
Seismic refraction
Encyclopedia
Seismic refraction is a geophysical principle (see refraction
) governed by Snell's Law
. Used in the fields of engineering geology
, geotechnical engineering
and exploration geophysics
, seismic refraction traverses (seismic lines) are performed using a seismograph(s) and/or geophone
(s), in an array and an energy source. The seismic refraction method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves on geologic layers and rock/soil units in order to characterize the subsurface geologic conditions and geologic structure
.
The methods depend on the fact that seismic waves have differing velocities in different types of soil (or rock): in addition, the waves are refracted when they cross the boundary between different types (or conditions) of soil or rock. The methods enable the general soil types and the approximate depth to strata boundaries, or to bedrock
, to be determined.
V0 - velocity of the first layer
V1 - velocity of the second layer
h0 - thickness of the first layer
T01 - intercept
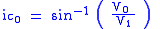
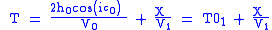
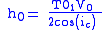
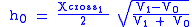
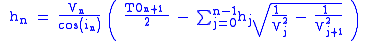
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
) governed by Snell's Law
Snell's law
In optics and physics, Snell's law is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water and glass...
. Used in the fields of engineering geology
Engineering geology
Engineering geology is the application of the geologic sciences to engineering practice for the purpose of assuring that the geologic factors affecting the location, design, construction, operation and maintenance of engineering works are recognized and adequately provided for...
, geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. Geotechnical engineering is important in civil engineering, but is also used by military, mining, petroleum, or any other engineering concerned with construction on or in the ground...
and exploration geophysics
Exploration geophysics
Exploration geophysics is the applied branch of geophysics which uses surface methods to measure the physical properties of the subsurface Earth, in order to detect or infer the presence and position of ore minerals, hydrocarbons, geothermal reservoirs, groundwater reservoirs, and other geological...
, seismic refraction traverses (seismic lines) are performed using a seismograph(s) and/or geophone
Geophone
The term geophone derives from the Greek word "geo" meaning "earth" and "phone" meaning "sound".A geophone is a device which converts ground movement into voltage, which may be recorded at a recording station...
(s), in an array and an energy source. The seismic refraction method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves on geologic layers and rock/soil units in order to characterize the subsurface geologic conditions and geologic structure
Structural geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation in the rocks, and...
.
The methods depend on the fact that seismic waves have differing velocities in different types of soil (or rock): in addition, the waves are refracted when they cross the boundary between different types (or conditions) of soil or rock. The methods enable the general soil types and the approximate depth to strata boundaries, or to bedrock
Bedrock
In stratigraphy, bedrock is the native consolidated rock underlying the surface of a terrestrial planet, usually the Earth. Above the bedrock is usually an area of broken and weathered unconsolidated rock in the basal subsoil...
, to be determined.
P-Wave Refraction (aka Compression Wave Refraction)
P-wave refraction evaluates the compression wave generated by the seismic source located at a known distance from the array. The wave is generated by vertically striking a striker plate with a sledgehammer, shooting a seismic shotgun into the ground, or detonating an explosive charge in the ground. Since the compression wave is the fastest of the seismic waves, it is sometimes referred to as the primary wave and is usually more-readily identifiable within the seismic recording as compared to the other seismic waves.S-Wave Refraction (aka Shear Wave Refraction)
S-wave refraction evaluates the shear wave generated by the seismic source located at a known distance from the array. The wave is generated by horizontally striking an object on the ground surface to induce the shear wave. Since the shear wave is the second fastest wave, it is sometimes referred to as the secondary wave. When compared to the compression wave, the shear wave is approximately one-half (but may vary significantly from this estimate) the velocity depending on the medium.Two Horizontal Layers.
ic0 - critical angleV0 - velocity of the first layer
V1 - velocity of the second layer
h0 - thickness of the first layer
T01 - intercept
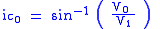
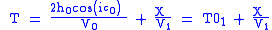
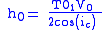
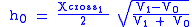
Several Horizontal Layers.
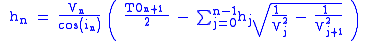
Inversion Methods
- The General Reciprocal Method
- The Plus/Minus Method
- Refraction Inversion Modeling (Refraction Tomography)
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Genetic Algorithms

