Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal
Encyclopedia
The Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal is an objection to the Doomsday argument
(that there is only a 5% chance of more than twenty times the historic number of humans ever being born) by arguing that the chance of being born is not one, but is an increasing function of the number of people who will be born.
(1992), developed by Bartha & Hitchcock (1999), and expanded by Ken Olum (2001), is that the possibility of you existing at all depends on how many humans will ever exist (N). If N is big, then the chance of you existing is higher than if only a few humans will ever exist. Since you do indeed exist, this is evidence that N is high. The argument
is sometimes expressed in an alternative way by having the posterior
marginal distribution of n based on N without explicitly invoking a non-zero chance of existing. The Bayesian inference mathematics are identical.
The current name for this attack within the (very active) DA community is the "Self-Indication Assumption" (SIA
), proposed by one of its opponents, the DA-advocate Nick Bostrom
. His (2000) definition reads:
A development of Dieks's original paper by Kopf, Krtous and Page (1994), showed that the SIA precisely cancels out the effect of the Doomsday Argument, and therefore, one's birth position (n) gives no information about the total number of humans that will exist (N). This conclusion of SIA is uncontroversial with modern DA-proponents, who instead question the validity of the assumption itself, not the conclusion which would follow, if the SIA were true.
of two separate events, both of which must be true:
This means that the pdf
for n, is concentrated at P(n = 0) = 1 - P(b), and that for P(n > 0) the marginal
distribution can be calculated from the conditional:
 Where n > 0
Where n > 0
J. Richard Gott
's DA could be formulated similarly up to this point, where it has P(b | N) = P(b) = 1, producing Gott's inference of n from N. However, Dennis Dieks
argues that P(b) < 1, and that P(b | N) rises proportionally in N (which is a SIA). This can be expressed mathematically:
 Where c is a constant
Where c is a constant
.
The SIA
’s effect was expressed by Page et al. as Assumption 2 for the prior probability distribution
, P(N):
They note that similar assumptions had been dismissed by Leslie
on the grounds that: "it seems wrong to treat ourselves as if we were once immaterial souls harbouring hopes of becoming embodied, hopes that would have been greater, the greater the number of bodies to be created." (1992)
One argument given for P(b | N) rising in N that doesn’t create Leslie’s “immaterial souls” is the possibility of being born into any of a large number of universes within a multiverse
. You can only be born into one, so the indifference principle
within this (humans-across-universes) reference class would mean that the chance of being born into a particular universe is proportional to its weight in humans, N. (Echoing the weak anthropic principle
.)
Whatever the reasoning, the essential idea of the Self-Indication Assumption is that the prior probability of birth into this universe is rising in N, and is generally considered to be proportional to N. (The following discussion assumes they are proportional so P(b | N) = 2 P(b | 2N), since other functions increasing in N produce similar results.)
Therefore:
 Where n > 0
Where n > 0
 . (This prevents N’s distribution being an improper prior.)
. (This prevents N’s distribution being an improper prior.)
 is the largest possible value for N if all living space in the 'universe' is consumed. The
is the largest possible value for N if all living space in the 'universe' is consumed. The  limit has no specified upper bounds (to habitable planets in the Galaxy
limit has no specified upper bounds (to habitable planets in the Galaxy
, say) but makes N’s posterior
distribution more tractable
:

The factor normalizes the N’s probability, allowing calculation of the marginal
factor normalizes the N’s probability, allowing calculation of the marginal
P(n > 0) by integration of P(b|N) across the [1, ] range of possible N:
] range of possible N:

This range starts at n rather than 1, because n can’t be greater than N. It uses the Principle of indifference
for n’s distribution given N, and implies:

Substituting these marginals into the conditional
equation (assuming N below ) gives:
) gives:


Therefore, given the posterior information that we have been born and that we are nth in line: For any factor, x << ( / n), of the current population:
/ n), of the current population:

 The finite
The finite  is essential to this solution in order to produce finite integrals. In a bounded universe,
is essential to this solution in order to produce finite integrals. In a bounded universe,  actually must be finite, although this is not usually an argument used by those proposing the SIA rebuttal. However, other proponents of indefinite survival of human (and posthuman
actually must be finite, although this is not usually an argument used by those proposing the SIA rebuttal. However, other proponents of indefinite survival of human (and posthuman
) intelligence have postulated a finite endpoint, as the (extremely high) “Omega
”.
Specifying any finite upper limit, , was not a part of Dieks's argument, and critics of the SIA have argued that an infinite upper bound on N creates an Improper integral
, was not a part of Dieks's argument, and critics of the SIA have argued that an infinite upper bound on N creates an Improper integral
(or summation) in the bayesian inference on N, which is a challenge to the logic of the critique. (For example Eastmond, and Bostrom
, who argues that if the SIA cannot rule out an infinite number of potential humans, it is fatally flawed.)
The unbounded vague prior is scale invariant
, in that the mean
is arbitrary. Therefore no finite value can be selected with more than a 50% chance of being above N (the marginal distribution of N). Olum's critique depends on such a limit existing; without this his critique is technically not applicable. Therefore it must be cautioned that the simplification here (to bound Ns distribution at ) omits a significant hurdle to the credibility of the Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal.
) omits a significant hurdle to the credibility of the Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal.
) believe the leading candidate for Doomsday argument refutation is a Self-Indication Assumption
of some kind. It is popular partly because it is a purely Bayesian
argument which accepts some of the DA's premises (such as the Indifference
and Copernican
principles). Other observations:
Under the Self-Indication Assumption the 'reference class' of which we are part includes a potentially vast number of the unborn (at least into this universe). In order to overturn the conventional DA calculation so completely the reservoir of souls (potential births) in the reference class must be astoundingly large. For instance, the certain-birth DA estimates the chance of reaching the trillionth ( th) birth at around 5%; to shift this probability above 90% the SIA requires a potential number of humans (
th) birth at around 5%; to shift this probability above 90% the SIA requires a potential number of humans ( ) in the order of
) in the order of  (a septillion births). This might be feasible physically, and is also possible within the conventional DA model (though staggeringly unlikely). However, the SIA differs from the normal DA in having the reference class include all septillion unborn potential-humans at this point in history, when only sixty billion have been born. Including unborn people in the reference class we sample from means including in the reference class things for which we can never have any evidence. This puts the SIA at odds with philosophical approaches requiring strictly falsifiable constructs, such as Logical positivism
(a septillion births). This might be feasible physically, and is also possible within the conventional DA model (though staggeringly unlikely). However, the SIA differs from the normal DA in having the reference class include all septillion unborn potential-humans at this point in history, when only sixty billion have been born. Including unborn people in the reference class we sample from means including in the reference class things for which we can never have any evidence. This puts the SIA at odds with philosophical approaches requiring strictly falsifiable constructs, such as Logical positivism
.
changes the distribution because everyday cases where a null result can be returned don't change the statistics significantly. The following two examples of estimating the size of a darkened space show how the probability shift can occur:
The Bayesian inference shifts from the cloak-room case to the lost-property case, because of the chance that the coat would not be found in the aisle it was found in, and some estimate of the aisle's dimensions. Using the SIA Bayesian inference
equation with = 100, n = 1, x = 20 gives the chance that the aisle is above 20 feet long in the Lost-property case:
= 100, n = 1, x = 20 gives the chance that the aisle is above 20 feet long in the Lost-property case:
The confidence that the unseen space is longer than 20 feet is directly analogous to the confidence that the human race will become more than 20 times as numerous as it has been. Using an of one hundred times the current value only increases the subjective chance seven times (from 5% to 35%), but this is a very small limit for the purposes of exposition.
of one hundred times the current value only increases the subjective chance seven times (from 5% to 35%), but this is a very small limit for the purposes of exposition.
Doomsday argument
The Doomsday argument is a probabilistic argument that claims to predict the number of future members of the human species given only an estimate of the total number of humans born so far...
(that there is only a 5% chance of more than twenty times the historic number of humans ever being born) by arguing that the chance of being born is not one, but is an increasing function of the number of people who will be born.
History
This objection to the Doomsday Argument (DA), originally by Dennis DieksDennis Dieks
Dennis Dieks is a Dutch physicist and philosopher of physics. In 1982 he proved the no-cloning theorem . In 1989 he proposed a new interpretation of quantum mechanics, later known as a version of the modal interpretation of quantum mechanics...
(1992), developed by Bartha & Hitchcock (1999), and expanded by Ken Olum (2001), is that the possibility of you existing at all depends on how many humans will ever exist (N). If N is big, then the chance of you existing is higher than if only a few humans will ever exist. Since you do indeed exist, this is evidence that N is high. The argument
Argument
In philosophy and logic, an argument is an attempt to persuade someone of something, or give evidence or reasons for accepting a particular conclusion.Argument may also refer to:-Mathematics and computer science:...
is sometimes expressed in an alternative way by having the posterior
Posterior probability
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the conditional probability that is assigned after the relevant evidence is taken into account...
marginal distribution of n based on N without explicitly invoking a non-zero chance of existing. The Bayesian inference mathematics are identical.
The current name for this attack within the (very active) DA community is the "Self-Indication Assumption" (SIA
Self-Indication Assumption
The Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
), proposed by one of its opponents, the DA-advocate Nick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk and the anthropic principle. He holds a PhD from the London School of Economics...
. His (2000) definition reads:
- SIA: Given the fact that you exist, you should (other things equal) favor hypotheses according to which many observers exist over hypotheses on which few observers exist.
A development of Dieks's original paper by Kopf, Krtous and Page (1994), showed that the SIA precisely cancels out the effect of the Doomsday Argument, and therefore, one's birth position (n) gives no information about the total number of humans that will exist (N). This conclusion of SIA is uncontroversial with modern DA-proponents, who instead question the validity of the assumption itself, not the conclusion which would follow, if the SIA were true.
The Bayesian inference of N from n under the SIA
The SIA-mathematics considers the chance of being the nth human as being conditioned on the joint probabilityConditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
of two separate events, both of which must be true:
- Being born: With marginal probabilityConditional probabilityIn probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
P(b). - Being nth in line: With marginal probabilityProbabilityProbability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
(1/N), under the Principle of indifferencePrinciple of indifferenceThe principle of indifference is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities.Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive possibilities....
.
This means that the pdf
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
for n, is concentrated at P(n = 0) = 1 - P(b), and that for P(n > 0) the marginal
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
distribution can be calculated from the conditional:
 Where n > 0
Where n > 0J. Richard Gott
J. Richard Gott
John Richard Gott III is a professor of astrophysical sciences at Princeton University. He is known for developing and advocating two cosmological theories with the flavor of science fiction: Time travel and the Doomsday argument.- Exotic matter time travel theories :Paul Davies's bestseller How...
's DA could be formulated similarly up to this point, where it has P(b | N) = P(b) = 1, producing Gott's inference of n from N. However, Dennis Dieks
Dennis Dieks
Dennis Dieks is a Dutch physicist and philosopher of physics. In 1982 he proved the no-cloning theorem . In 1989 he proposed a new interpretation of quantum mechanics, later known as a version of the modal interpretation of quantum mechanics...
argues that P(b) < 1, and that P(b | N) rises proportionally in N (which is a SIA). This can be expressed mathematically:
 Where c is a constant
Where c is a constantNormalizing constant
The concept of a normalizing constant arises in probability theory and a variety of other areas of mathematics.-Definition and examples:In probability theory, a normalizing constant is a constant by which an everywhere non-negative function must be multiplied so the area under its graph is 1, e.g.,...
.
The SIA
Self-Indication Assumption
The Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
’s effect was expressed by Page et al. as Assumption 2 for the prior probability distribution
Prior probability
In Bayesian statistical inference, a prior probability distribution, often called simply the prior, of an uncertain quantity p is the probability distribution that would express one's uncertainty about p before the "data"...
, P(N):
- "The probability for the observer to exist somewhere in a history of length N is proportional to the probability for that history and to the number of people in that history." (1994 - Emphasis added to: http://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9407002)
They note that similar assumptions had been dismissed by Leslie
John A. Leslie
John Andrew Leslie is a Canadian philosopher. He was educated at Wadham College, Oxford, earning his B.A. in English Literature in 1962 and his M.Litt. in Classics in 1968...
on the grounds that: "it seems wrong to treat ourselves as if we were once immaterial souls harbouring hopes of becoming embodied, hopes that would have been greater, the greater the number of bodies to be created." (1992)
One argument given for P(b | N) rising in N that doesn’t create Leslie’s “immaterial souls” is the possibility of being born into any of a large number of universes within a multiverse
Multiverse (science)
The multiverse is the hypothetical set of multiple possible universes that together comprise everything that exists and can exist: the entirety of space, time, matter, and energy as well as the physical laws and constants that describe them...
. You can only be born into one, so the indifference principle
Principle of indifference
The principle of indifference is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities.Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive possibilities....
within this (humans-across-universes) reference class would mean that the chance of being born into a particular universe is proportional to its weight in humans, N. (Echoing the weak anthropic principle
Anthropic principle
In astrophysics and cosmology, the anthropic principle is the philosophical argument that observations of the physical Universe must be compatible with the conscious life that observes it. Some proponents of the argument reason that it explains why the Universe has the age and the fundamental...
.)
- In this framework, the chance of 'not being born' is zero, but the chance of 'not being born into this universe is non-zero.
Whatever the reasoning, the essential idea of the Self-Indication Assumption is that the prior probability of birth into this universe is rising in N, and is generally considered to be proportional to N. (The following discussion assumes they are proportional so P(b | N) = 2 P(b | 2N), since other functions increasing in N produce similar results.)
Therefore:
 Where n > 0
Where n > 0Effect of the “unborn” on the Bayesian inference
To clarify the exposition, Gott’s vague prior N distribution is ‘capped’ at some “universal carrying capacity”, . (This prevents N’s distribution being an improper prior.)
. (This prevents N’s distribution being an improper prior.) is the largest possible value for N if all living space in the 'universe' is consumed. The
is the largest possible value for N if all living space in the 'universe' is consumed. The  limit has no specified upper bounds (to habitable planets in the Galaxy
limit has no specified upper bounds (to habitable planets in the GalaxyDrake equation
The Drake equation is an equation used to estimate the number of detectable extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way galaxy. It is used in the fields of exobiology and the Search for ExtraTerrestrial Intelligence...
, say) but makes N’s posterior
Posterior probability
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the conditional probability that is assigned after the relevant evidence is taken into account...
distribution more tractable
Improper integral
In calculus, an improper integral is the limit of a definite integral as an endpoint of the interval of integration approaches either a specified real number or ∞ or −∞ or, in some cases, as both endpoints approach limits....
:

The
 factor normalizes the N’s probability, allowing calculation of the marginal
factor normalizes the N’s probability, allowing calculation of the marginalConditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
P(n > 0) by integration of P(b|N) across the [1,
 ] range of possible N:
] range of possible N:
This range starts at n rather than 1, because n can’t be greater than N. It uses the Principle of indifference
Principle of indifference
The principle of indifference is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities.Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive possibilities....
for n’s distribution given N, and implies:

Substituting these marginals into the conditional
Posterior probability
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the conditional probability that is assigned after the relevant evidence is taken into account...
equation (assuming N below
 ) gives:
) gives:
The probabilistic bounds on
N with the SIA The chance of doomsday before an arbitrary factor of the current population, x, is born can be inferred, by integrating the chance of N having any value above xn. (Normally x = 20.)
Therefore, given the posterior information that we have been born and that we are nth in line: For any factor, x << (
 / n), of the current population:
/ n), of the current population:
- Conclusion:
Significance of Omega

 is essential to this solution in order to produce finite integrals. In a bounded universe,
is essential to this solution in order to produce finite integrals. In a bounded universe,  actually must be finite, although this is not usually an argument used by those proposing the SIA rebuttal. However, other proponents of indefinite survival of human (and posthuman
actually must be finite, although this is not usually an argument used by those proposing the SIA rebuttal. However, other proponents of indefinite survival of human (and posthumanPosthuman
Posthuman may refer to:*Posthuman, a hypothetical future being whose basic capacities so radically exceed those of present humans as to be no longer human by our current standards...
) intelligence have postulated a finite endpoint, as the (extremely high) “Omega
Omega
Omega is the 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system, it has a value of 800. The word literally means "great O" , as opposed to omicron, which means "little O"...
”.
Specifying any finite upper limit,
 , was not a part of Dieks's argument, and critics of the SIA have argued that an infinite upper bound on N creates an Improper integral
, was not a part of Dieks's argument, and critics of the SIA have argued that an infinite upper bound on N creates an Improper integralImproper integral
In calculus, an improper integral is the limit of a definite integral as an endpoint of the interval of integration approaches either a specified real number or ∞ or −∞ or, in some cases, as both endpoints approach limits....
(or summation) in the bayesian inference on N, which is a challenge to the logic of the critique. (For example Eastmond, and Bostrom
Nick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk and the anthropic principle. He holds a PhD from the London School of Economics...
, who argues that if the SIA cannot rule out an infinite number of potential humans, it is fatally flawed.)
The unbounded vague prior is scale invariant
Scale invariance
In physics and mathematics, scale invariance is a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energy, or other variables, are multiplied by a common factor...
, in that the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
is arbitrary. Therefore no finite value can be selected with more than a 50% chance of being above N (the marginal distribution of N). Olum's critique depends on such a limit existing; without this his critique is technically not applicable. Therefore it must be cautioned that the simplification here (to bound Ns distribution at
 ) omits a significant hurdle to the credibility of the Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal.
) omits a significant hurdle to the credibility of the Self-Indication Assumption Doomsday argument rebuttal.Remarks
Many people, (such as BostromNick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk and the anthropic principle. He holds a PhD from the London School of Economics...
) believe the leading candidate for Doomsday argument refutation is a Self-Indication Assumption
Self-Indication Assumption
The Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
of some kind. It is popular partly because it is a purely Bayesian
Bayesian probability
Bayesian probability is one of the different interpretations of the concept of probability and belongs to the category of evidential probabilities. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of logic that enables reasoning with propositions, whose truth or falsity is...
argument which accepts some of the DA's premises (such as the Indifference
Principle of indifference
The principle of indifference is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities.Suppose that there are n > 1 mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive possibilities....
and Copernican
Copernican principle
In physical cosmology, the Copernican principle, named after Nicolaus Copernicus, states that the Earth is not in a central, specially favored position. More recently, the principle has been generalized to the relativistic concept that humans are not privileged observers of the universe...
principles). Other observations:
- The joint prior distribution, P(n|N), can be manipulated to produce a wide range of links between n and N by defining various birth probabilities given N. Since this distribution must be assumed prior to evidence, any particular choice of P(b|N) is faithFaithFaith is confidence or trust in a person or thing, or a belief that is not based on proof. In religion, faith is a belief in a transcendent reality, a religious teacher, a set of teachings or a Supreme Being. Generally speaking, it is offered as a means by which the truth of the proposition,...
-based. Many writers feel a joint distribution with no link N to n is more natural than the strong link given by the vague prior, making the DA "Irrelevant" (Page et al.) Others, such as GottJ. Richard GottJohn Richard Gott III is a professor of astrophysical sciences at Princeton University. He is known for developing and advocating two cosmological theories with the flavor of science fiction: Time travel and the Doomsday argument.- Exotic matter time travel theories :Paul Davies's bestseller How...
feel the opposite, and are more comfortable using the pure vague prior as the prior joint probability, with P(b|N) = 1 at all N. - The SIA rebuttal is a very special form of the "a priori" rebuttal of the DADoomsday argumentThe Doomsday argument is a probabilistic argument that claims to predict the number of future members of the human species given only an estimate of the total number of humans born so far...
, and differs from that approach in being purely statistical. - If the SIASelf-Indication AssumptionThe Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
is true then the mere fact of existence leads credence to "any" theory that postulates a "high" number of conscious beings in the universe, and controversially implies that a theory which does not is unlikely to be true. (For instance, the SIA implies that N is likely to be very high, so the probability of an upcoming ArmageddonArmageddonArmageddon is, according to the Bible, the site of a battle during the end times, variously interpreted as either a literal or symbolic location...
is correspondingly low, which makes the Doomsday clockDoomsday ClockThe Doomsday Clock is a symbolic clock face, maintained since 1947 by the board of directors of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists at the University of Chicago. The closer the clock is to midnight, the closer the world is estimated to be to global disaster. , the Doomsday Clock now stands at six...
’s warning of relatively imminent destruction a mistake.)
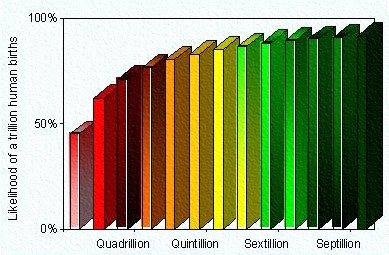
Under the Self-Indication Assumption the 'reference class' of which we are part includes a potentially vast number of the unborn (at least into this universe). In order to overturn the conventional DA calculation so completely the reservoir of souls (potential births) in the reference class must be astoundingly large. For instance, the certain-birth DA estimates the chance of reaching the trillionth (
 th) birth at around 5%; to shift this probability above 90% the SIA requires a potential number of humans (
th) birth at around 5%; to shift this probability above 90% the SIA requires a potential number of humans ( ) in the order of
) in the order of  (a septillion births). This might be feasible physically, and is also possible within the conventional DA model (though staggeringly unlikely). However, the SIA differs from the normal DA in having the reference class include all septillion unborn potential-humans at this point in history, when only sixty billion have been born. Including unborn people in the reference class we sample from means including in the reference class things for which we can never have any evidence. This puts the SIA at odds with philosophical approaches requiring strictly falsifiable constructs, such as Logical positivism
(a septillion births). This might be feasible physically, and is also possible within the conventional DA model (though staggeringly unlikely). However, the SIA differs from the normal DA in having the reference class include all septillion unborn potential-humans at this point in history, when only sixty billion have been born. Including unborn people in the reference class we sample from means including in the reference class things for which we can never have any evidence. This puts the SIA at odds with philosophical approaches requiring strictly falsifiable constructs, such as Logical positivismLogical positivism
Logical positivism is a philosophy that combines empiricism—the idea that observational evidence is indispensable for knowledge—with a version of rationalism incorporating mathematical and logico-linguistic constructs and deductions of epistemology.It may be considered as a type of analytic...
.
SIA Intuition: the lost-property metaphor
It can be hard to visualize how the Self-Indication AssumptionSelf-Indication Assumption
The Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
changes the distribution because everyday cases where a null result can be returned don't change the statistics significantly. The following two examples of estimating the size of a darkened space show how the probability shift can occur:
- Cloak-room case: Imagine looking for your coatCoat (clothing)A coat is a long garment worn by both men and women, for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, a belt, or a combination of some of these...
in a dark room and finding it one foot from the door; the Bayesian inference from a vague prior is that the room is less than 20 feet long (with 95% confidence). - Lost-property case: Your coat has been filed somewhere in a huge lost-property warehouseWarehouseA warehouse is a commercial building for storage of goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial areas of cities and towns. They usually have loading docks to load and unload...
, and as you search through its many aisleAisleAn aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of seats on both sides or with rows of seats on one side and a wall on the other...
s you see that they are all filled to capacityPlenitude principleThe plenitude principle or principle of plenitude asserts that everything that can happen will happen.The historian of ideas Arthur Lovejoy was the first to discuss this philosophically important Principle explicitly, it back to Aristotle, who said that no possibilities which remain eternally...
with belongings, and are various lengths. The aisle lengths are distributed according to the Vague prior, except that none are more than 100 feet long. Finally, you find your coat one foot into a dark aisle, and wonder whether that aisle is more than twenty feet long.
The Bayesian inference shifts from the cloak-room case to the lost-property case, because of the chance that the coat would not be found in the aisle it was found in, and some estimate of the aisle's dimensions. Using the SIA Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
equation with
 = 100, n = 1, x = 20 gives the chance that the aisle is above 20 feet long in the Lost-property case:
= 100, n = 1, x = 20 gives the chance that the aisle is above 20 feet long in the Lost-property case:
- Cloak-room case: The confidence that the room is shorter than 20 feet long given the position of the coat = 95%
- Lost-property case: The confidence that the aisle is less than 20 feet long given exactly the same information about the coat's position in it = 65%
The confidence that the unseen space is longer than 20 feet is directly analogous to the confidence that the human race will become more than 20 times as numerous as it has been. Using an
 of one hundred times the current value only increases the subjective chance seven times (from 5% to 35%), but this is a very small limit for the purposes of exposition.
of one hundred times the current value only increases the subjective chance seven times (from 5% to 35%), but this is a very small limit for the purposes of exposition.Problems with the SIA
The SIA is not an assumption or axiom of Dieks' system. In fact, as stated, the negation of the SIA is a theorem of Dieks' system. A proposition similar to the SIA can be derived from Dieks' system, but it is necessary to revise the SIA to limit it to situations where you don't know the date or your birth order number. Even this related proposition is not an axiom of Dieks. It is a theorem, derived from other fundamental assumptions. In Dieks, you may never have been born and the end of the human race is independent of your birth order number. A proposition related to the SIA, but not the SIA itself, can be derived from these assumptions. Hence, no one assumes the SIA. It should be called the Self-Indication Corollary, perhaps.External links
- 2005 version of Dennis Dieks's refutation (Requires a PostScriptPostScriptPostScript is a dynamically typed concatenative programming language created by John Warnock and Charles Geschke in 1982. It is best known for its use as a page description language in the electronic and desktop publishing areas. Adobe PostScript 3 is also the worldwide printing and imaging...
viewer.) - 2001 version of Dennis Dieks's refutation in pdf
- Analysis of the SIA by Milan M. Ćirković (Finds no compelling reason to accept the Self-Indication AssumptionSelf-Indication AssumptionThe Self Indication Assumption Nick Bostrom originally used the term SIA in a slightly different way. What is here referred to as SIA, he referred to as the combined SSA+SIA, a philosophical principle defined by Nick Bostrom, one of the two major schools of anthropic probability , states that:Note...
, and suggests that some of its consequences are implausible.)

