
Smart ligands
Encyclopedia
Smart ligands are affinity ligands selected with pre-defined equilibrium (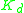 ), kinetic (
), kinetic (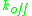 ,
, 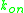 ) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.
) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.
Ligands with desired parameters can be selected from large combinatorial libraries of biopolymers using instrumental separation techniques with well-described kinetic behaviour, such as Kinetic capillary electrophoresis
(KCE), Surface Plasmon Resonance
(SPR), Microscale Thermophoresis
(MST) and etc. Known examples of smart ligands include DNA smart aptamers; however, RNA and peptide smart aptamer
s can also be developed.
Smart ligands can find a set of unique applications in biomedical research, drug discovery and proteomic studies. For example, a panel of DNA smart aptamers has been recently used to develop affinity analysis of proteins with ultra-wide dynamic range of measured concentrations.
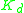 ), kinetic (
), kinetic (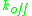 ,
, 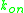 ) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.
) and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of biomolecular interaction.Ligands with desired parameters can be selected from large combinatorial libraries of biopolymers using instrumental separation techniques with well-described kinetic behaviour, such as Kinetic capillary electrophoresis
Kinetic capillary electrophoresis
Kinetic capillary electrophoresis or KCE is capillary electrophoresis of molecules that interact during electrophoresis. KCE was introduced and developed by Professor Sergey Krylov and his research group at York University, Toronto, Canada...
(KCE), Surface Plasmon Resonance
Surface plasmon resonance
The excitation of surface plasmons by light is denoted as a surface plasmon resonance for planar surfaces or localized surface plasmon resonance for nanometer-sized metallic structures....
(SPR), Microscale Thermophoresis
Microscale Thermophoresis
Microscale Thermophoresis is a technology for the analysis of biomolecules. Microscale Thermophoresis is the directed movement of particles in a microscopic temperature gradient...
(MST) and etc. Known examples of smart ligands include DNA smart aptamers; however, RNA and peptide smart aptamer
Aptamer
Aptamers are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule. Aptamers are usually created by selecting them from a large random sequence pool, but natural aptamers also exist in riboswitches. Aptamers can be used for both basic research and clinical purposes as...
s can also be developed.
Smart ligands can find a set of unique applications in biomedical research, drug discovery and proteomic studies. For example, a panel of DNA smart aptamers has been recently used to develop affinity analysis of proteins with ultra-wide dynamic range of measured concentrations.

