
Smith predictor
Encyclopedia
The Smith predictor is a type of predictive controller
for systems with pure time delay. The idea can be illustrated as follows.
Suppose the plant consists of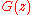 followed by a pure time delay
followed by a pure time delay 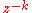 .
.
As a first step, suppose we only consider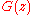 (the plant without a delay) and design a controller
(the plant without a delay) and design a controller 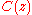 with a closed loop transfer function
with a closed loop transfer function 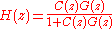 that we consider satisfactory.
that we consider satisfactory.
Next, our objective is to design a controller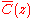 for the plant
for the plant 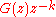 so that the closed loop transfer function
so that the closed loop transfer function 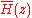 equals
equals 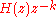 .
.
Solving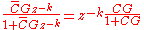 ,
,
we obtain
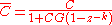 . The controller is implemented as shown in the following figure, where
. The controller is implemented as shown in the following figure, where 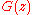 has been changed to
has been changed to 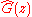 to indicate that it is a model used by the controller.
to indicate that it is a model used by the controller.
Note that there are two feedback loops. The outer control loop feeds the output back to the input, as usual. However, this loop alone would not provide satisfactory control, because of the delay; this loop is feeding back outdated information. Intuitively, for the k seconds during which no fresh information is available, the system is controlled by the inner loop which contains a predictor of what the (unobservable) output of the plant G currently is.
To check that this works, a re-arrangement can be made as follows:
Here we can see that if the model used in the controller,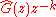 , matches the plant
, matches the plant 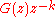 perfectly, then the outer and middle feedback loops cancel each other, and the controller generates the "correct" control action.
perfectly, then the outer and middle feedback loops cancel each other, and the controller generates the "correct" control action.
Controller (control theory)
In control theory, a controller is a device which monitors and affects the operational conditions of a given dynamical system. The operational conditions are typically referred to as output variables of the system which can be affected by adjusting certain input variables...
for systems with pure time delay. The idea can be illustrated as follows.
Suppose the plant consists of
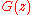 followed by a pure time delay
followed by a pure time delay 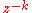 .
.As a first step, suppose we only consider
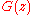 (the plant without a delay) and design a controller
(the plant without a delay) and design a controller 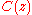 with a closed loop transfer function
with a closed loop transfer function 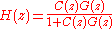 that we consider satisfactory.
that we consider satisfactory.Next, our objective is to design a controller
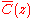 for the plant
for the plant 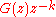 so that the closed loop transfer function
so that the closed loop transfer function 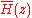 equals
equals 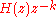 .
.Solving
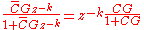 ,
,we obtain
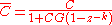 . The controller is implemented as shown in the following figure, where
. The controller is implemented as shown in the following figure, where 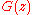 has been changed to
has been changed to 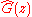 to indicate that it is a model used by the controller.
to indicate that it is a model used by the controller.Note that there are two feedback loops. The outer control loop feeds the output back to the input, as usual. However, this loop alone would not provide satisfactory control, because of the delay; this loop is feeding back outdated information. Intuitively, for the k seconds during which no fresh information is available, the system is controlled by the inner loop which contains a predictor of what the (unobservable) output of the plant G currently is.
To check that this works, a re-arrangement can be made as follows:
Here we can see that if the model used in the controller,
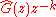 , matches the plant
, matches the plant 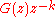 perfectly, then the outer and middle feedback loops cancel each other, and the controller generates the "correct" control action.
perfectly, then the outer and middle feedback loops cancel each other, and the controller generates the "correct" control action.

