
Segmentation based object categorization
Encyclopedia
The image segmentation problem is concerned with partitioning an image into multiple regions according to some homogeneity criterion. This article is primarily concerned with graph theoretic approaches to image segmentation.
 of an edge
of an edge  is a function of the similarity between the nodes
is a function of the similarity between the nodes  and
and  . In this context, we can formulate the image segmentation problem as a graph partitioning problem that asks for a partition
. In this context, we can formulate the image segmentation problem as a graph partitioning problem that asks for a partition  of the vertex set
of the vertex set  , where, according to some measure, the vertices in any set
, where, according to some measure, the vertices in any set  have high similarity, and the vertices in two different sets
have high similarity, and the vertices in two different sets  have low similarity.
have low similarity.
 and
and  be two subsets of vertices.
be two subsets of vertices.
Let:



In the normalized cuts approach, for any cut in
in  ,
,  measures the similarity between different parts, and
measures the similarity between different parts, and  measures the total similarity of vertices in the same part.
measures the total similarity of vertices in the same part.
Since , a cut
, a cut  that minimizes
that minimizes  also maximizes
also maximizes  .
.
Computing a cut that minimizes
that minimizes  is an NP-hard
is an NP-hard
problem. However, we can find in polynomial time a cut of small normalized weight
of small normalized weight  using spectral techniques
using spectral techniques
.

Also, let D be an diagonal matrix with
diagonal matrix with  on the diagonal, and let
on the diagonal, and let  be an
be an  symmetrical matrix with
symmetrical matrix with  .
.
After some algebraic manipulations, we get:

subject to the constraints:
Minimizing subject to the constraints above is NP-hard
subject to the constraints above is NP-hard
. To make the problem tractable, we relax the constraints on , and allow it to take real values. The relaxed problem can be solved by solving the generalized eigenvalue problem
, and allow it to take real values. The relaxed problem can be solved by solving the generalized eigenvalue problem  for the second smallest generalized eigenvalue.
for the second smallest generalized eigenvalue.
The partitioning algorithm:
, for instance) takes time. This is impractical for image segmentation applications where
time. This is impractical for image segmentation applications where  is the number of pixels in the image.
is the number of pixels in the image.
Given an image D containing an instance of a known object category, e.g. cows, the OBJ CUT algorithm computes a segmentation of the object, that is, it infers a set of labels m.
Let m be a set of binary labels, and let be a shape parameter(
be a shape parameter( is a shape prior on the labels from a Layered Pictorial Structure (LPS) model). We define an energy function
is a shape prior on the labels from a Layered Pictorial Structure (LPS) model). We define an energy function  as follows.
as follows.
 (1)
(1)
The term is called a unary term, and the term
is called a unary term, and the term  is called a pairwise term.
is called a pairwise term.
An unary term consists of the likelihood based on color, and the unary potential
based on color, and the unary potential  based on the distance from
based on the distance from  . A pairwise term consists of a prior
. A pairwise term consists of a prior  and a contrast term
and a contrast term  .
.
The best labeling minimizes
minimizes  , where
, where  is the weight of the parameter
is the weight of the parameter  .
.
 (2)
(2)
Applications of Image Segmentation
- Image Compression
- Segment the image into homogeneous components, and use the most suitable compression algorithm for each component to improve compression.
- Medical Diagnosis
- Automatic segmentation of MRI images for identification of cancerous regions.
- Mapping and Measurement
- Automatic analysis of remote sensing data from satellites to identify and measure regions of interest.
Graph theoretic formulation
The set of points in an arbitrary feature space can be represented as a weighted undirected complete graph G = (V, E), where the nodes of the graph are the points in the feature space. The weight of an edge
of an edge  is a function of the similarity between the nodes
is a function of the similarity between the nodes  and
and  . In this context, we can formulate the image segmentation problem as a graph partitioning problem that asks for a partition
. In this context, we can formulate the image segmentation problem as a graph partitioning problem that asks for a partition  of the vertex set
of the vertex set  , where, according to some measure, the vertices in any set
, where, according to some measure, the vertices in any set  have high similarity, and the vertices in two different sets
have high similarity, and the vertices in two different sets  have low similarity.
have low similarity.Normalized Cuts
Let G = (V, E) be a weighted graph. Let and
and  be two subsets of vertices.
be two subsets of vertices.Let:



In the normalized cuts approach, for any cut
 in
in  ,
,  measures the similarity between different parts, and
measures the similarity between different parts, and  measures the total similarity of vertices in the same part.
measures the total similarity of vertices in the same part.Since
 , a cut
, a cut  that minimizes
that minimizes  also maximizes
also maximizes  .
.Computing a cut
 that minimizes
that minimizes  is an NP-hard
is an NP-hardNP-hard
NP-hard , in computational complexity theory, is a class of problems that are, informally, "at least as hard as the hardest problems in NP". A problem H is NP-hard if and only if there is an NP-complete problem L that is polynomial time Turing-reducible to H...
problem. However, we can find in polynomial time a cut
 of small normalized weight
of small normalized weight  using spectral techniques
using spectral techniquesSpectral graph theory
In mathematics, spectral graph theory is the study of properties of a graph in relationship to the characteristic polynomial, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors of matrices associated to the graph, such as its adjacency matrix or Laplacian matrix....
.
The Ncut Algorithm
Let:
Also, let D be an
 diagonal matrix with
diagonal matrix with  on the diagonal, and let
on the diagonal, and let  be an
be an  symmetrical matrix with
symmetrical matrix with  .
.After some algebraic manipulations, we get:

subject to the constraints:
-
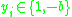 , for some constant
, for some constant 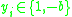
-
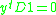
Minimizing
 subject to the constraints above is NP-hard
subject to the constraints above is NP-hardNP-hard
NP-hard , in computational complexity theory, is a class of problems that are, informally, "at least as hard as the hardest problems in NP". A problem H is NP-hard if and only if there is an NP-complete problem L that is polynomial time Turing-reducible to H...
. To make the problem tractable, we relax the constraints on
 , and allow it to take real values. The relaxed problem can be solved by solving the generalized eigenvalue problem
, and allow it to take real values. The relaxed problem can be solved by solving the generalized eigenvalue problem  for the second smallest generalized eigenvalue.
for the second smallest generalized eigenvalue.The partitioning algorithm:
- Given a set of features, set up a weighted graph
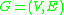 , compute the weight of each edge, and summarize the information in
, compute the weight of each edge, and summarize the information in 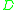 and
and 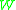 .
. - Solve
 for eigenvectors with the smallest eigenvalues.
for eigenvectors with the smallest eigenvalues. - Use the eigenvector with the smallest eigenvalue to bipartition the graph (e.g. grouping according to sign).
- Decide if the current partition should be subdivided.
- Recursively partition the segmented parts, if necessary.
Limitations
Solving a standard eigenvalue problem for all eigenvectors (using the QR algorithmQR algorithm
In numerical linear algebra, the QR algorithm is an eigenvalue algorithm: that is, a procedure to calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix. The QR transformation was developed in the late 1950s by John G.F. Francis and by Vera N. Kublanovskaya , working independently...
, for instance) takes
 time. This is impractical for image segmentation applications where
time. This is impractical for image segmentation applications where  is the number of pixels in the image.
is the number of pixels in the image.OBJ CUT
OBJ CUT is an efficient method that automatically segments an object. The OBJ CUT method is a generic method, and therefore it is applicable to any object category model.Given an image D containing an instance of a known object category, e.g. cows, the OBJ CUT algorithm computes a segmentation of the object, that is, it infers a set of labels m.
Let m be a set of binary labels, and let
 be a shape parameter(
be a shape parameter( is a shape prior on the labels from a Layered Pictorial Structure (LPS) model). We define an energy function
is a shape prior on the labels from a Layered Pictorial Structure (LPS) model). We define an energy function  as follows.
as follows. (1)
(1)The term
 is called a unary term, and the term
is called a unary term, and the term  is called a pairwise term.
is called a pairwise term.An unary term consists of the likelihood
 based on color, and the unary potential
based on color, and the unary potential  based on the distance from
based on the distance from  . A pairwise term consists of a prior
. A pairwise term consists of a prior  and a contrast term
and a contrast term  .
.The best labeling
 minimizes
minimizes  , where
, where  is the weight of the parameter
is the weight of the parameter  .
. (2)
(2)The OBJ CUT algorithm
- Given an image D, an object category is chosen, e.g. cows or horses.
- The corresponding LPS model is matched to D to obtain the samples
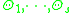
- The objective function given by equation (2) is determined by computing
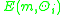 and using
and using 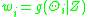
- The objective function is minimized using a single MINCUTMax-flow min-cut theoremIn optimization theory, the max-flow min-cut theorem states that in a flow network, the maximum amount of flow passing from the source to the sink is equal to the minimum capacity which when removed in a specific way from the network causes the situation that no flow can pass from the source to the...
operation to obtain the segmentation m.
Other approaches
- Jigsaw approach
- Image parsing
- Interleaved segmentation
- LOCUS
- LayoutCRF
- Minimum Spanning Tree-based segmentationMinimum spanning tree-based segmentation-Image segmentation introduction:Image segmentation strives to partition a digital image into regions of pixels with similar properties, e.g. homogeneity. The higher-level region representation simplifies image analysis tasks such as counting objects or detecting changes, because region attributes...

