. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Music Colleges will receive extra...
were added in 2004.
By 2008 approximately 90% of maintained secondary schools had become specialist schools.
Extension of the specialist programme to primary schools is being trialled at 34 schools in England, starting in 2007.
The specialisms involved in the pilot are Arts, Music, Languages, Science and Physical Education/Sport.
A specialist schools programme has been trialled by the Department of Education
Department of Education (Northern Ireland)
The Department of Education is a devolved Northern Ireland government department in the Northern Ireland Executive...
of Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
from 2006, with 44 schools being awarded the status by September 2009.
Gaining specialist school status
To apply for specialist school status, a school must demonstrate reasonable standards of achievement, and produce a four-year development plan with quantified targets related to learning outcomes. The school must also raise £50,000 in private sector sponsorship.Private sector
Private sector
In economics, the private sector is that part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is run by private individuals or groups, usually as a means of enterprise for profit, and is not controlled by the state...
sponsorship includes charitable trusts, internal fund raising and donations from private companies. In some cases donations can be made in cash from entities in the private sector such as Arcadia
Arcadia Group
The Arcadia Group Limited a British company that owns the high street clothing retailers Burton, Dorothy Perkins, Evans, Miss Selfridge, Topman, Topshop, Wallis and BHS, and the out of town chain Outfit, which sells lines from the other group chains...
and HSBC
HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a global banking and financial services company headquartered in Canary Wharf, London, United Kingdom. it is the world's second-largest banking and financial services group and second-largest public company according to a composite measure by Forbes magazine...
, but may also be donations "in kind" of goods or services. The total sponsorship to date is of the order of £100m.
A school may specialise in any of the following fields, or combine specialisms in two of them (at the same level of funding):
- ArtsArts CollegeArts Colleges were introduced in 1997 as part of the now defunct Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enabled secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, the performing, visual and/or media arts...
(can be Media, Performing Arts, Visual Arts, or combination of these) - Business & EnterpriseBusiness and Enterprise CollegeBusiness and Enterprise Colleges were introduced in 2002 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields...
- EngineeringEngineering collegeEngineering colleges generally refer to institutes of higher education which offer an engineering course at degree level. The duration of the course is four to five years depending upon the university to which the college is affiliated. The students learn little of basic science concentrating...
- HumanitiesHumanities CollegeHumanities Colleges were introduced in 2004 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, humanities. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Humanities...
- LanguagesLanguage CollegeLanguage Colleges were introduced in 1995 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, modern foreign languages...
- Mathematics & ComputingMathematics and Computing CollegeMathematics and Computing Colleges were introduced in England in 2002 as part of the Government's Specialist Schools Programme which was designed to raise standards in secondary education. Specialist schools focus specifically on their chosen specialism but must also meet the requirements of the...
- MusicMusic CollegeMusic Colleges were introduced in 2004 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in England. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, music. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Music Colleges will receive extra...
- ScienceScience CollegeScience Colleges were introduced in 2002 as part of the now defunct Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enabled secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, science and mathematics...
- SportsSports CollegeSports Colleges were introduced in 1997 as part of the Specialist Schools Programme in the United Kingdom. The system enables secondary schools to specialise in certain fields, in this case, PE, sports and dance. Schools that successfully apply to the Specialist Schools Trust and become Sports...
- TechnologyTechnology CollegeTechnology College is a term used in the United Kingdom for a secondary specialist school that focuses on design and technology, mathematics and science. These were the first type of specialist schools, beginning in 1994. In 2008 there were 598 Technology Colleges in England, of which 12 also...
Specialist schools must still meet the full requirements of the English national curriculum, so the specialism is seen as adding value to the existing statutory provision rather than being a radical departure from it. The important aspect in the eyes of the government is the focus that the specialism provides for providing leadership in the quest for whole school improvement.
The reward for achieving specialist status is a government grant of £100,000 to go with the £50,000 in sponsorship for a capital project related to the specialism and an extra £129 per pupil per year for four years to support the development plan. This is normally targeted on additional staffing and professional development, though up to 30% may be spent on equipment.
Schools that make a good attempt at achieving their targets over the 4 year development plan period normally have their grants renewed at 3-year intervals with no further need to raise sponsorship. However since 2008, the government has sought to encourage long-term relationships with business partners by offering a matching grant to redesignating specialist schools that are able to raise a further £25,000 in private sponsorship.
High Performing Specialist Status
Schools that demonstrate that they are achieving significantly higher results than other schools may be invited to apply to be designated as High Performing Specialist Schools. This typically allows the school to apply for a further specialism, which brings with it additional funding so that the school can develop that further specialism.By 2009 some 900 schools (30% of specialist schools) had achieved this status.
Results
David Jesson of the University of YorkUniversity of York
The University of York , is an academic institution located in the city of York, England. Established in 1963, the campus university has expanded to more than thirty departments and centres, covering a wide range of subjects...
has published a series of annual studies of the results of the specialist schools program, on behalf of the SSAT.
These studies report that non-selective specialist schools scored achieve significantly higher results at GCSE results than non-specialist comprehensive school
Comprehensive school
A comprehensive school is a state school that does not select its intake on the basis of academic achievement or aptitude. This is in contrast to the selective school system, where admission is restricted on the basis of a selection criteria. The term is commonly used in relation to the United...
s, that they achieve higher added value when prior achievement is taken into account, and that the gains increase with the length of time the school has been specialist.
Jesson's statistical methodology has been criticised, and others have pointed out that early specialist schools were chosen for the programme because they were already successful.
Other studies have found that specialist schools perform slightly better at GCSE, particularly benefitting more able pupils and narrowing the gap between boys and girls.
The most recent studies attribute this increase to the additional funding, and report that the effect is diminishing as a greater proportion of schools become specialist.
Systemic effects
Specialist schools and academies have been promoted, notably by Estelle MorrisEstelle Morris
Estelle Morris, Baroness Morris of Yardley, PC was a British Labour Party politician, who was the Member of Parliament for Birmingham Yardley from 1992 to 2005, and served briefly in the Cabinet as Education Secretary.-Early life:...
(Education Secretary 2001–2002), as part of a drive to improve standards by increasing diversity in secondary schools.
Left wing commentators have criticised this move away from the comprehensive ideal.
The two biggest UK teaching unions have opposed the programme because they say that it creates a two-tier education system, made up of specialist schools with extra funding and non-specialist schools which cannot benefit from any extra money.
There is also evidence that specialist schools take fewer children from poorer families than non-specialist schools..
One possible cause is that it may be easier for middle-class parents to raise the necessary sponsorship.

