
Solvation shell
Encyclopedia
Chemical species
Chemical species are atoms, molecules, molecular fragments, ions, etc., being subjected to a chemical process or to a measurement. Generally, a chemical species can be defined as an ensemble of chemically identical molecular entities that can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a...
acting as a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
, surrounding a solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
species. When the solvent is water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
it is often referred to as a hydration shell or hydration sphere.
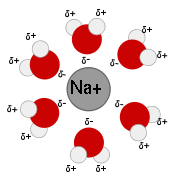
A classic example is water molecules solvating a metal ion. The electronegative oxygen atom contained in the water molecule attracts electrostatically to the positive charge on the metal ion. The result is a 'solvation shell' of water molecules surrounding the ion. This shell can be several molecules thick, dependent on the charge of the ion.
Hydration Shells of Proteins
The hydration shell (also sometimes called hydration layer) that forms around proteins is of particular importance in biochemistry. This interaction of the protein surface with the surrounding water is often referred to as protein hydration and is fundamental to the activity of the protein. The hydration layer around a protein has been found to have dynamics distinct from the bulk water to a distance of 1 nm with effects on the surrounding water network extending beyond 2 nm. The duration of contact of a specific water molecule with the protein surface may be in the subnanosecond range while molecular dynamicsMolecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
simulations suggest the time water spends in the hydration shell before mixing with the outside bulk water could be in the femtosecond to picosecond range.
With other solvents and solutes, varying steric and kinetic factors can also affect the solvation shell. It is a very useful concept in Biochemistry (why exactly...?).

