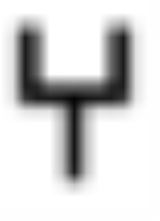
South Arabian alphabet
Encyclopedia
The ancient Yemeni alphabet (also known as musnad المُسند) branched from the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
in about the 9th century BC
. It was used for writing the Yemeni Old South Arabic languages of the Sabaean
, Qatabanian, Hadramautic
, Minaean
, Himyarite, and proto-Ge'ez
(or proto-Ethiosemitic
) in Dʿmt. The earliest inscriptions in the alphabet date to the 9th century BC
in Akkele Guzay
, Eritrea
and in the 8th century BC
, found in Babylonia
and in Yemen
. There are no vowels, instead using the mater lectionis
to mark them.
Its mature form was reached around 500 BC, and its use continued until the 7th century AD, including Old North Arabian inscriptions in variants of the alphabet, when it was displaced by the Arabic alphabet
. In Ethiopia it evolved later into the Ge'ez alphabet
, which, with added symbols throughout the centuries, has been used to write Amharic
, Tigrinya
and Tigre
, as well as other languages (including various Semitic
, Cushitic
, and Nilo-Saharan languages
).
) in addition to their monumental script, or musnad
(see, e.g., Ryckmans, J., Müller, W. W., and ‛Abdallah, Yu., Textes du Yémen Antique inscrits sur bois. Louvain-la-Neuve
, Belgium, 1994 (Publications de l'Institut Orientaliste de Louvain, 43)).
The cursive
zabur script—also known as "South Arabian minuscules"—was used by the ancient Yemenis to inscribe everyday documents on wooden sticks in addition to the rock-cut monumental musnad letters displayed below.

Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Old South Arabian is U+10A60–U+10A7F:
Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
Proto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script...
in about the 9th century BC
9th century BC
The 9th century BC started the first day of 900 BC and ended the last day of 801 BC.- Overview :The 9th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Africa, Carthage is founded by the Phoenicians...
. It was used for writing the Yemeni Old South Arabic languages of the Sabaean
Sabaean language
Sabaean , also known as Himyarite , was an Old South Arabian language spoken in Yemen from c. 1000 BC to the 6th century AD, by the Sabaeans; it was used as a written language by some other peoples of Ancient Yemen, including the Hashidites, Sirwahites, Humlanites, Ghaymanites, Himyarites,...
, Qatabanian, Hadramautic
Hadramautic language
One of the four known dialects of Old South Arabian, Hadramautic was spoken in what is known as present-day Yemen between 100 BC and 600 AD, in particular, but not exclusively, in the area known as Hadramawt....
, Minaean
Minaean language
The Minaean language was an Old South Arabian language spoken in Yemen between 1200 BC and AD 100. The main area of its use may be localized in al-Jawf part of North-East Yemen, first of all in the Wadi Madhab...
, Himyarite, and proto-Ge'ez
Ge'ez language
Ge'ez is an ancient South Semitic language that developed in the northern region of Ethiopia and southern Eritrea in the Horn of Africa...
(or proto-Ethiosemitic
Ethiopian Semitic languages
Ethiopian Semitic is a language group, which together with Old South Arabian forms the Western branch of the South Semitic languages. The languages are spoken in both Ethiopia and Eritrea...
) in Dʿmt. The earliest inscriptions in the alphabet date to the 9th century BC
9th century BC
The 9th century BC started the first day of 900 BC and ended the last day of 801 BC.- Overview :The 9th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Africa, Carthage is founded by the Phoenicians...
in Akkele Guzay
Akkele Guzay
Akkele Guzay was a province in the interior of Eritrea until 1996, when the newly independent government of Eritrea consolidated all provinces into six regions. Akkele Guzay's population predominantly consisted of followers of the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahdo Church. Traditionally being part of the...
, Eritrea
Eritrea
Eritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast...
and in the 8th century BC
8th century BC
The 8th century BC started the first day of 800 BC and ended the last day of 701 BC.-Overview:The 8th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Egypt, the 23rd and 24th dynasties led to rule from Nubia in the 25th Dynasty...
, found in Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
and in Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
. There are no vowels, instead using the mater lectionis
Mater lectionis
In the spelling of Hebrew and some other Semitic languages, matres lectionis , refers to the use of certain consonants to indicate a vowel. The letters that do this in Hebrew are aleph, he, waw and yod...
to mark them.
Its mature form was reached around 500 BC, and its use continued until the 7th century AD, including Old North Arabian inscriptions in variants of the alphabet, when it was displaced by the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
. In Ethiopia it evolved later into the Ge'ez alphabet
Ge'ez alphabet
Ge'ez , also called Ethiopic, is a script used as an abugida for several languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea but originated in an abjad used to write Ge'ez, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian and Eritrean Orthodox Church...
, which, with added symbols throughout the centuries, has been used to write Amharic
Amharic language
Amharic is a Semitic language spoken in Ethiopia. It is the second most-spoken Semitic language in the world, after Arabic, and the official working language of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Thus, it has official status and is used nationwide. Amharic is also the official or working...
, Tigrinya
Tigrinya language
Tigrinya , also spelled Tigrigna, Tigrnia, Tigrina, Tigriña, less commonly Tigrinian, Tigrinyan, is a Semitic language spoken by the Tigrinya people in central Eritrea , where it is one of the two main languages of Eritrea, and in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia , where it...
and Tigre
Tigre language
For other uses please see Tigre Tigre is a Semitic language, which, along with Tigrinya, is believed to be one of direct descendants of the extinct Ge'ez language...
, as well as other languages (including various Semitic
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
, Cushitic
Cushitic languages
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in the Horn of Africa, Tanzania, Kenya, Sudan and Egypt. They are named after the Biblical character Cush, who was identified as an ancestor of the speakers of these specific languages as early as AD 947...
, and Nilo-Saharan languages
Nilo-Saharan languages
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers , including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of Nile meet...
).
Zabur script
Zabur is the name of the cursive form of the South Arabian script that was used by the ancient Yemenis (SabaeansSabaeans
The Sabaeans or Sabeans were an ancient people speaking an Old South Arabian language who lived in what is today Yemen, in the south west of the Arabian Peninsula.Some scholars suggest a link between the Sabaeans and the Biblical land of Sheba....
) in addition to their monumental script, or musnad
Musnad
Musnad may refer to:*South Arabian alphabet*Musnad hadith*Musnad Ahmad ibn Hanbal...
(see, e.g., Ryckmans, J., Müller, W. W., and ‛Abdallah, Yu., Textes du Yémen Antique inscrits sur bois. Louvain-la-Neuve
Louvain-la-Neuve
Louvain-la-Neuve is a planned city in the municipality of Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, situated 30 km southeast of Brussels, in the French-speaking part of the country...
, Belgium, 1994 (Publications de l'Institut Orientaliste de Louvain, 43)).
The cursive
Cursive
Cursive, also known as joined-up writing, joint writing, or running writing, is any style of handwriting in which the symbols of the language are written in a simplified and/or flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing easier or faster...
zabur script—also known as "South Arabian minuscules"—was used by the ancient Yemenis to inscribe everyday documents on wooden sticks in addition to the rock-cut monumental musnad letters displayed below.
Sign inventory
| (epigraphic) Old Yemeni alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character Transcription IPA |
 h [h] |
 l [l] |
 ḥ [ħ] |
 m [m] |
 q [q] |
 w [w] |
 s2 Sawt Sawt is a kind of popular music found in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, especially in Kuwait and Bahrain. Sawt is a complex form of urban music, originally performed by 'ud and mirwas , with a violin later supplementing the arrangement.Two men perform the dance, which is called “Zaffan”.... [ɬ] |
 r [r] |
 b [b] |
 t [t] |
 s1 [s] |
 k [k] |
 n [n] |
 ḫ [x] |
 s3 [s̪] |
 f [f] |
 'ʾ [ʔ] |
 'ʿ [ʕ] |
 ḍ [ɬˤ] |
 g [ɡ] |
 d [d] |
 ġ [ɣ] |
 ṭ [tˤ] |
z [z] |
 ḏ [ð] |
 y [j] |
ṯ [θ] |
 ṣ [sˤ] |
ẓ [θˤ] |
|||
| Other transcriptions | ś Sawt Sawt is a kind of popular music found in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, especially in Kuwait and Bahrain. Sawt is a complex form of urban music, originally performed by 'ud and mirwas , with a violin later supplementing the arrangement.Two men perform the dance, which is called “Zaffan”.... ,š |
š,s | s,ś | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By shape | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character Transcription IPA |
 r [r] |
 'ʿ [ʕ] |
 w [w] |
 q [q] |
 y [j] |
ṯ [θ] |
 ṣ [tsˤ] |
ẓ [θˤ] |
 h [h] |
 ḥ [ħ] |
 ḫ [x] |
 'ʾ [ʔ] |
 s1 [s] |
 k [k] |
 ġ [ɣ] |
 b [b] |
 n [n] |
 g [ɡ] |
 l [l] |
 m [m] |
 s2 Sawt Sawt is a kind of popular music found in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, especially in Kuwait and Bahrain. Sawt is a complex form of urban music, originally performed by 'ud and mirwas , with a violin later supplementing the arrangement.Two men perform the dance, which is called “Zaffan”.... [ɬ] |
 s3 [s̪] |
 t [t] |
 f [f] |
z [z] |
 d [d] |
 ḏ [ð] |
 ḍ [ɬˤ] |
 ṭ [tˤ] |
| Circle | Y | Π | Vertical | Diagonal | Box | ||||||||||||||||||||||||

Properties
- It is usually written from right to left but can also be written from left to right. When written from left to right the characters are flipped horizontally (see the photo).
- The spacing or separation between words is done with a vertical bar mark (|).
- Letters in words are not connected together.
- It does not implement any diacritical marks (dots, etc.), differing in this respect from the modern Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
.
Unicode
Old South Arabian was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Old South Arabian is U+10A60–U+10A7F:
Gallery of some inscriptions
- Photos from National Museum of Yemen (Sana'a):
- Photos from Military Museum of Yemen (Sana'a):

