
Shaping codes
Encyclopedia
In digital communications shaping codes are a method of encoding that changes the distribution of signals to improve efficiency.
(QAM) to communicate thorough an analog channel (specifically a channel
with Gaussian noise
). For Higher bit rates(M) the minimum Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) required by a QAM system with Error Correcting Codes is about 1.53 dB
higher than minimum SNR required by a Gaussian source(>30% more transmitter power) as given in Shannon–Hartley theorem
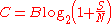
where
This 1.53 dB difference is called the shaping gap. Typically digital system will encode bits with uniform probability to maximize the entropy. Shaping code act as buffer between digital sources and modulator communication system. They will receive uniformly distributed data and convert it to Gaussian like distribution before presenting to the modulator. Shaping codes are helpful in reducing transmit power and thus reduce the cost of Power amplifier and the interference caused to other users in the vicinity.
Shell mapping is used in V.34 modems to get a shaping gain of .8 dB
.
All the shaping schemes in the literature try to reduce the transmitted signal power. In future this may have find application in wireless network
s where the interference from other nodes are becoming the major issue.
Description
Typical digital communication systems uses M-Quadrature Amplitude ModulationQuadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
(QAM) to communicate thorough an analog channel (specifically a channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
with Gaussian noise
Gaussian noise
Gaussian noise is statistical noise that has its probability density function equal to that of the normal distribution, which is also known as the Gaussian distribution. In other words, the values that the noise can take on are Gaussian-distributed. A special case is white Gaussian noise, in which...
). For Higher bit rates(M) the minimum Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) required by a QAM system with Error Correcting Codes is about 1.53 dB
DB
DB may refer to:In science and technology:*Decibel , a logarithmic unit of measurement in acoustics and electronics*Dubnium , a chemical element*DB connector, a size of D-subminiature electrical connector...
higher than minimum SNR required by a Gaussian source(>30% more transmitter power) as given in Shannon–Hartley theorem
Shannon–Hartley theorem
In information theory, the Shannon–Hartley theorem tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise. It is an application of the noisy channel coding theorem to the archetypal case of a continuous-time...
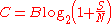
where
- C is the channel capacityChannel capacityIn electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
in bits per second; - B is the bandwidth of the channel in hertzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
; - S is the total signal power over the bandwidth and
- N is the total noise power over the bandwidth.
- S/N is the signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
of the communication signal to the Gaussian noise interference expressed as a straight power ratio (not as decibels).
This 1.53 dB difference is called the shaping gap. Typically digital system will encode bits with uniform probability to maximize the entropy. Shaping code act as buffer between digital sources and modulator communication system. They will receive uniformly distributed data and convert it to Gaussian like distribution before presenting to the modulator. Shaping codes are helpful in reducing transmit power and thus reduce the cost of Power amplifier and the interference caused to other users in the vicinity.
Application
Some of the methods used for shaping are described in the trellis shaping paper by Dr. G. D. Forney Jr.Shell mapping is used in V.34 modems to get a shaping gain of .8 dB
DB
DB may refer to:In science and technology:*Decibel , a logarithmic unit of measurement in acoustics and electronics*Dubnium , a chemical element*DB connector, a size of D-subminiature electrical connector...
.
All the shaping schemes in the literature try to reduce the transmitted signal power. In future this may have find application in wireless network
Wireless network
Wireless network refers to any type of computer network that is not connected by cables of any kind. It is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and enterprise installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment...
s where the interference from other nodes are becoming the major issue.

