
Silicon bandgap temperature sensor
Encyclopedia
The silicon bandgap temperature sensor is an extremely common form of temperature sensor (thermometer
) used in electronic equipment. Its main advantage is that it can be included in a silicon integrated circuit
at very low cost. The principle of the sensor is that the forward voltage of a silicon
diode
is temperature-dependent, according to the following equation: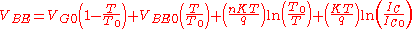
where
By comparing the bandgap voltages at two different currents, IC1 and IC2, many of the variables in the above equation can be eliminated, resulting in the relationship: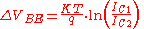
An electronic circuit, such as the Brokaw bandgap reference
, that measures ΔVBE can therefore be used to calculate the temperature of the diode. The result remains valid up to about 200 °C to 250 °C, when leakage currents become large enough to corrupt the measurement. Above these temperatures, materials such as silicon carbide
can be used instead of silicon.
If high precision is not required it is enough to bias a diode with any constant low current and use its −2 mV/˚C thermal coefficient for temperature calculation, however this requires calibration for each diode type. This method is common in monolithic temperature sensors.[citation required]
Thermometer
Developed during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient using a variety of different principles. A thermometer has two important elements: the temperature sensor Developed during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer (from the...
) used in electronic equipment. Its main advantage is that it can be included in a silicon integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
at very low cost. The principle of the sensor is that the forward voltage of a silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
is temperature-dependent, according to the following equation:
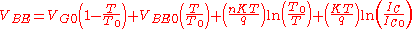
where
- T = temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s - T0 = reference temperature
- VG0 = bandgap voltage at absolute zeroAbsolute zeroAbsolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
- VBE0 = bandgap voltage at temperature T0 and current IC0
- K = Boltzmann's constant
- q = charge on an electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
- n = a device-dependent constant
By comparing the bandgap voltages at two different currents, IC1 and IC2, many of the variables in the above equation can be eliminated, resulting in the relationship:
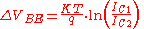
An electronic circuit, such as the Brokaw bandgap reference
Brokaw bandgap reference
Brokaw bandgap reference is a voltage reference circuit widely used in integrated circuits, with an output voltage around 1.25 V with only little temperature dependence...
, that measures ΔVBE can therefore be used to calculate the temperature of the diode. The result remains valid up to about 200 °C to 250 °C, when leakage currents become large enough to corrupt the measurement. Above these temperatures, materials such as silicon carbide
Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide , also known as carborundum, is a compound of silicon and carbon with chemical formula SiC. It occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite. Silicon carbide powder has been mass-produced since 1893 for use as an abrasive...
can be used instead of silicon.
If high precision is not required it is enough to bias a diode with any constant low current and use its −2 mV/˚C thermal coefficient for temperature calculation, however this requires calibration for each diode type. This method is common in monolithic temperature sensors.[citation required]
External links
- Temperature Sensing Theory and Practical Techniques, Analog Devices
- Precision Monolithic Temperature Sensors, National Semiconductor

